Fahrenheit Thermometer Using LM35 Temperature Sensor IC
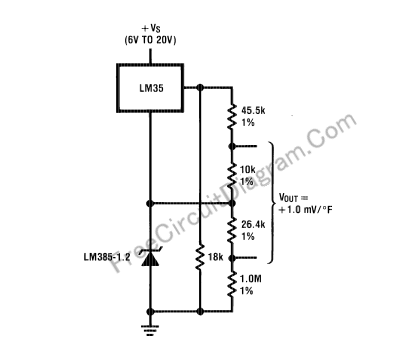
A digital voltmeter, or any voltmeter with millivolt resolution and high input impedance, can be utilized as a temperature-to-voltage adapter.
The described temperature-to-voltage adapter is designed to convert temperature readings into corresponding voltage outputs, suitable for interfacing with digital voltmeters. This adapter typically employs a temperature sensor, such as a thermocouple or thermistor, which generates a voltage that varies with temperature changes.
To implement this circuit, the temperature sensor is connected to a signal conditioning stage, which may include an operational amplifier to amplify the small voltage signal produced by the sensor. The output from the signal conditioning stage is then fed into the digital voltmeter.
The high input impedance of the voltmeter ensures that it does not load the sensor output, allowing for accurate temperature readings without affecting the sensor's performance. The millivolt resolution of the voltmeter enables precise measurements, making it suitable for applications requiring fine temperature resolution.
Additional components that may be included in the circuit are resistors for setting gain, capacitors for filtering noise, and possibly a microcontroller for digital processing if more complex functionality is desired. The design should also consider the temperature range of interest to select an appropriate sensor and ensure linearity in the voltage output across that range.
Overall, this setup allows for effective temperature monitoring and can be integrated into various applications, including HVAC systems, environmental monitoring, and industrial process control.If you have a digital voltmeter, or any voltmeter with millivolt resolution and high input impedance, then you can use this temperature-to-voltage adapter. 🔗 External reference
The described temperature-to-voltage adapter is designed to convert temperature readings into corresponding voltage outputs, suitable for interfacing with digital voltmeters. This adapter typically employs a temperature sensor, such as a thermocouple or thermistor, which generates a voltage that varies with temperature changes.
To implement this circuit, the temperature sensor is connected to a signal conditioning stage, which may include an operational amplifier to amplify the small voltage signal produced by the sensor. The output from the signal conditioning stage is then fed into the digital voltmeter.
The high input impedance of the voltmeter ensures that it does not load the sensor output, allowing for accurate temperature readings without affecting the sensor's performance. The millivolt resolution of the voltmeter enables precise measurements, making it suitable for applications requiring fine temperature resolution.
Additional components that may be included in the circuit are resistors for setting gain, capacitors for filtering noise, and possibly a microcontroller for digital processing if more complex functionality is desired. The design should also consider the temperature range of interest to select an appropriate sensor and ensure linearity in the voltage output across that range.
Overall, this setup allows for effective temperature monitoring and can be integrated into various applications, including HVAC systems, environmental monitoring, and industrial process control.If you have a digital voltmeter, or any voltmeter with millivolt resolution and high input impedance, then you can use this temperature-to-voltage adapter. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713