Ensemble RXTX Builders 1
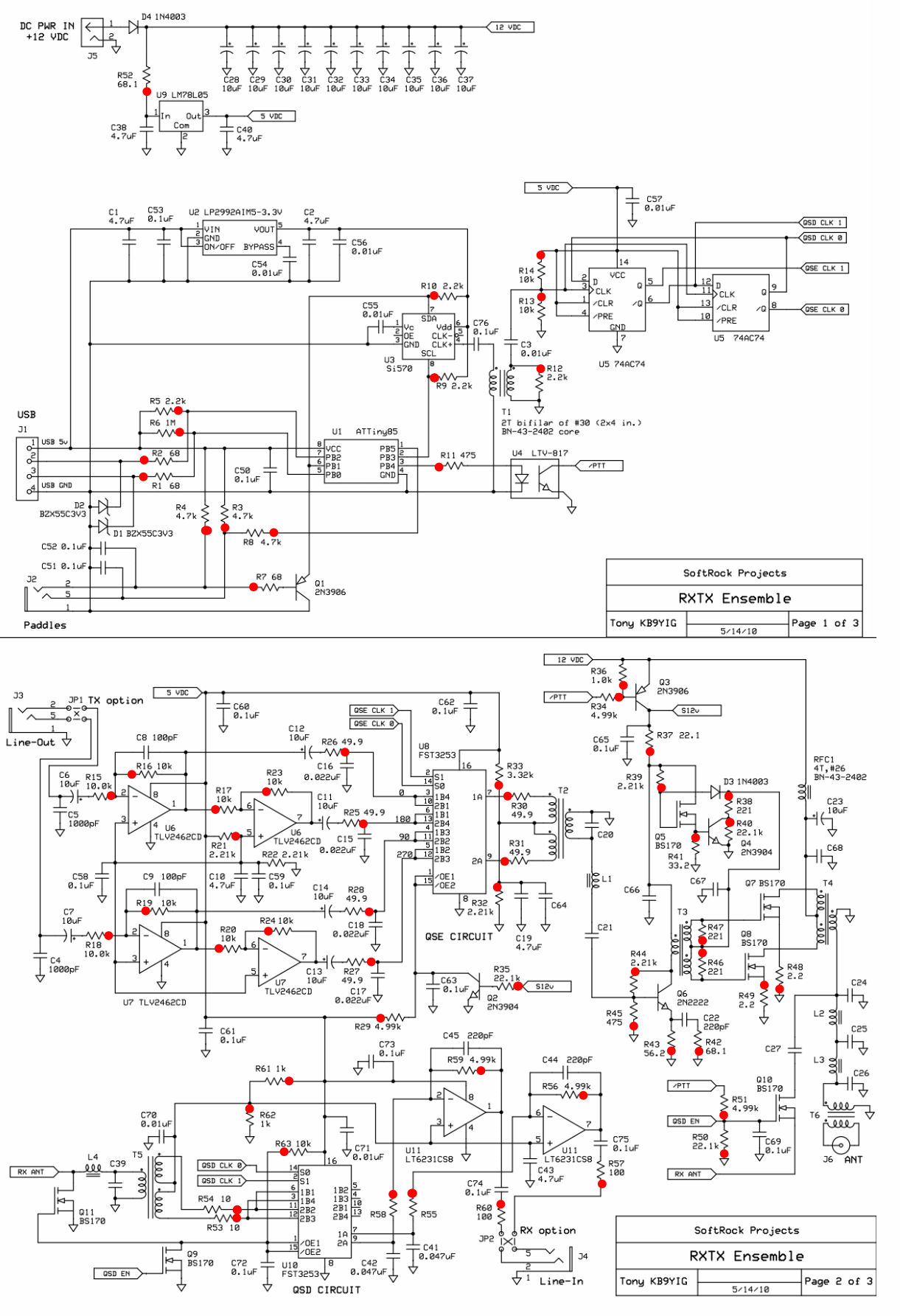
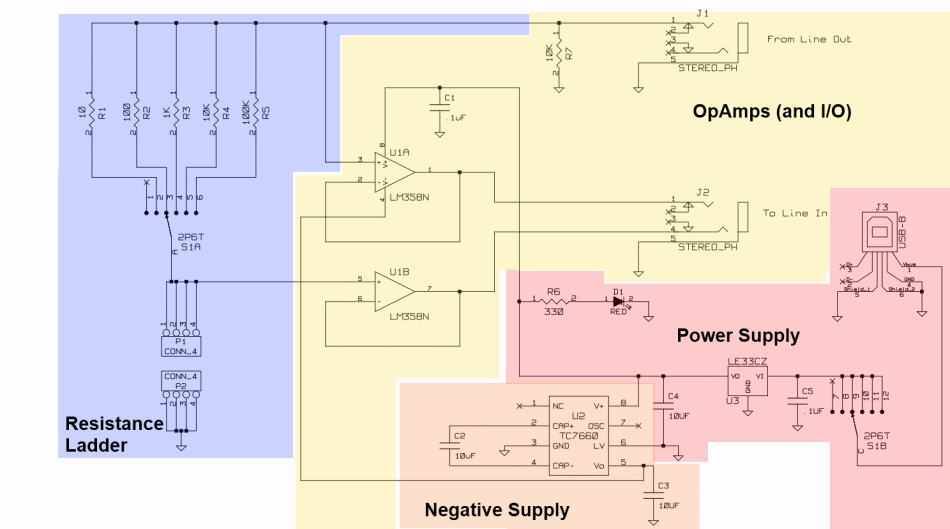
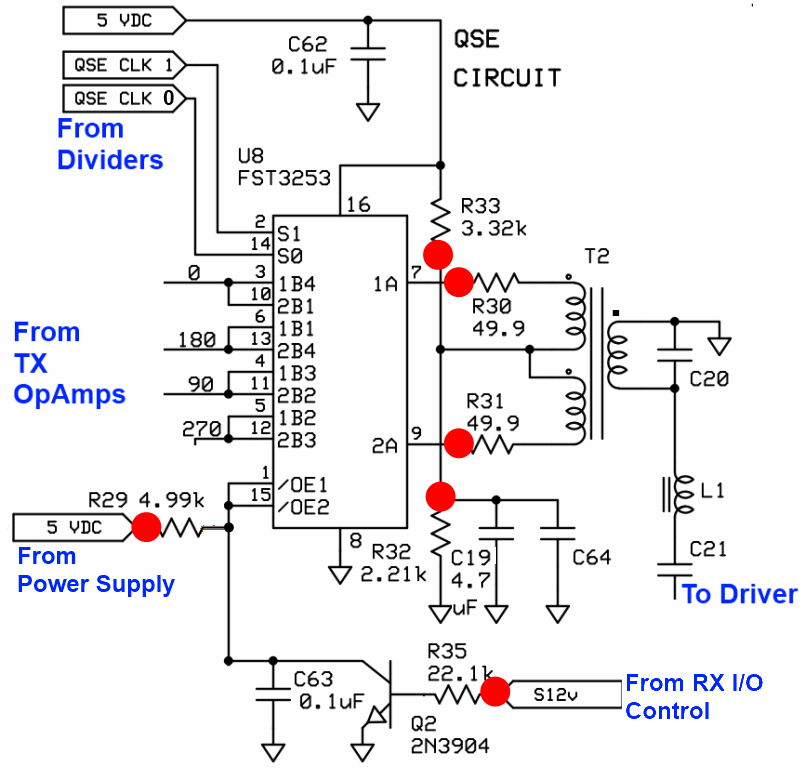
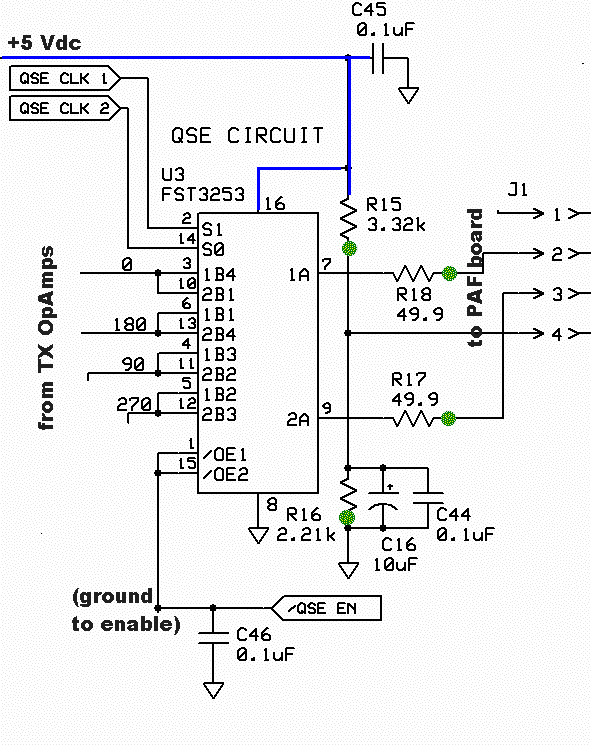
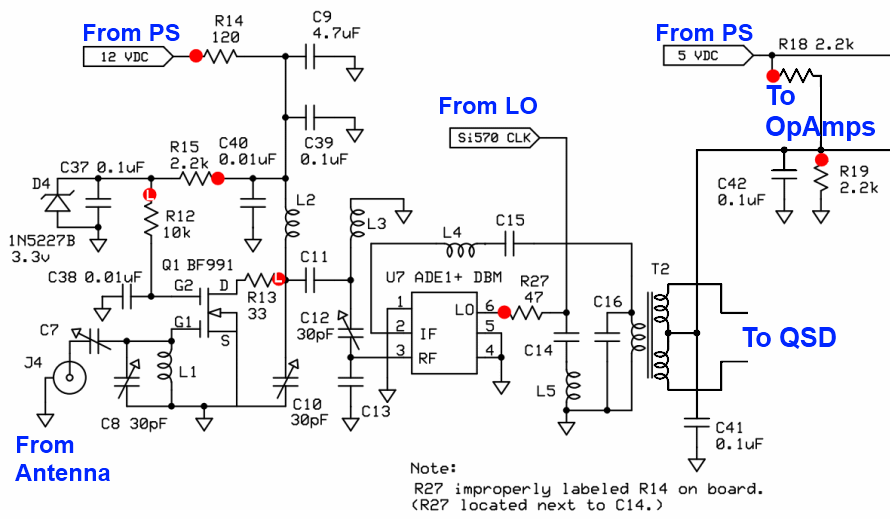
The mixer stage, known as the Quadrature Sampling Detector (QSD), functions similarly to two conventional direct conversion mixers operating in parallel. Each mixer processes half of the filtered RF signal from the bandpass filter stage alongside one of the quadrature center frequency signals, resulting in the down-conversion of these signals. The output comprises the traditional mixer products, specifically two audio frequency signals that represent the difference between the RF input and the Local Oscillator. These outputs are designated as the detected I (in-phase) and Q (Quadrature) signals, which are subsequently directed to a high-gain operational amplifier stage for amplification before being sent to the audio outputs and, ultimately, to the PC's sound card. The mixer is activated via the QSD enable line, controlled by the Q9 switch in the RF I/O Control Stage. When the Push-To-Talk (PTT) line is engaged, the QSD enabling line is activated, which in turn disables the RX Mixer.
The Quadrature Sampling Detector (QSD) is a critical component in modern communication systems, particularly in software-defined radios (SDRs). It allows for the effective demodulation of signals by separating the in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components of the received RF signal. This separation is essential for accurately reconstructing the original information contained within the RF signal, which can include voice, data, or other forms of modulation.
In the mixer stage, the RF signal, after passing through a bandpass filter to eliminate unwanted frequencies, is divided into two paths. Each path is fed into its respective mixer, where it interacts with a local oscillator signal that is phase-shifted by 90 degrees to create the quadrature component. The mixing process generates two output signals: the I signal, which is aligned with the original RF signal, and the Q signal, which is phase-shifted. These outputs are crucial for digital signal processing (DSP) applications, where they can be further manipulated to extract the desired information.
