FET used as a silencer tube headphone circuit
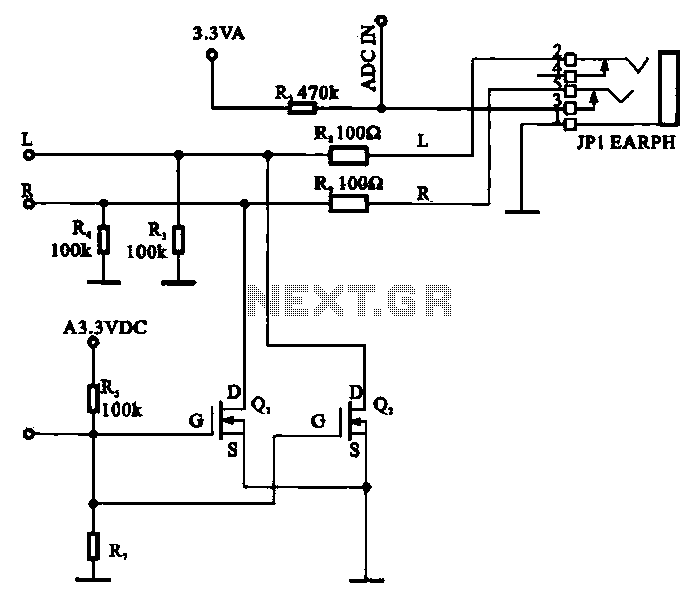
A field-effect transistor (FET) is utilized in a headphone circuit designed to function as a silencer tube. The circuit integrates L from the digital signal processing unit and R from the audio signal into the headphone jack's mute control circuit. Transistors Q1 and Q2 are connected to the drain of the FET, receiving the input signals L and R. When the control circuit sends a signal to activate the silencer, a control voltage is applied, turning on Q1 and Q2. This action shorts the L and R signals to ground, resulting in no output signal and placing the MP3/MP4 device in a mute state.
The schematic for the FET-based silencer tube headphone circuit incorporates several critical components to achieve its functionality. The field-effect transistor serves as the primary switching element, allowing for the control of audio signals transmitted to the headphones. The circuit begins with the audio input, designated as L (left channel) and R (right channel), which are fed from a digital signal processing unit. These signals are routed to the drains of two N-channel FETs, Q1 and Q2, which act as electronic switches.
The control circuit is essential for managing the mute function. It generates a control voltage that determines the operational state of Q1 and Q2. When the control voltage is applied, both transistors are turned on, creating a conductive path from the input signals to ground. This effectively shorts the audio signals to ground, preventing any audio output to the headphones and ensuring that the device enters a mute state.
To enhance the circuit's performance, decoupling capacitors may be included in parallel with the power supply lines to filter out noise and stabilize voltage levels. Additionally, resistors can be employed to limit the current flowing through the FETs, protecting them from potential damage due to overcurrent conditions.
This design is particularly useful in applications where quick and efficient muting of audio is required, such as in portable media players or smartphones, allowing users to silence audio output without the need for mechanical switches. The overall simplicity and effectiveness of this circuit make it a practical solution for integrating mute functionality into headphone systems.FET used as a silencer tube headphone circuit Field-effect transistor is shown as a headphone circuit silencer tube. L from the digital signal processing circuit, R audio signa l to the headphone jack mute control circuit, Ql, Q2 are respectively connected to the drain of the field effect transistor input line L, R signal, when the control circuit sending to the silencer when the control voltage, Ql, Q2 is turned on, the L, R signal is shorted to ground, no signal output, MP3/MP4 is in mute state.
The schematic for the FET-based silencer tube headphone circuit incorporates several critical components to achieve its functionality. The field-effect transistor serves as the primary switching element, allowing for the control of audio signals transmitted to the headphones. The circuit begins with the audio input, designated as L (left channel) and R (right channel), which are fed from a digital signal processing unit. These signals are routed to the drains of two N-channel FETs, Q1 and Q2, which act as electronic switches.
The control circuit is essential for managing the mute function. It generates a control voltage that determines the operational state of Q1 and Q2. When the control voltage is applied, both transistors are turned on, creating a conductive path from the input signals to ground. This effectively shorts the audio signals to ground, preventing any audio output to the headphones and ensuring that the device enters a mute state.
To enhance the circuit's performance, decoupling capacitors may be included in parallel with the power supply lines to filter out noise and stabilize voltage levels. Additionally, resistors can be employed to limit the current flowing through the FETs, protecting them from potential damage due to overcurrent conditions.
This design is particularly useful in applications where quick and efficient muting of audio is required, such as in portable media players or smartphones, allowing users to silence audio output without the need for mechanical switches. The overall simplicity and effectiveness of this circuit make it a practical solution for integrating mute functionality into headphone systems.FET used as a silencer tube headphone circuit Field-effect transistor is shown as a headphone circuit silencer tube. L from the digital signal processing circuit, R audio signa l to the headphone jack mute control circuit, Ql, Q2 are respectively connected to the drain of the field effect transistor input line L, R signal, when the control circuit sending to the silencer when the control voltage, Ql, Q2 is turned on, the L, R signal is shorted to ground, no signal output, MP3/MP4 is in mute state.