field strength meter
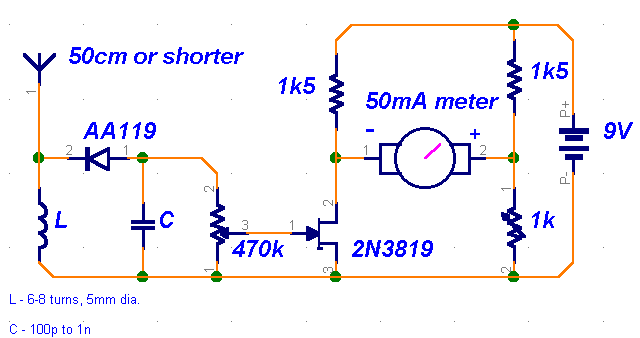
One cannot expect high performance from a simple detector-based meter. The sensitivity is only sufficient to provide a basic understanding of the power output that the transmitter can achieve.
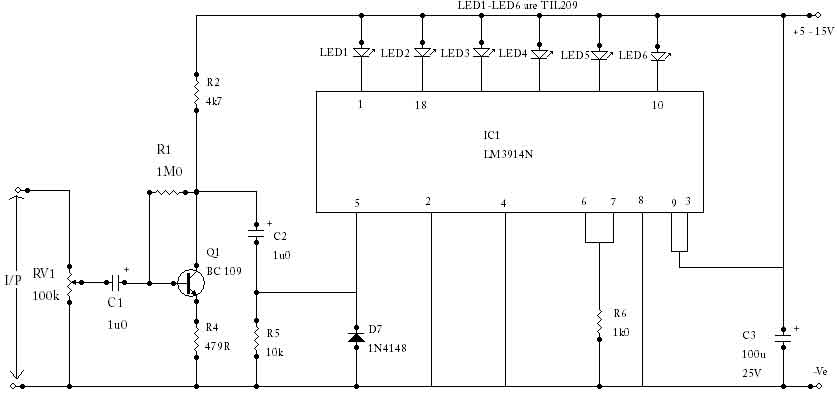
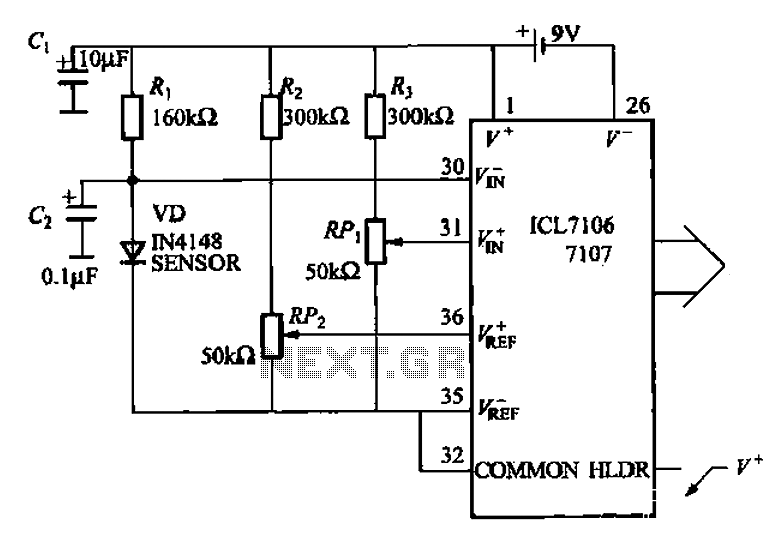
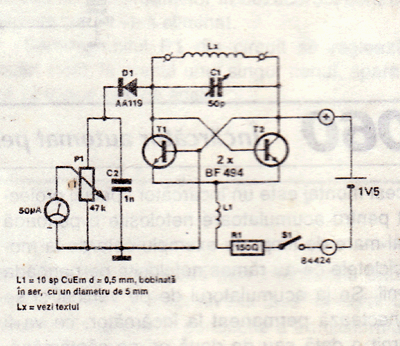
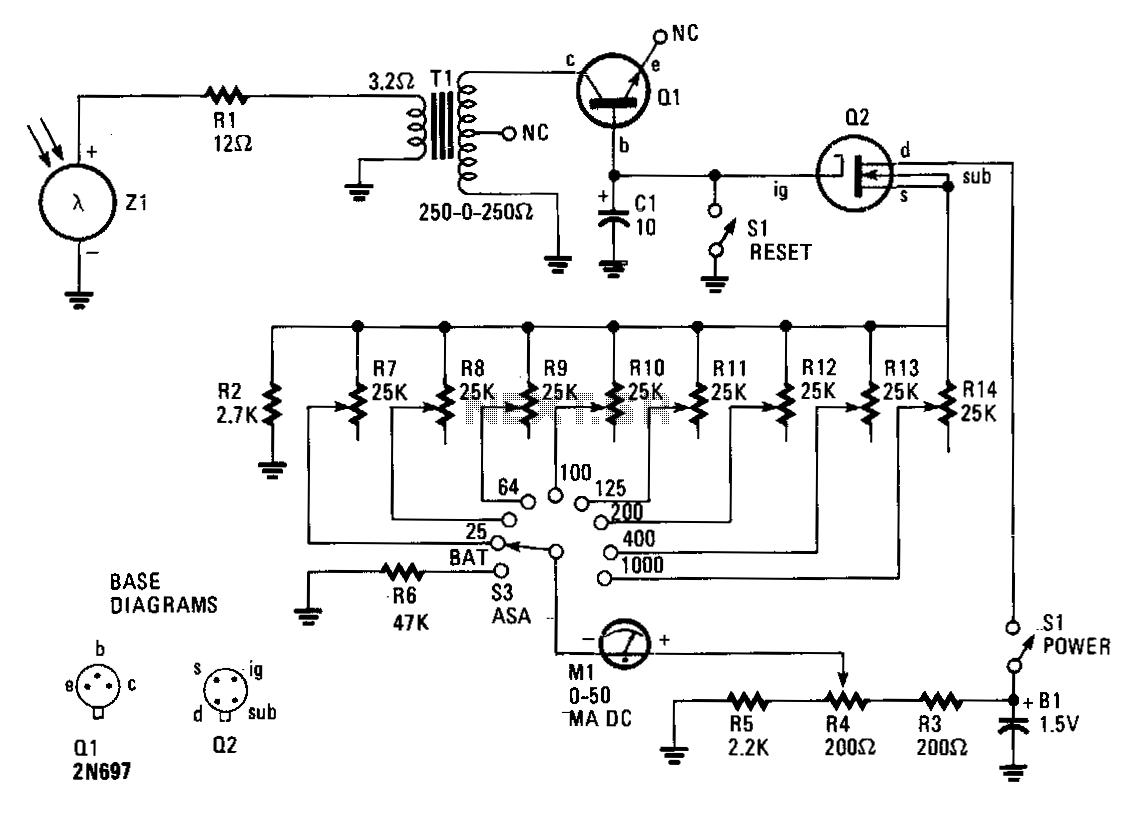
A detector-based meter operates on the principle of rectifying the RF signal to provide a DC output that is proportional to the input power level. These meters typically utilize a diode as the detection element, which converts the alternating current (AC) signal into a direct current (DC) signal. The output is then usually displayed on an analog or digital meter, allowing the user to gauge the transmitter's power.
While detector-based meters are advantageous for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, they have limitations in terms of accuracy and sensitivity. The performance of such meters is often constrained by the characteristics of the diode used, including its forward voltage drop and response time. As a result, the readings may not be precise, particularly at lower power levels or in the presence of fluctuations in the RF signal.
For applications requiring more accurate power measurements, alternative methods such as using a true RMS power meter or a directional coupler may be more appropriate. These devices provide improved sensitivity and accuracy by employing more advanced circuitry and components, allowing for a better assessment of the transmitter's performance.You can`t expect great performance from such a simple detector-based meter. Sensitivity is just adequate enough to get a basic idea of the power that your transmitter is capable of.. 🔗 External reference
A detector-based meter operates on the principle of rectifying the RF signal to provide a DC output that is proportional to the input power level. These meters typically utilize a diode as the detection element, which converts the alternating current (AC) signal into a direct current (DC) signal. The output is then usually displayed on an analog or digital meter, allowing the user to gauge the transmitter's power.
While detector-based meters are advantageous for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, they have limitations in terms of accuracy and sensitivity. The performance of such meters is often constrained by the characteristics of the diode used, including its forward voltage drop and response time. As a result, the readings may not be precise, particularly at lower power levels or in the presence of fluctuations in the RF signal.
For applications requiring more accurate power measurements, alternative methods such as using a true RMS power meter or a directional coupler may be more appropriate. These devices provide improved sensitivity and accuracy by employing more advanced circuitry and components, allowing for a better assessment of the transmitter's performance.You can`t expect great performance from such a simple detector-based meter. Sensitivity is just adequate enough to get a basic idea of the power that your transmitter is capable of.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713