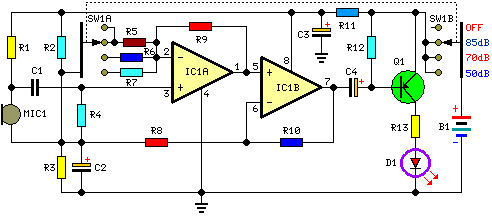
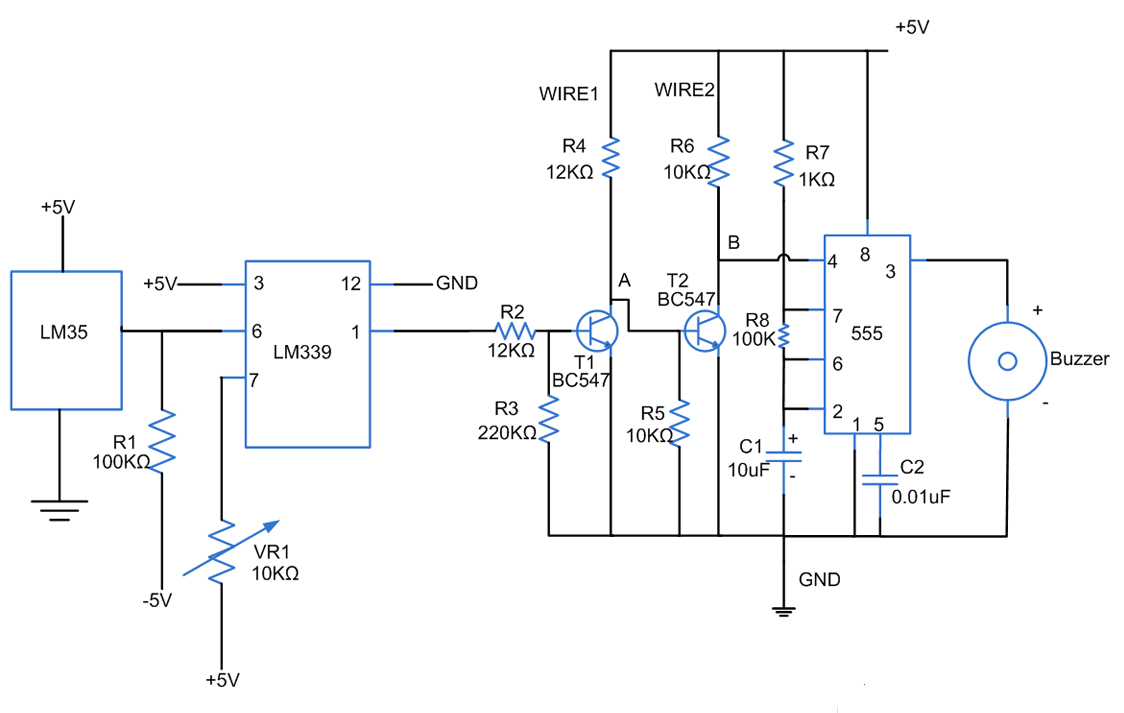
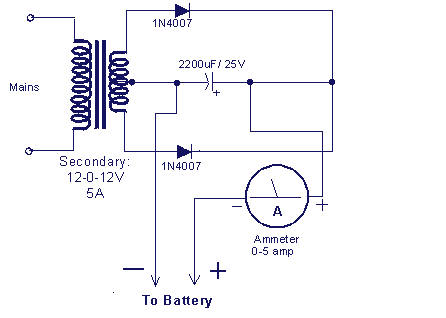
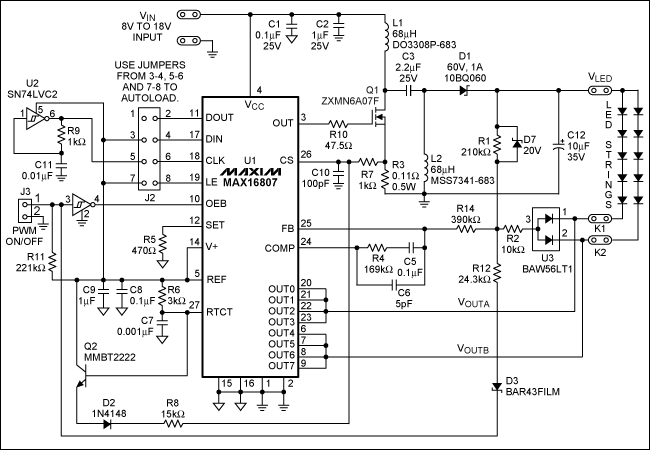
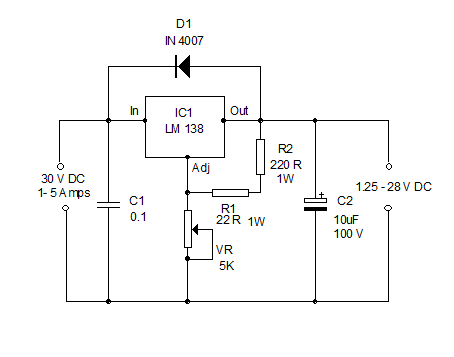
Stock dial telephone line power supply circuit diagram
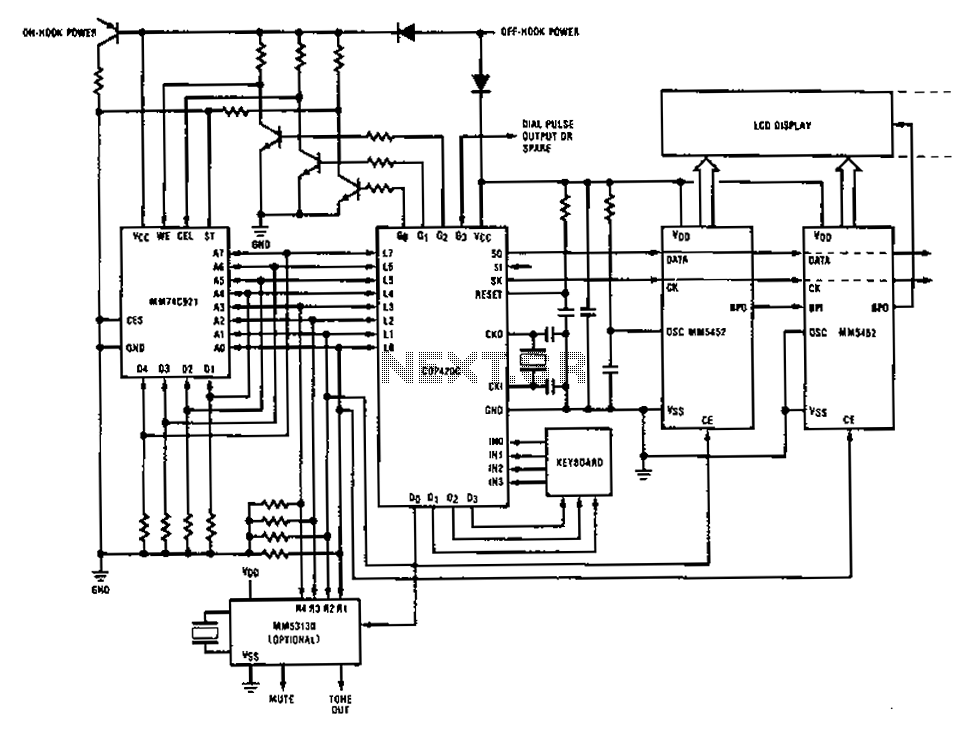
A compilation of dial phone numbers, including 15 commonly used libraries and the dialed number, is stored in standard CMOS RAM. A single-button keypad facilitates the input of a phone number, which can be dialed directly or stored in RAM for automatic dialing.
The circuit design involves a standard CMOS RAM chip responsible for storing up to 15 frequently used phone numbers in a binary format. Each phone number is typically represented as a series of digits, and the RAM allows for easy retrieval and storage of these numbers. The keypad interface consists of a single-button input that enables users to input a phone number directly. When the button is pressed, the circuit captures the number entered and temporarily stores it in RAM.
The automatic dialing feature is facilitated by a microcontroller that interfaces with both the RAM and the telephone line. Upon storing a number in RAM, the microcontroller can initiate a dialing sequence by sending the appropriate signals to the telephone line. The design may also include a debounce circuit to ensure that a single button press is registered accurately, preventing multiple inputs from being registered due to mechanical bounce.
Power supply considerations are crucial for this circuit, with a regulated power source required to ensure stable operation of the CMOS RAM and microcontroller. Additional components such as resistors and capacitors may be employed for signal conditioning and noise reduction.
