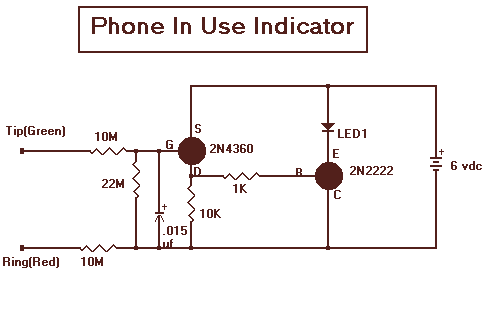
joule thief circuit project
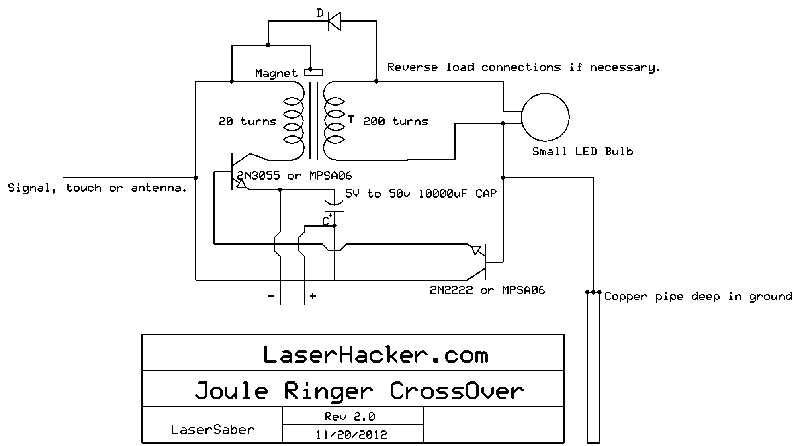
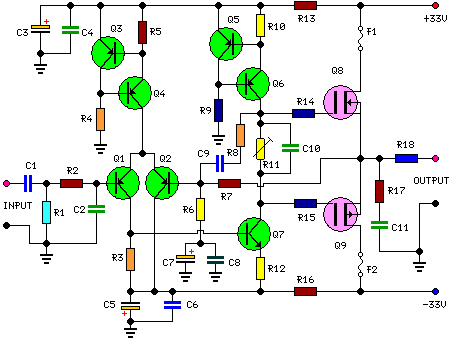
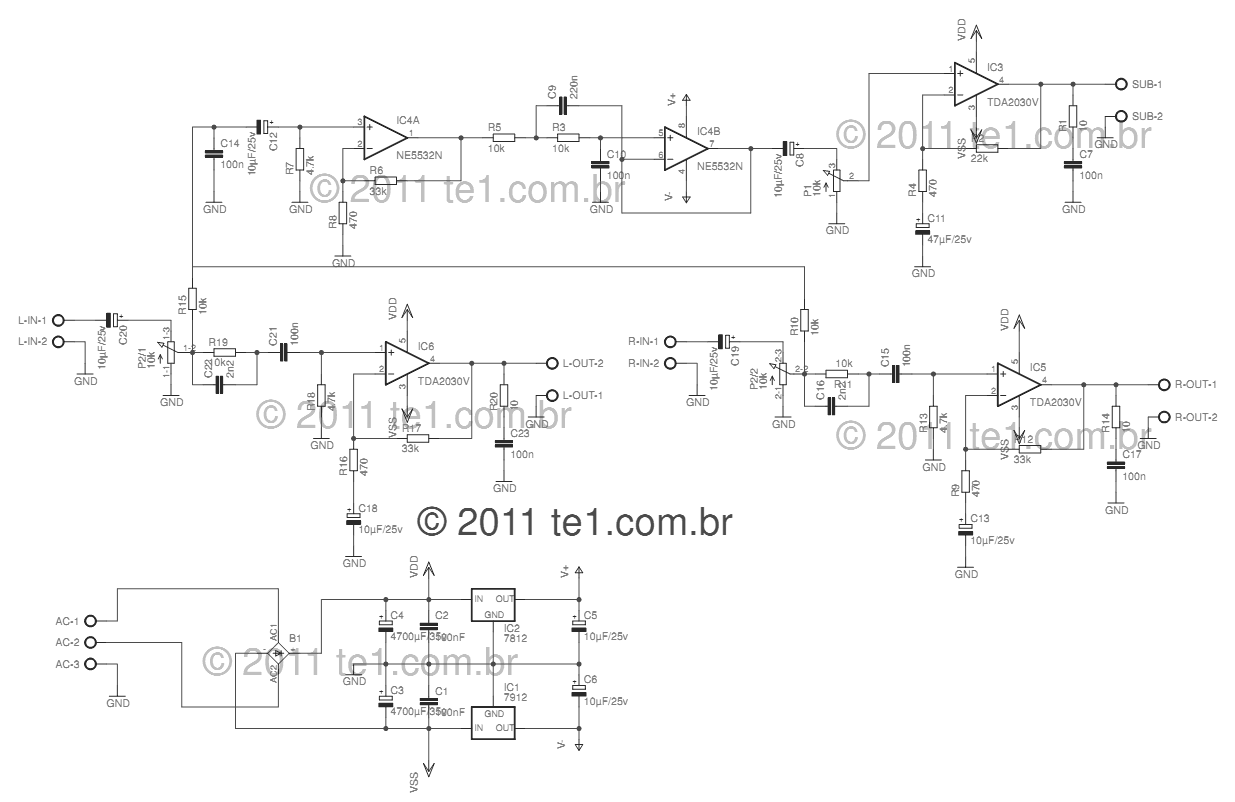
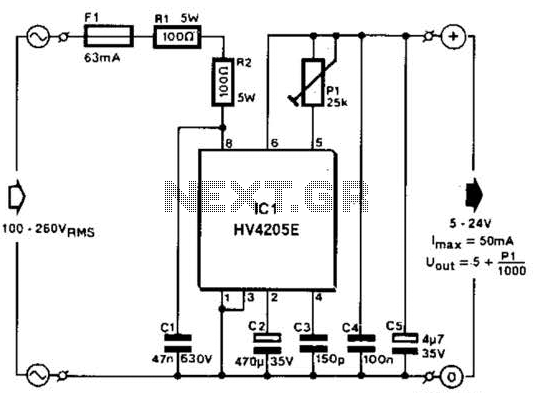
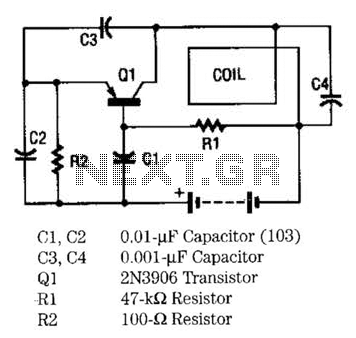
The conversion of a circuit from NPN to PNP configuration is in progress, along with a switch in polarity. Parts are being ordered for this modification.
The conversion from an NPN to a PNP transistor involves several key changes in the circuit design. NPN transistors are configured to conduct current when a positive voltage is applied to the base relative to the emitter, while PNP transistors require a negative voltage for the same effect. This fundamental difference necessitates a re-evaluation of the biasing and connection of components within the circuit.
In a typical NPN circuit, the collector is connected to a positive voltage supply, and the emitter is grounded. During conversion to a PNP configuration, the collector must be connected to a negative voltage supply, and the emitter should be connected to the positive voltage. The base resistor values may also need to be adjusted to ensure proper biasing of the PNP transistor, which typically involves changing the resistor values to accommodate the new voltage levels.
Additionally, any other components that interact with the transistor, such as diodes or capacitors, may require reconfiguration to maintain the desired functionality. It is crucial to ensure that the signal flow remains consistent with the original design's intent, despite the polarity and transistor type changes.
When ordering parts, it is advisable to select PNP transistors with similar specifications to the original NPN components, including current rating, voltage rating, and frequency response, to ensure compatibility and performance. Proper attention to these details will facilitate a successful transition to the PNP configuration while maintaining circuit integrity.I convert this to PNP from NPN entirely + switch polarity I am ordering parts. 🔗 External reference
The conversion from an NPN to a PNP transistor involves several key changes in the circuit design. NPN transistors are configured to conduct current when a positive voltage is applied to the base relative to the emitter, while PNP transistors require a negative voltage for the same effect. This fundamental difference necessitates a re-evaluation of the biasing and connection of components within the circuit.
In a typical NPN circuit, the collector is connected to a positive voltage supply, and the emitter is grounded. During conversion to a PNP configuration, the collector must be connected to a negative voltage supply, and the emitter should be connected to the positive voltage. The base resistor values may also need to be adjusted to ensure proper biasing of the PNP transistor, which typically involves changing the resistor values to accommodate the new voltage levels.
Additionally, any other components that interact with the transistor, such as diodes or capacitors, may require reconfiguration to maintain the desired functionality. It is crucial to ensure that the signal flow remains consistent with the original design's intent, despite the polarity and transistor type changes.
When ordering parts, it is advisable to select PNP transistors with similar specifications to the original NPN components, including current rating, voltage rating, and frequency response, to ensure compatibility and performance. Proper attention to these details will facilitate a successful transition to the PNP configuration while maintaining circuit integrity.I convert this to PNP from NPN entirely + switch polarity I am ordering parts. 🔗 External reference