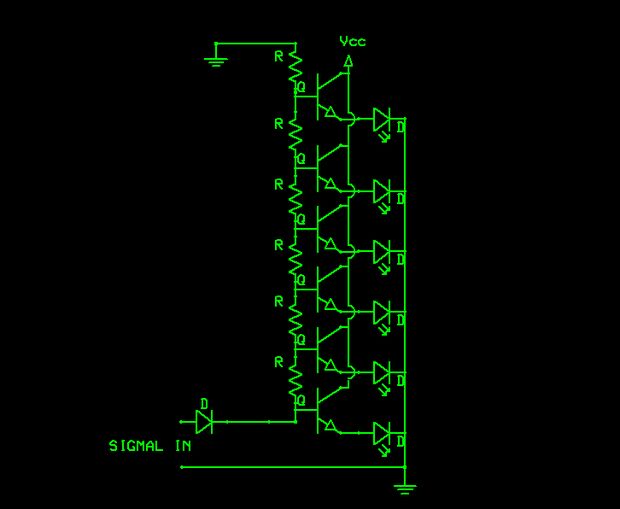
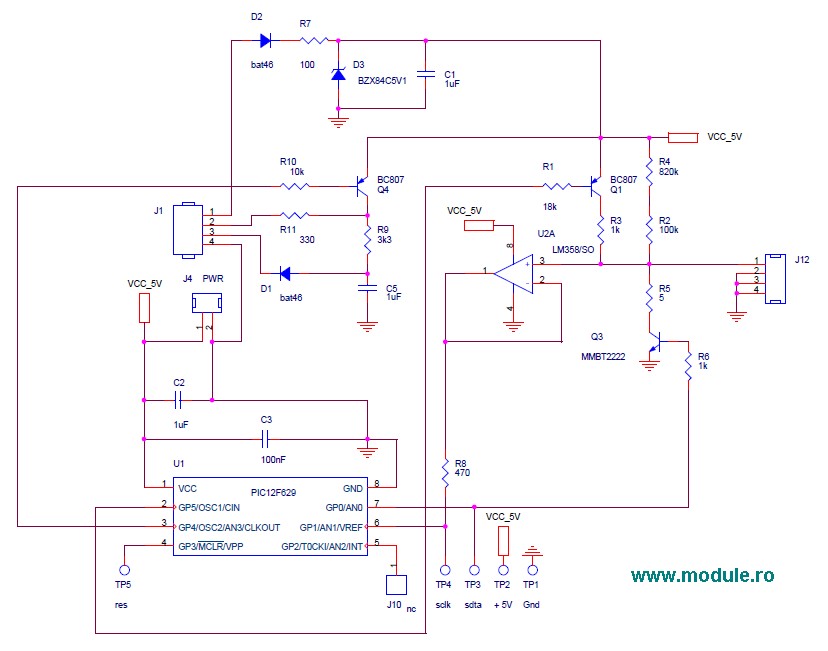
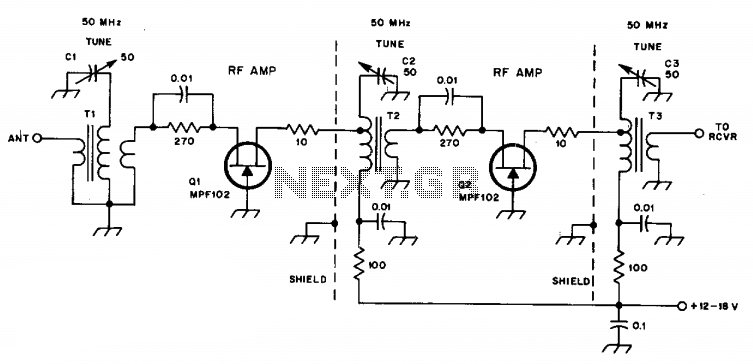
Expanded scale meter
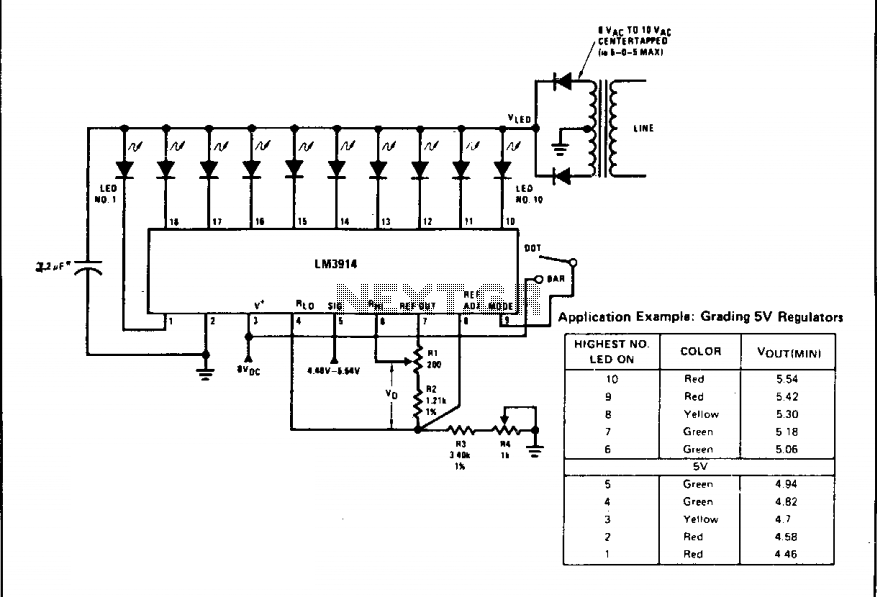
A bar graph driver IC LM314 drives an XED display. The LEDs may be separate or in a combined (integral) bar graph display. Calibration: With a precision meter between pins 4 and 6, adjust R1 for voltage Vq of 1.20V. Apply 4.94V to pin 5, and adjust R4 until LED No. 5 just lights. The adjustments are non-interacting.