Overall, this schematic provides a user-friendly solution for dialing frequently used phone numbers, enhancing efficiency and convenience in telecommunication. Compilation dial phone numbers with 15 commonly used libraries (plus number dialed) are stored in a standard CMOS RAM, one button keypad makes typing a phone number can be dial ed directly and, or may make the phone are stored in RAM and then automatically dialed.
The circuit design involves a standard CMOS RAM chip responsible for storing up to 15 frequently used phone numbers in a binary format. Each phone number is typically represented as a series of digits, and the RAM allows for easy retrieval and storage of these numbers. The keypad interface consists of a single-button input that enables users to input a phone number directly. When the button is pressed, the circuit captures the number entered and temporarily stores it in RAM.
The automatic dialing feature is facilitated by a microcontroller that interfaces with both the RAM and the telephone line. Upon storing a number in RAM, the microcontroller can initiate a dialing sequence by sending the appropriate signals to the telephone line. The design may also include a debounce circuit to ensure that a single button press is registered accurately, preventing multiple inputs from being registered due to mechanical bounce.
Power supply considerations are crucial for this circuit, with a regulated power source required to ensure stable operation of the CMOS RAM and microcontroller. Additional components such as resistors and capacitors may be employed for signal conditioning and noise reduction.
Overall, this schematic provides a user-friendly solution for dialing frequently used phone numbers, enhancing efficiency and convenience in telecommunication. Compilation dial phone numbers with 15 commonly used libraries (plus number dialed) are stored in a standard CMOS RAM, one button keypad makes typing a phone number can be dial ed directly and, or may make the phone are stored in RAM and then automatically dialed.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713