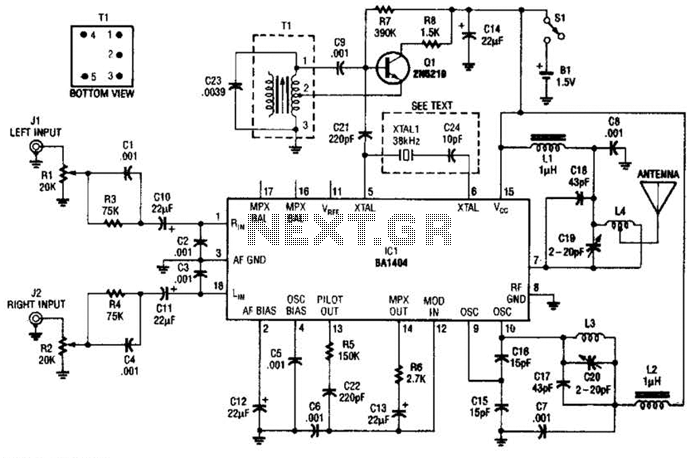
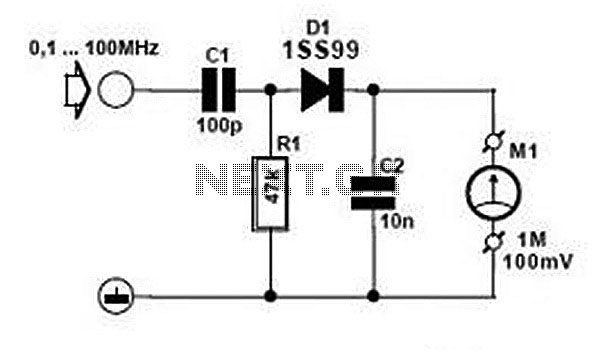
FET Preamplifier Circuit

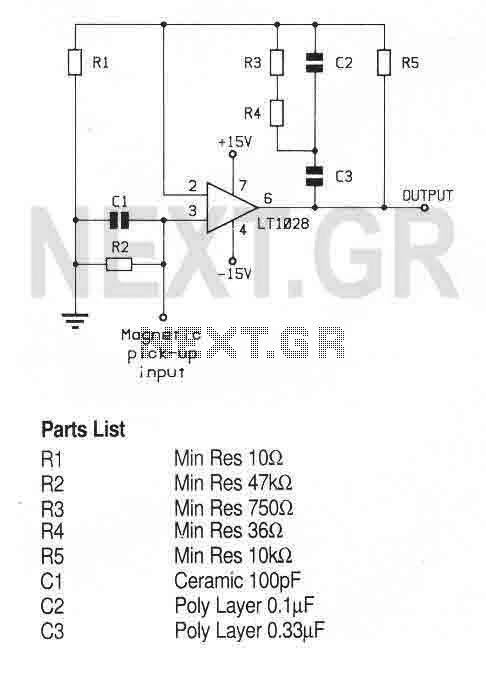
A Field Effect Transistor (FET) is an amplifying device where the output current is influenced by the input voltage. The FET preamplifier described here is sensitive.
The Field Effect Transistor (FET) operates by utilizing an electric field to control the flow of current. In this configuration, the input voltage applied to the gate terminal modulates the conductivity of a channel, allowing for amplification of signals. The FET preamplifier is particularly effective in low-level signal applications due to its high input impedance and low output impedance, which minimizes loading effects on the preceding stage of the circuit.
In a typical FET preamplifier circuit, the FET is connected in a common-source configuration, where the source terminal is grounded. The input signal is applied to the gate, and the amplified output is taken from the drain terminal. Biasing resistors are employed to set the operating point of the FET, ensuring linear amplification over the desired range of input signals. Coupling capacitors may also be used to block DC components while allowing AC signals to pass through.
The sensitivity of the FET preamplifier allows it to effectively amplify small signals, such as those from sensors or microphones, making it suitable for various applications in audio processing, instrumentation, and communication systems. The design considerations for the FET preamplifier include selecting an appropriate FET type, determining the biasing resistors' values, and ensuring proper power supply decoupling to maintain stability and performance.Field Effect Transistor is an amplifying device in which the output current depends on the input voltage. The FET Pre Amplifier described here is a sensiti.. 🔗 External reference
The Field Effect Transistor (FET) operates by utilizing an electric field to control the flow of current. In this configuration, the input voltage applied to the gate terminal modulates the conductivity of a channel, allowing for amplification of signals. The FET preamplifier is particularly effective in low-level signal applications due to its high input impedance and low output impedance, which minimizes loading effects on the preceding stage of the circuit.
In a typical FET preamplifier circuit, the FET is connected in a common-source configuration, where the source terminal is grounded. The input signal is applied to the gate, and the amplified output is taken from the drain terminal. Biasing resistors are employed to set the operating point of the FET, ensuring linear amplification over the desired range of input signals. Coupling capacitors may also be used to block DC components while allowing AC signals to pass through.
The sensitivity of the FET preamplifier allows it to effectively amplify small signals, such as those from sensors or microphones, making it suitable for various applications in audio processing, instrumentation, and communication systems. The design considerations for the FET preamplifier include selecting an appropriate FET type, determining the biasing resistors' values, and ensuring proper power supply decoupling to maintain stability and performance.Field Effect Transistor is an amplifying device in which the output current depends on the input voltage. The FET Pre Amplifier described here is a sensiti.. 🔗 External reference