The LM314 is a versatile integrated circuit designed to drive bar graph displays, commonly used in various electronic applications to visually represent data levels. The device can operate with separate LEDs or a combined bar graph display configuration, providing flexibility in design.
In the calibration process, a precision meter is utilized to measure the voltage between pins 4 and 6 of the LM314. The resistor R1 is adjusted to achieve a target voltage (Vq) of 1.20V, ensuring that the output levels are accurate for the intended application. This step is critical for achieving the desired performance of the display, as it sets the reference point for the LED activation thresholds.
Following the adjustment of R1, a voltage of 4.94V is applied to pin 5 of the LM314. This pin typically serves as a reference or control input, influencing the behavior of the driver IC. The next step involves adjusting resistor R4, which controls the current through the LEDs. The goal is to calibrate the circuit so that LED No. 5 lights up just at the correct threshold, indicating that the system is properly calibrated for the specific application.
The non-interacting nature of the adjustments means that changing the setting of one resistor does not significantly affect the other, simplifying the calibration process. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in applications where multiple parameters must be fine-tuned without causing cascading effects on the overall performance of the display.
Overall, the LM314 bar graph driver IC provides an efficient solution for driving LED displays, with straightforward calibration procedures that ensure accurate visual representation of varying signal levels.A bar graph driver IC LM314 drives anXED display. The LEDs may be separate or in a combined (integral) bar graph display. Calibration: With a precision meter be-tvveen pins 4 and 6 adjust Rl for voltage Vq of 1 20V. Apply 4.94V to pin 5, and adjust R4 until LED No. 5 iust lights. The adjustments are non-interacting. 🔗 External reference
The LM314 is a versatile integrated circuit designed to drive bar graph displays, commonly used in various electronic applications to visually represent data levels. The device can operate with separate LEDs or a combined bar graph display configuration, providing flexibility in design.
In the calibration process, a precision meter is utilized to measure the voltage between pins 4 and 6 of the LM314. The resistor R1 is adjusted to achieve a target voltage (Vq) of 1.20V, ensuring that the output levels are accurate for the intended application. This step is critical for achieving the desired performance of the display, as it sets the reference point for the LED activation thresholds.
Following the adjustment of R1, a voltage of 4.94V is applied to pin 5 of the LM314. This pin typically serves as a reference or control input, influencing the behavior of the driver IC. The next step involves adjusting resistor R4, which controls the current through the LEDs. The goal is to calibrate the circuit so that LED No. 5 lights up just at the correct threshold, indicating that the system is properly calibrated for the specific application.
The non-interacting nature of the adjustments means that changing the setting of one resistor does not significantly affect the other, simplifying the calibration process. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in applications where multiple parameters must be fine-tuned without causing cascading effects on the overall performance of the display.
Overall, the LM314 bar graph driver IC provides an efficient solution for driving LED displays, with straightforward calibration procedures that ensure accurate visual representation of varying signal levels.A bar graph driver IC LM314 drives anXED display. The LEDs may be separate or in a combined (integral) bar graph display. Calibration: With a precision meter be-tvveen pins 4 and 6 adjust Rl for voltage Vq of 1 20V. Apply 4.94V to pin 5, and adjust R4 until LED No. 5 iust lights. The adjustments are non-interacting. 🔗 External reference