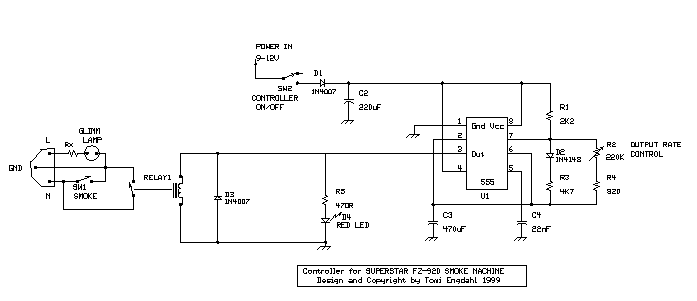
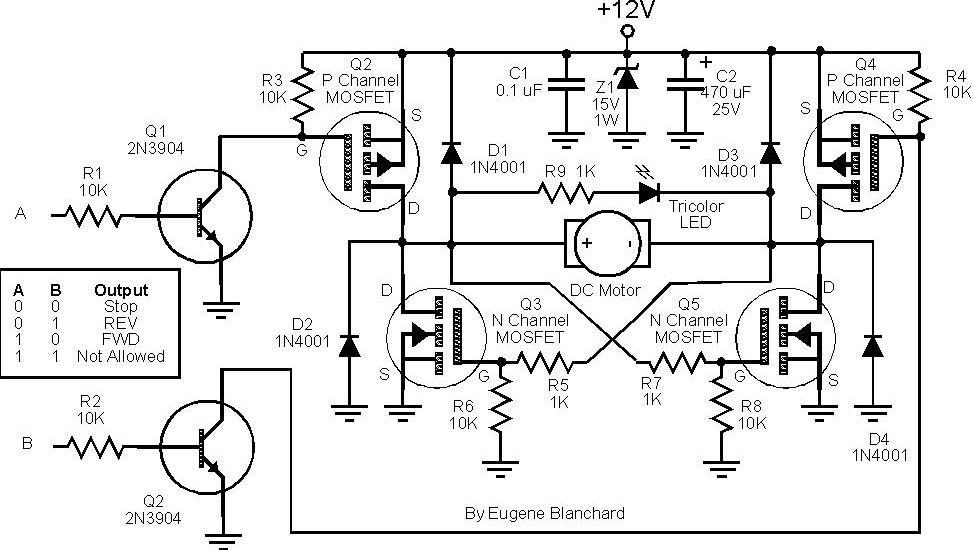
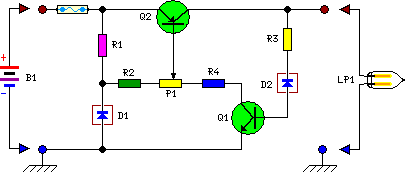
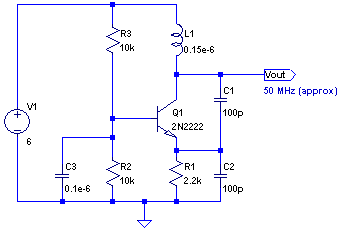
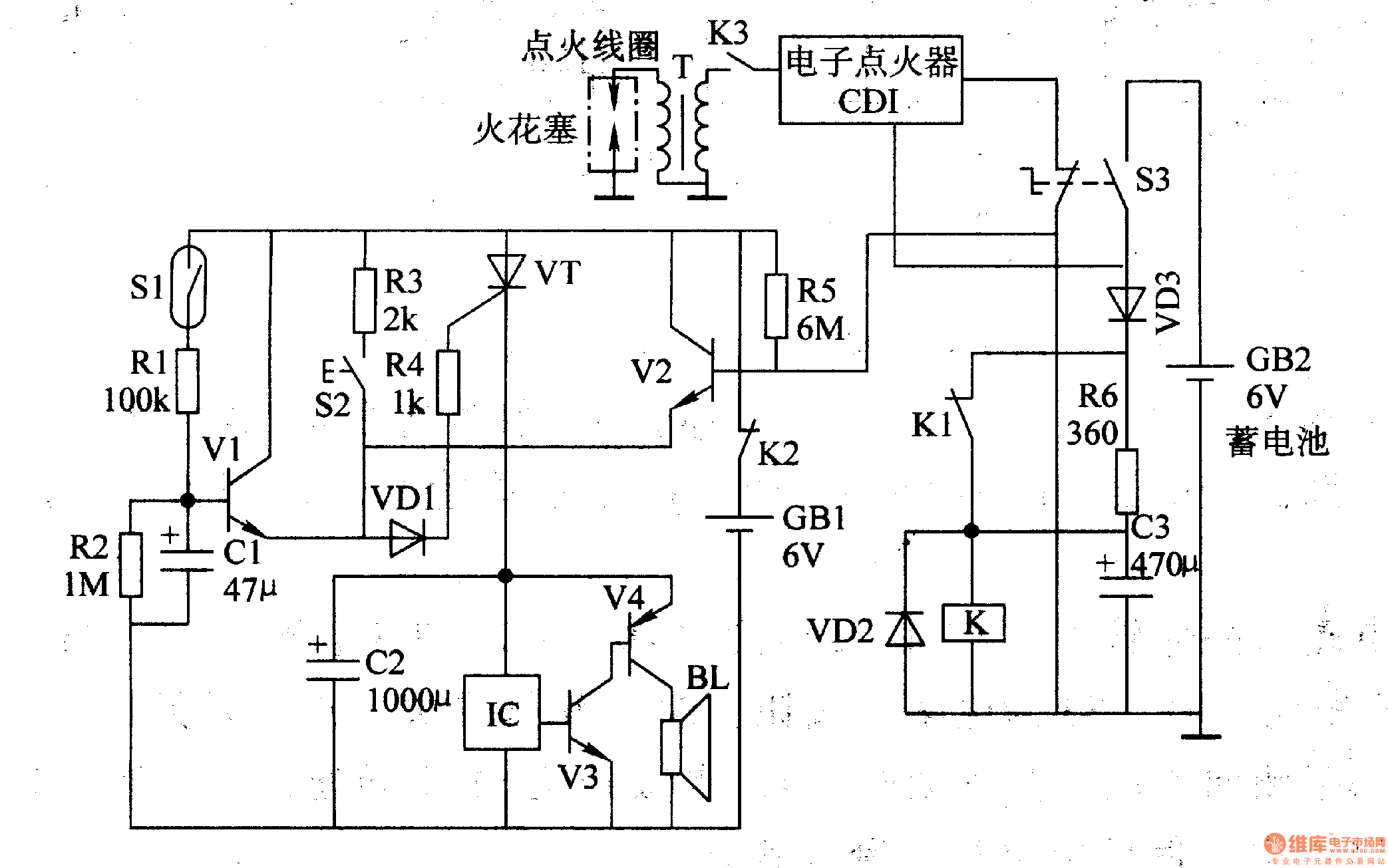
Electronics Motor Controller AC Motor
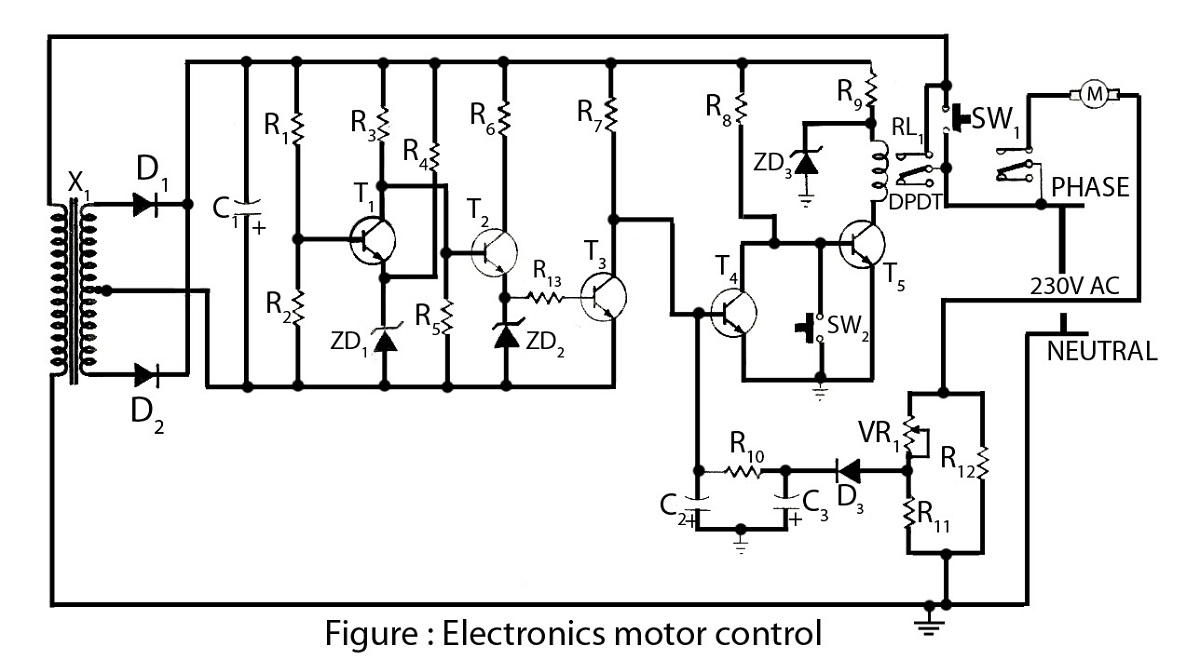
Electronics motor control is a simple circuit made without an integrated circuit (IC). It involves the electronic control of an AC motor and includes a circuit diagram along with a description of the electronics motor controller.
The electronics motor control circuit operates without the need for integrated circuits, making it a straightforward design suitable for basic applications. This circuit typically utilizes discrete components such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, and transistors to manage the operation of an AC motor.
A common configuration for such a circuit includes a triac or a thyristor, which serves as the primary control element. The triac is responsible for switching the AC voltage to the motor on and off, thereby controlling its speed and direction. The gate of the triac can be triggered by a control circuit, which may include a variable resistor (potentiometer) to adjust the firing angle, allowing for speed control.
