fet audio mixer schematics
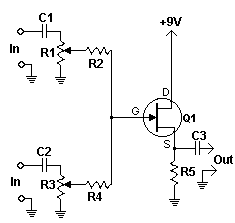
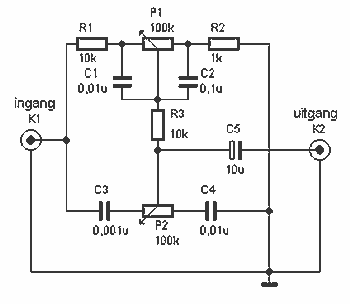
This simple circuit combines two or more audio channels into a single channel (for example, mixing stereo into mono). The circuit is capable of mixing an arbitrary number of channels while consuming minimal power. Although the schematic illustrates two inputs, additional inputs can be incorporated by duplicating the clearly defined sections shown in the schematic.
The circuit operates by utilizing resistive mixing techniques, which allow for the summation of multiple audio signals without significant distortion or loss of quality. Each input channel is connected to a resistor network that ensures proper impedance matching, thereby preventing loading effects that could degrade the audio signals.
Typically, the circuit will consist of a series of resistors connected to the inputs, with their outputs converging into a single output node. The values of the resistors can be selected based on the desired mixing ratio and to maintain a consistent output level. For example, equal-value resistors can be used for a balanced mix, while varying resistor values can create a weighted mix favoring certain channels.
Power consumption in this circuit is kept low due to the passive nature of the resistive components, making it suitable for battery-operated devices or low-power applications. The overall design can be easily modified to accommodate additional inputs, enhancing its versatility in various audio mixing scenarios.
For implementation, it is essential to ensure that the circuit is housed in a suitable enclosure to minimize interference and maintain signal integrity. Additionally, proper grounding techniques should be employed to reduce noise and improve performance. This circuit is ideal for applications such as audio processing in home theater systems, musical instruments, or any device requiring audio channel mixing.This simple circuit mixes two or more channels into one channel (eg. stereo into mono). The circuit can mix as many or as few channels as you like and consumes very little power. The mixer is shown with two inputs, but you can add as many as you want by just duplicating the "sections" which are clearly visible on the schematic. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing resistive mixing techniques, which allow for the summation of multiple audio signals without significant distortion or loss of quality. Each input channel is connected to a resistor network that ensures proper impedance matching, thereby preventing loading effects that could degrade the audio signals.
Typically, the circuit will consist of a series of resistors connected to the inputs, with their outputs converging into a single output node. The values of the resistors can be selected based on the desired mixing ratio and to maintain a consistent output level. For example, equal-value resistors can be used for a balanced mix, while varying resistor values can create a weighted mix favoring certain channels.
Power consumption in this circuit is kept low due to the passive nature of the resistive components, making it suitable for battery-operated devices or low-power applications. The overall design can be easily modified to accommodate additional inputs, enhancing its versatility in various audio mixing scenarios.
For implementation, it is essential to ensure that the circuit is housed in a suitable enclosure to minimize interference and maintain signal integrity. Additionally, proper grounding techniques should be employed to reduce noise and improve performance. This circuit is ideal for applications such as audio processing in home theater systems, musical instruments, or any device requiring audio channel mixing.This simple circuit mixes two or more channels into one channel (eg. stereo into mono). The circuit can mix as many or as few channels as you like and consumes very little power. The mixer is shown with two inputs, but you can add as many as you want by just duplicating the "sections" which are clearly visible on the schematic. 🔗 External reference