The operational amplifier stage following the mixer plays a vital role in ensuring that the I and Q signals are amplified to suitable levels for further processing. The gain of these amplifiers must be carefully designed to avoid distortion and maintain signal integrity. The amplified signals are then routed to the audio outputs, which connect to a sound card in a computer system for digital processing.
The QSD's functionality is controlled through the QSD enable line, which is managed by the RF I/O Control Stage. This control mechanism ensures that the mixer operates only when required, preventing unnecessary power consumption and interference. The integration of the PTT line provides an additional layer of control, allowing the user to activate the mixer only during transmission, which is essential for efficient operation in communication systems.
Overall, the QSD is a sophisticated component that enhances the performance of radio receivers by enabling effective signal demodulation and processing, thereby facilitating clearer communication and improved data transmission capabilities.The mixer stage ("QSD" - Quadrature Sampling Detector) acts like two traditional direct conversion mixers operating in tandem. Each takes in half of the filtered RF from the bandpass filter stage and one of the quadrature center frequency signals, then "mixes"/down-converts them to with an output being the traditional mixer products, in this case,
two (infra) audio frequency signals that represent the difference between the two inputs (RF and Local Oscillator). These two signals are referred to as the detected I (in-phase) and Q (Quadrature) signals and are fed into the high gain Op-Amps stage for amplification and delivery to the audio outputs (and, thence, to the PC`s sound card).
The mixer is enabled by the QSD enable line, switched in the RF I/O Control Stage`s Q9. When the PTT line is activated, the QSD Enabling line goes high and disables the RX Mixer. 🔗 External reference
The Quadrature Sampling Detector (QSD) is a critical component in modern communication systems, particularly in software-defined radios (SDRs). It allows for the effective demodulation of signals by separating the in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components of the received RF signal. This separation is essential for accurately reconstructing the original information contained within the RF signal, which can include voice, data, or other forms of modulation.
In the mixer stage, the RF signal, after passing through a bandpass filter to eliminate unwanted frequencies, is divided into two paths. Each path is fed into its respective mixer, where it interacts with a local oscillator signal that is phase-shifted by 90 degrees to create the quadrature component. The mixing process generates two output signals: the I signal, which is aligned with the original RF signal, and the Q signal, which is phase-shifted. These outputs are crucial for digital signal processing (DSP) applications, where they can be further manipulated to extract the desired information.
The operational amplifier stage following the mixer plays a vital role in ensuring that the I and Q signals are amplified to suitable levels for further processing. The gain of these amplifiers must be carefully designed to avoid distortion and maintain signal integrity. The amplified signals are then routed to the audio outputs, which connect to a sound card in a computer system for digital processing.
The QSD's functionality is controlled through the QSD enable line, which is managed by the RF I/O Control Stage. This control mechanism ensures that the mixer operates only when required, preventing unnecessary power consumption and interference. The integration of the PTT line provides an additional layer of control, allowing the user to activate the mixer only during transmission, which is essential for efficient operation in communication systems.
Overall, the QSD is a sophisticated component that enhances the performance of radio receivers by enabling effective signal demodulation and processing, thereby facilitating clearer communication and improved data transmission capabilities.The mixer stage ("QSD" - Quadrature Sampling Detector) acts like two traditional direct conversion mixers operating in tandem. Each takes in half of the filtered RF from the bandpass filter stage and one of the quadrature center frequency signals, then "mixes"/down-converts them to with an output being the traditional mixer products, in this case,
two (infra) audio frequency signals that represent the difference between the two inputs (RF and Local Oscillator). These two signals are referred to as the detected I (in-phase) and Q (Quadrature) signals and are fed into the high gain Op-Amps stage for amplification and delivery to the audio outputs (and, thence, to the PC`s sound card).
The mixer is enabled by the QSD enable line, switched in the RF I/O Control Stage`s Q9. When the PTT line is activated, the QSD Enabling line goes high and disables the RX Mixer. 🔗 External reference