The circuit may also incorporate a zero-crossing detector to ensure that the triac is triggered at the appropriate point in the AC waveform, minimizing electrical noise and reducing stress on the motor. Additionally, snubber circuits can be included to protect the triac from voltage spikes caused by inductive loads, ensuring reliable operation.
In terms of the circuit diagram, it typically displays the connections between the AC power source, the control components, and the motor. The diagram should clearly indicate the positions of the triac, control resistors, and any protective components. Proper labeling of each component is essential for clarity and ease of understanding.
Overall, this electronics motor control circuit is a practical solution for controlling AC motors in various applications, ranging from small appliances to industrial machinery, while maintaining simplicity in design.Electronics motor control is a simple circuit made without IC.electronics control of AC motor.circuit diagram with description of electronics motor controller. 🔗 External reference
The electronics motor control circuit operates without the need for integrated circuits, making it a straightforward design suitable for basic applications. This circuit typically utilizes discrete components such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, and transistors to manage the operation of an AC motor.
A common configuration for such a circuit includes a triac or a thyristor, which serves as the primary control element. The triac is responsible for switching the AC voltage to the motor on and off, thereby controlling its speed and direction. The gate of the triac can be triggered by a control circuit, which may include a variable resistor (potentiometer) to adjust the firing angle, allowing for speed control.
The circuit may also incorporate a zero-crossing detector to ensure that the triac is triggered at the appropriate point in the AC waveform, minimizing electrical noise and reducing stress on the motor. Additionally, snubber circuits can be included to protect the triac from voltage spikes caused by inductive loads, ensuring reliable operation.
In terms of the circuit diagram, it typically displays the connections between the AC power source, the control components, and the motor. The diagram should clearly indicate the positions of the triac, control resistors, and any protective components. Proper labeling of each component is essential for clarity and ease of understanding.
Overall, this electronics motor control circuit is a practical solution for controlling AC motors in various applications, ranging from small appliances to industrial machinery, while maintaining simplicity in design.Electronics motor control is a simple circuit made without IC.electronics control of AC motor.circuit diagram with description of electronics motor controller. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713