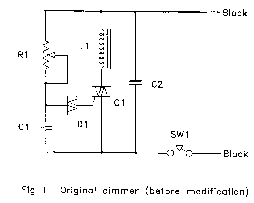
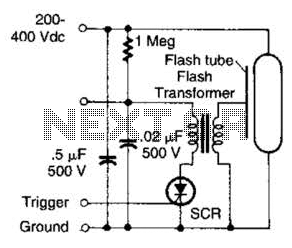
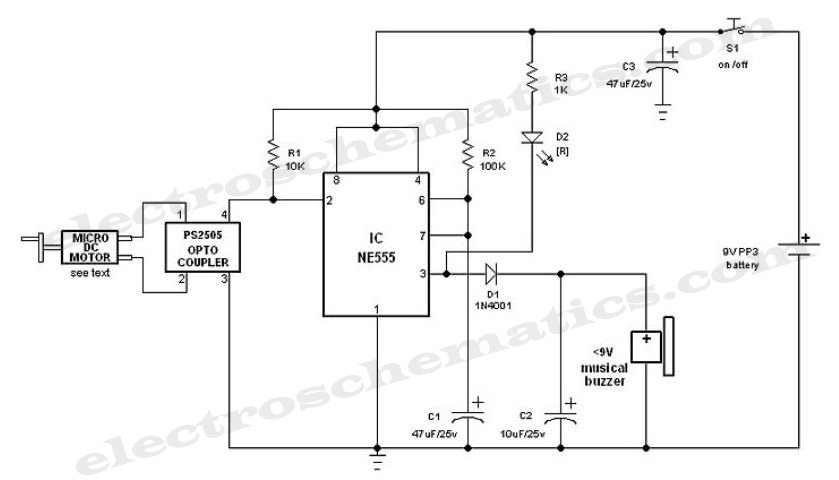
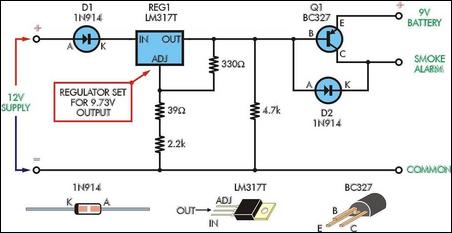
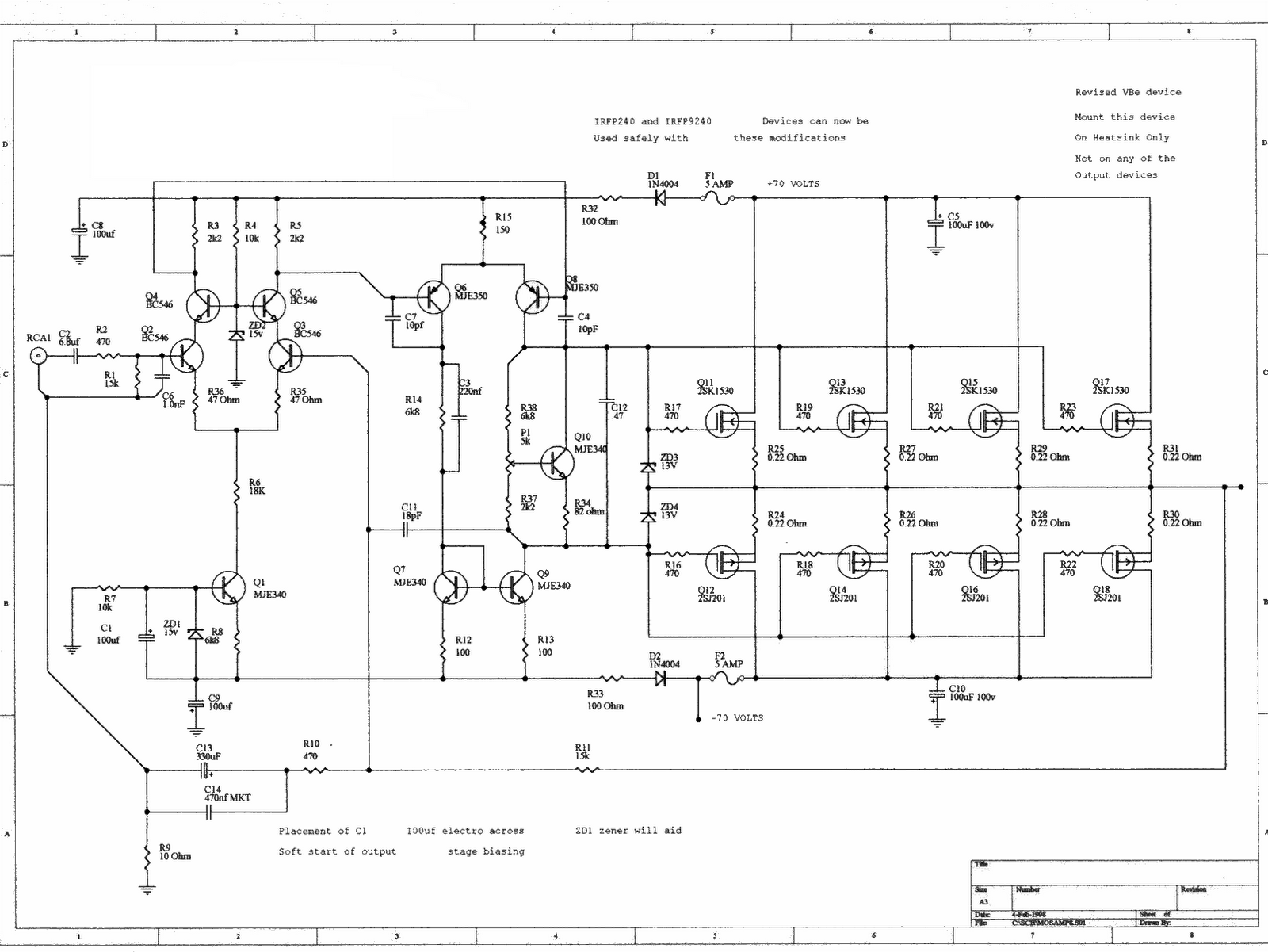
Entry Alarm Circuit

This is an infrared-based broken beam alarm designed to protect doors and entry passages. It emits a loud alarm when someone crosses the invisible infrared barrier.
The infrared-based broken beam alarm system operates by utilizing a pair of infrared emitters and receivers positioned across the entryway. The emitter continuously transmits infrared light, creating an invisible barrier. When an object, such as a person, interrupts this beam, the receiver detects the absence of the infrared signal, triggering the alarm system.
The key components of this circuit include an infrared LED (emitter), a photodiode or phototransistor (receiver), a microcontroller or comparator circuit for processing the signal, and an audible alarm such as a piezo buzzer or siren. The infrared LED operates at a specific wavelength, typically around 940 nm, which is not visible to the human eye but can be detected by the photodiode.
The circuit can be powered by a low-voltage DC power supply, making it suitable for indoor and outdoor applications. To enhance performance, the system may incorporate features such as adjustable sensitivity, time delay settings, and a battery backup for uninterrupted operation during power outages.
Additionally, the alarm can be integrated with other security systems, including motion detectors and CCTV cameras, to provide a comprehensive security solution. Proper placement of the emitters and receivers is crucial to ensure effective coverage and minimize false alarms caused by environmental factors such as pets or small animals.
