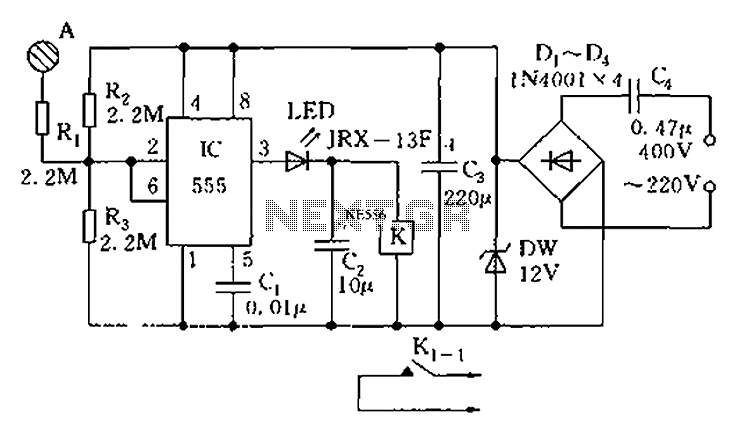
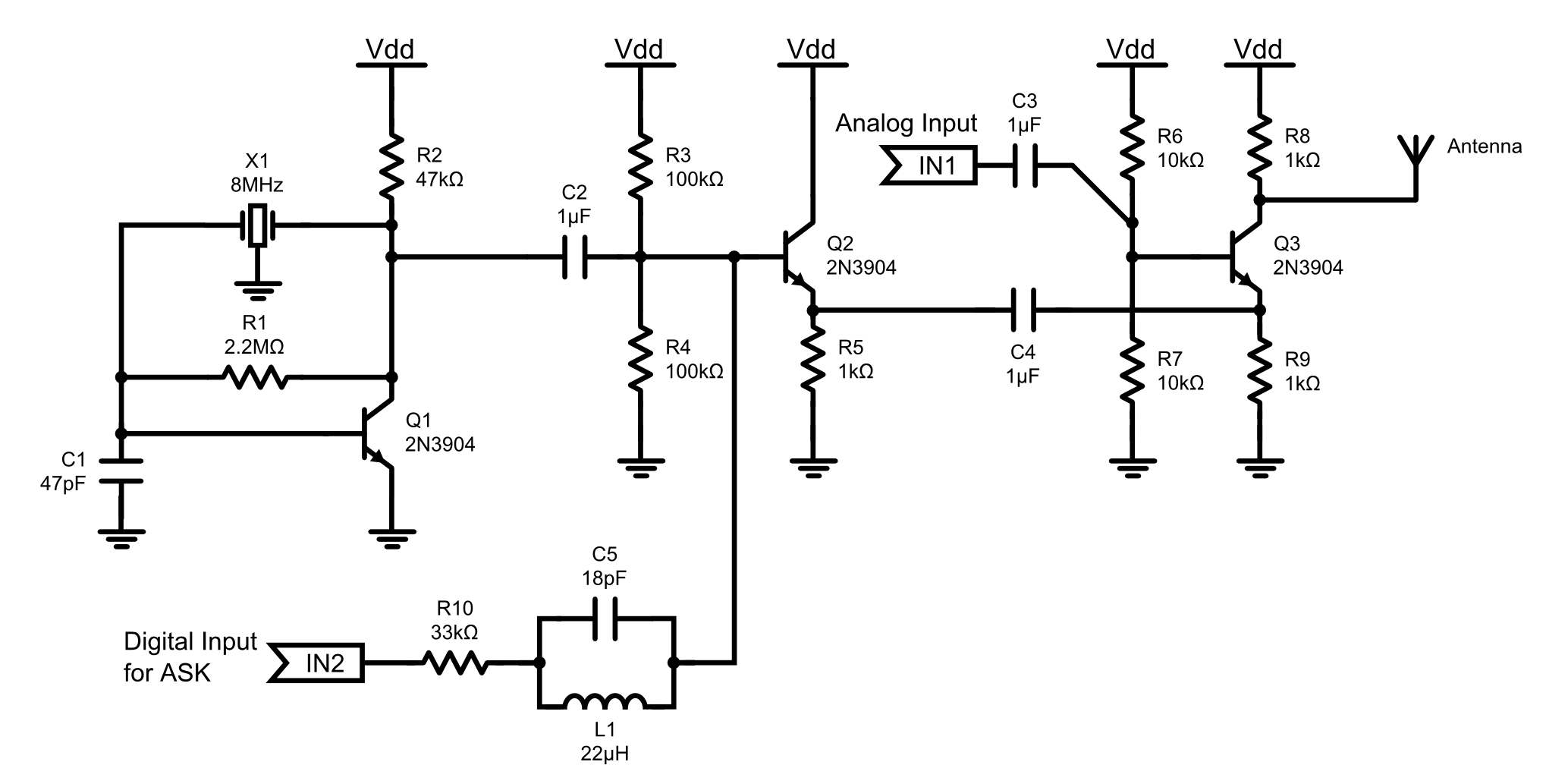
Energy Consumption Monitor Circuit
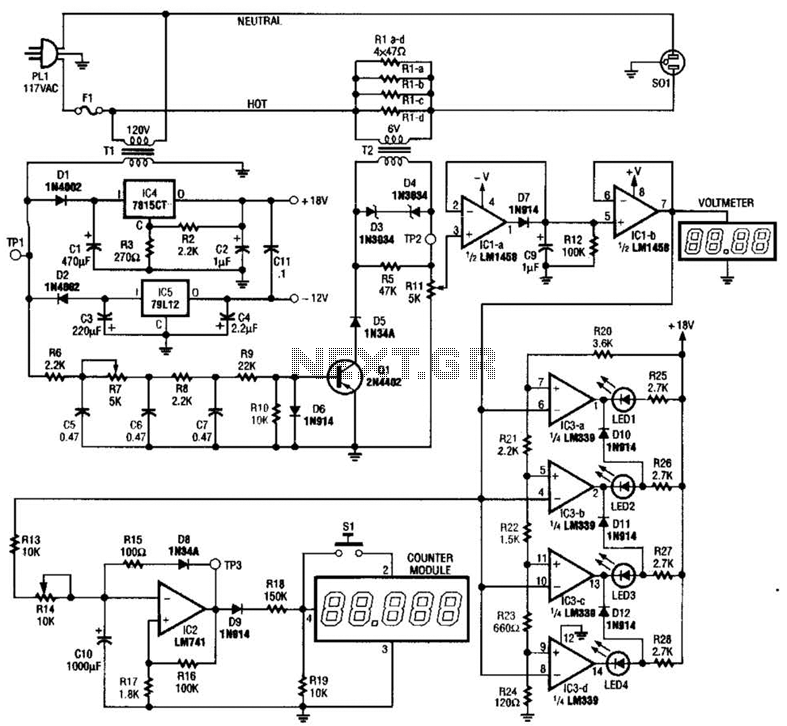
The ECM circuit comprises four sections, as illustrated in the block diagram. A power converter generates a voltage that correlates with the actual real power consumed by the load. This voltage supplies both a bar graph and a voltage-to-pulse converter. The bar graph provides an approximate indication of the power used, while the voltage-to-pulse converter generates a pulse whose frequency is proportional to the power consumption. This pulse activates the counter module, which displays the cost of powering the monitored load.
The ECM circuit is designed to monitor and display power consumption in a clear and efficient manner. The power converter is a critical component that transforms the electrical characteristics of the load into a usable voltage signal. This voltage is typically derived from a current transformer or a shunt resistor, ensuring accurate representation of the real power consumed.
The bar graph serves as a visual representation of power usage, allowing users to quickly assess the load's energy consumption without needing to interpret numerical data. It is typically composed of a series of LEDs or a liquid crystal display (LCD) that lights up in proportion to the power consumed.
The voltage-to-pulse converter is essential for translating the analog voltage signal into a digital format that can be processed by the counter module. This converter operates by generating a pulse train where the frequency of the pulses is directly proportional to the input voltage, effectively encoding the power consumption into a frequency signal.
The counter module, often integrated with a microcontroller or a digital signal processor, counts the incoming pulses over a defined time interval. This count is then converted into a cost estimate based on predefined rates for energy consumption. The display can be a simple numeric readout or a more complex graphical interface, depending on the design requirements.
In summary, the ECM circuit provides a comprehensive solution for monitoring power consumption, converting it into useful visual and numerical data, and facilitating cost analysis for energy usage in various applications. Its modular design allows for flexibility and scalability in different environments, making it suitable for residential, commercial, or industrial applications. The ECM circuit consists of four sections, as shown in the block diagram. A power converter generates a voltage that is proportional to the true of real power consumed by the load. That voltage feeds both a bargraph and a voltage-to-pulse converter. The bargraph gives an approximate indication of the amount of power used, and the voltage-to-pulse converter produces a pulse whose frequency is proportional to the power.
