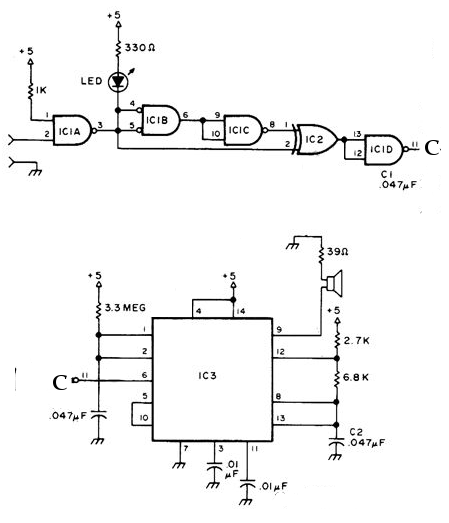
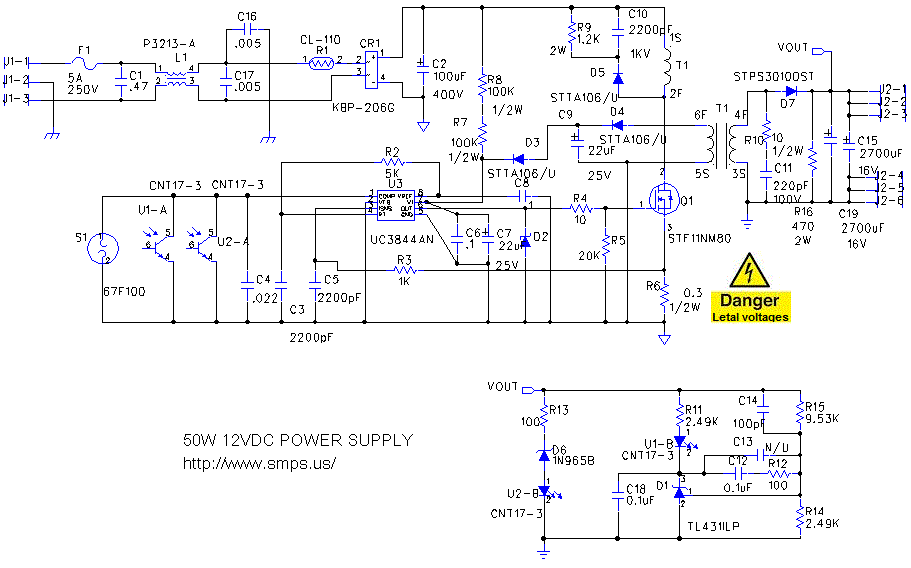
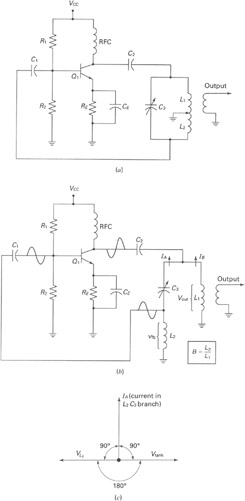
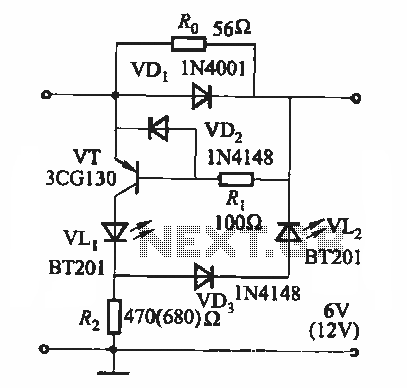
FET Audio Mixer Circuit
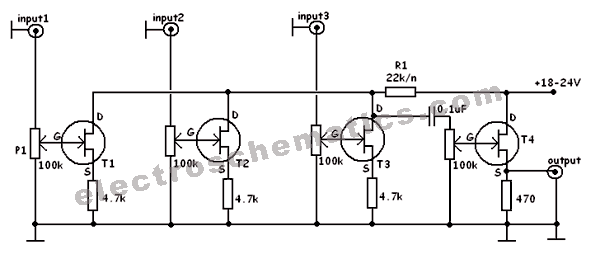
This FET audio mixer exemplifies the versatility of Field Effect Transistors (FETs). Although FETs were originally designed for high-frequency applications, they are also highly effective in audio frequency applications. The circuit can accommodate an unlimited number of inputs, provided that the value of R1 is selected according to the formula: R1 = 22K / n, where n represents the number of inputs.
The FET audio mixer circuit utilizes the unique properties of FETs to achieve high input impedance and low output impedance, which is advantageous for audio signal processing. The circuit typically consists of multiple FET stages, where each FET acts as a variable resistor controlled by the input signal. This allows for smooth mixing of audio signals from various sources without significant signal degradation.
In the schematic, each input channel is connected to its own FET, and the output of each FET is summed together to produce a mixed audio output. The resistive element R1 plays a crucial role in determining the input impedance and the overall gain of the mixer. As per the provided formula, adjusting R1 according to the number of inputs ensures that the circuit maintains optimal performance regardless of how many audio sources are connected.
Additionally, it is important to consider the power supply requirements for the FETs, which typically operate at low voltages. Proper decoupling capacitors should be included in the design to filter out any noise from the power supply, ensuring a clean audio output. The layout of the circuit should minimize the length of signal paths to reduce interference and maintain audio fidelity.
Overall, this FET audio mixer design showcases the adaptability of FET technology in audio applications, making it a valuable tool for audio engineers and enthusiasts alike.This FET audio mixer is an example of FET`s versatility. FETs are originally designed for high frequency applications but they can be used for audio frequencies and in fact they perform excellently in this area. The number of inputs that can be connected to the circuit is unlimited as long as the R1 value is chosen according to this formula: R1 =
22K / n, where n = the number of inputs. 🔗 External reference
The FET audio mixer circuit utilizes the unique properties of FETs to achieve high input impedance and low output impedance, which is advantageous for audio signal processing. The circuit typically consists of multiple FET stages, where each FET acts as a variable resistor controlled by the input signal. This allows for smooth mixing of audio signals from various sources without significant signal degradation.
In the schematic, each input channel is connected to its own FET, and the output of each FET is summed together to produce a mixed audio output. The resistive element R1 plays a crucial role in determining the input impedance and the overall gain of the mixer. As per the provided formula, adjusting R1 according to the number of inputs ensures that the circuit maintains optimal performance regardless of how many audio sources are connected.
Additionally, it is important to consider the power supply requirements for the FETs, which typically operate at low voltages. Proper decoupling capacitors should be included in the design to filter out any noise from the power supply, ensuring a clean audio output. The layout of the circuit should minimize the length of signal paths to reduce interference and maintain audio fidelity.
Overall, this FET audio mixer design showcases the adaptability of FET technology in audio applications, making it a valuable tool for audio engineers and enthusiasts alike.This FET audio mixer is an example of FET`s versatility. FETs are originally designed for high frequency applications but they can be used for audio frequencies and in fact they perform excellently in this area. The number of inputs that can be connected to the circuit is unlimited as long as the R1 value is chosen according to this formula: R1 =
22K / n, where n = the number of inputs. 🔗 External reference