Overall, this infrared broken beam alarm system offers a reliable and efficient method for monitoring entry points and enhancing security in residential and commercial settings.This is an Infrared based Broken beam alarm to protect doors and entry passages. It gives a loud alarm when somebody crosses the Invisible Infrared barrier.. 🔗 External reference
The infrared-based broken beam alarm system operates by utilizing a pair of infrared emitters and receivers positioned across the entryway. The emitter continuously transmits infrared light, creating an invisible barrier. When an object, such as a person, interrupts this beam, the receiver detects the absence of the infrared signal, triggering the alarm system.
The key components of this circuit include an infrared LED (emitter), a photodiode or phototransistor (receiver), a microcontroller or comparator circuit for processing the signal, and an audible alarm such as a piezo buzzer or siren. The infrared LED operates at a specific wavelength, typically around 940 nm, which is not visible to the human eye but can be detected by the photodiode.
The circuit can be powered by a low-voltage DC power supply, making it suitable for indoor and outdoor applications. To enhance performance, the system may incorporate features such as adjustable sensitivity, time delay settings, and a battery backup for uninterrupted operation during power outages.
Additionally, the alarm can be integrated with other security systems, including motion detectors and CCTV cameras, to provide a comprehensive security solution. Proper placement of the emitters and receivers is crucial to ensure effective coverage and minimize false alarms caused by environmental factors such as pets or small animals.
Overall, this infrared broken beam alarm system offers a reliable and efficient method for monitoring entry points and enhancing security in residential and commercial settings.This is an Infrared based Broken beam alarm to protect doors and entry passages. It gives a loud alarm when somebody crosses the Invisible Infrared barrier.. 🔗 External reference