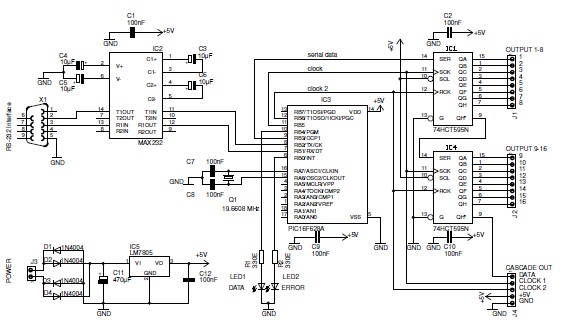
Thermocouple cold junction compensation RTD has XTR101 Input Circuit
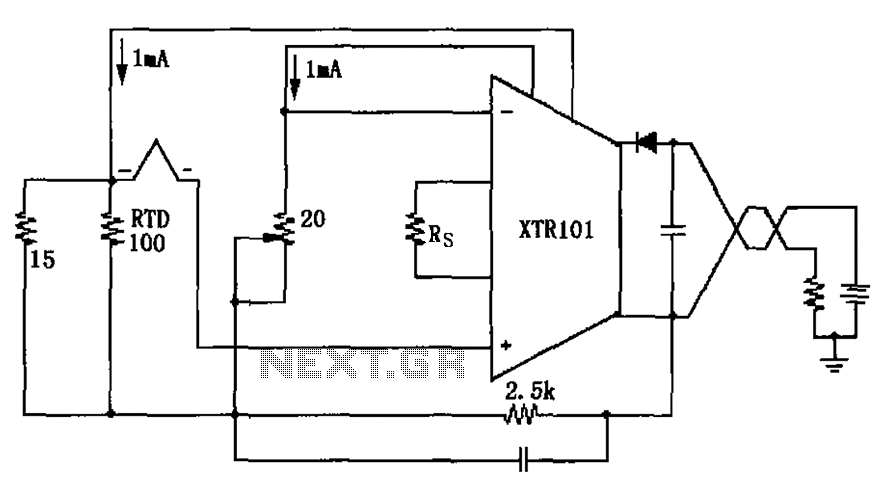
The circuit utilizes a type J RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector), where the resistance value is directly related to the temperature. Calibration of the zero point is facilitated by a 20-ohm adjustment potentiometer as specified by the manufacturer.
The schematic features a type J RTD, which operates on the principle that the resistance of the sensor varies with temperature changes. Specifically, a type J RTD typically has a resistance of 100 ohms at 0°C, with a temperature coefficient of approximately 0.00385 ohms per degree Celsius. This characteristic allows for accurate temperature measurements across a specified range.
The circuit includes an operational amplifier configured as a differential amplifier to process the small voltage signals generated by the RTD. The output from the RTD is fed into the non-inverting and inverting inputs of the op-amp. This configuration enhances the signal-to-noise ratio, ensuring precise readings.
In addition, a 20-ohm potentiometer is integrated into the circuit for zero-point calibration. This adjustment allows for fine-tuning the output to zero at a known reference temperature, ensuring accuracy in temperature readings. The potentiometer is connected in series with a resistor, allowing for smooth adjustments to the baseline output voltage.
The output from the op-amp is then typically connected to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital processing or to a microcontroller for further data handling and display. This setup enables the monitoring of temperature in real-time, making it suitable for applications in industrial processes, HVAC systems, or laboratory environments.
Overall, the described circuit effectively combines the properties of the type J RTD with appropriate signal conditioning and calibration techniques, resulting in a reliable temperature measurement system. As shown, the circuit uses type J RTD, its resistance value corresponds to the temperature of the RTD can check a form provided by the manufacturer, with 20 zero adjustment pot entiometer zero point calibration.
The schematic features a type J RTD, which operates on the principle that the resistance of the sensor varies with temperature changes. Specifically, a type J RTD typically has a resistance of 100 ohms at 0°C, with a temperature coefficient of approximately 0.00385 ohms per degree Celsius. This characteristic allows for accurate temperature measurements across a specified range.
The circuit includes an operational amplifier configured as a differential amplifier to process the small voltage signals generated by the RTD. The output from the RTD is fed into the non-inverting and inverting inputs of the op-amp. This configuration enhances the signal-to-noise ratio, ensuring precise readings.
In addition, a 20-ohm potentiometer is integrated into the circuit for zero-point calibration. This adjustment allows for fine-tuning the output to zero at a known reference temperature, ensuring accuracy in temperature readings. The potentiometer is connected in series with a resistor, allowing for smooth adjustments to the baseline output voltage.
The output from the op-amp is then typically connected to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital processing or to a microcontroller for further data handling and display. This setup enables the monitoring of temperature in real-time, making it suitable for applications in industrial processes, HVAC systems, or laboratory environments.
Overall, the described circuit effectively combines the properties of the type J RTD with appropriate signal conditioning and calibration techniques, resulting in a reliable temperature measurement system. As shown, the circuit uses type J RTD, its resistance value corresponds to the temperature of the RTD can check a form provided by the manufacturer, with 20 zero adjustment pot entiometer zero point calibration.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713