The pulse triggers the counter module, which displays the cost of powering the monitored load.
The ECM circuit is designed to monitor and display power consumption in a clear and efficient manner. The power converter is a critical component that transforms the electrical characteristics of the load into a usable voltage signal. This voltage is typically derived from a current transformer or a shunt resistor, ensuring accurate representation of the real power consumed.
The bar graph serves as a visual representation of power usage, allowing users to quickly assess the load's energy consumption without needing to interpret numerical data. It is typically composed of a series of LEDs or a liquid crystal display (LCD) that lights up in proportion to the power consumed.
The voltage-to-pulse converter is essential for translating the analog voltage signal into a digital format that can be processed by the counter module. This converter operates by generating a pulse train where the frequency of the pulses is directly proportional to the input voltage, effectively encoding the power consumption into a frequency signal.
The counter module, often integrated with a microcontroller or a digital signal processor, counts the incoming pulses over a defined time interval. This count is then converted into a cost estimate based on predefined rates for energy consumption. The display can be a simple numeric readout or a more complex graphical interface, depending on the design requirements.
In summary, the ECM circuit provides a comprehensive solution for monitoring power consumption, converting it into useful visual and numerical data, and facilitating cost analysis for energy usage in various applications. Its modular design allows for flexibility and scalability in different environments, making it suitable for residential, commercial, or industrial applications. The ECM circuit consists of four sections, as shown in the block diagram. A power converter generates a voltage that is proportional to the true of real power consumed by the load. That voltage feeds both a bargraph and a voltage-to-pulse converter. The bargraph gives an approximate indication of the amount of power used, and the voltage-to-pulse converter produces a pulse whose frequency is proportional to the power.
The pulse triggers the counter module, which displays the cost of powering the monitored load.