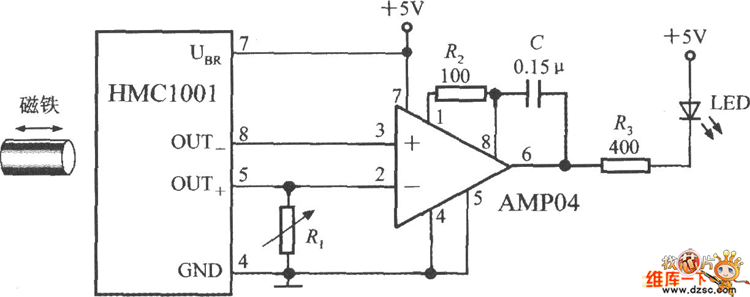
Thermistor electronic thermometer circuit diagram

The thermistor RT, along with resistors R1, R2, R3, and variable resistor RP1, creates a temperature measurement bridge. At a temperature of 20°C, the configuration of R1, R3, and the adjustment of RP1 enables the bridge to maintain balance. As the temperature increases, the resistance of the thermistor RT decreases, resulting in an unbalanced state of the bridge. The voltage difference output from the bridge is subsequently amplified by an operational amplifier.
The described circuit employs a Wheatstone bridge configuration to accurately measure temperature variations through the thermistor RT. The resistors R1, R2, and R3 are arranged to form a balanced bridge at a reference temperature, typically set at 20°C. The variable resistor RP1 allows for fine-tuning of the balance, compensating for any discrepancies in resistor values or thermistor characteristics.
As the temperature rises, the thermistor RT's resistance decreases, causing the bridge to become unbalanced. This unbalance generates a differential voltage across the bridge's output terminals. The magnitude of this voltage change is proportional to the change in temperature, enabling precise temperature measurement.
The operational amplifier connected to the output of the bridge amplifies the differential voltage signal. This amplification is crucial for enhancing the sensitivity of the measurement, allowing for the detection of small variations in temperature. The output of the operational amplifier can be further processed or displayed, providing a clear indication of the measured temperature.
This circuit design is commonly used in temperature sensing applications, where accurate and responsive temperature readings are essential. The integration of the thermistor with the resistive network and operational amplifier ensures reliable performance across a range of temperatures.The thermistor RT and R1, R2, R3 and RP1 form a temperature measurement bridge. When temperature is at 20 ?, using R1, R3 and adjusting RP1 can allow bridge to keep balance. When temperature rises, the resistance of the thermistor RT reduces, the bridge in an unbalanced state, the imbalanced voltage output by bridge is amplified by operational amplifier, th.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs a Wheatstone bridge configuration to accurately measure temperature variations through the thermistor RT. The resistors R1, R2, and R3 are arranged to form a balanced bridge at a reference temperature, typically set at 20°C. The variable resistor RP1 allows for fine-tuning of the balance, compensating for any discrepancies in resistor values or thermistor characteristics.
As the temperature rises, the thermistor RT's resistance decreases, causing the bridge to become unbalanced. This unbalance generates a differential voltage across the bridge's output terminals. The magnitude of this voltage change is proportional to the change in temperature, enabling precise temperature measurement.
The operational amplifier connected to the output of the bridge amplifies the differential voltage signal. This amplification is crucial for enhancing the sensitivity of the measurement, allowing for the detection of small variations in temperature. The output of the operational amplifier can be further processed or displayed, providing a clear indication of the measured temperature.
This circuit design is commonly used in temperature sensing applications, where accurate and responsive temperature readings are essential. The integration of the thermistor with the resistive network and operational amplifier ensures reliable performance across a range of temperatures.The thermistor RT and R1, R2, R3 and RP1 form a temperature measurement bridge. When temperature is at 20 ?, using R1, R3 and adjusting RP1 can allow bridge to keep balance. When temperature rises, the resistance of the thermistor RT reduces, the bridge in an unbalanced state, the imbalanced voltage output by bridge is amplified by operational amplifier, th.. 🔗 External reference