Field strength meter
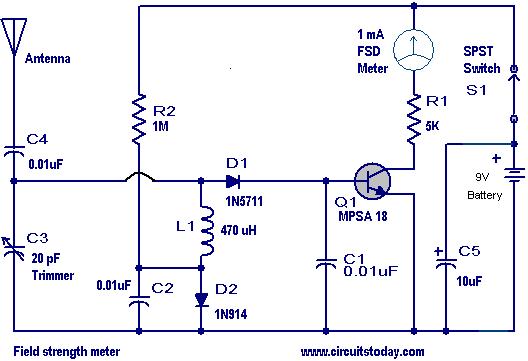
This is a practical field strength meter designed to measure the strength of AM radio signals. The circuit is particularly beneficial for individuals assembling radio transmitters, especially during the tuning of the final stage to achieve maximum range. Essentially, the circuit functions as an AM receiver. The capacitor C3 and inductor L1 create a tuned circuit to receive a specific frequency, corresponding to the transmitter's frequency. The diode D1 detects the signal and feeds it to the base of transistor Q1 (MPSA 18). The collector current of Q1 is proportional to the signal strength and is displayed on meter M1. Consequently, the meter reading indicates the strength of the signal at the tuned frequency received by the antenna. The value of C3 must be adjusted to tune into the transmitter's frequency. To do this, the antenna of the meter circuit should be positioned close to the transmitter's antenna, and C3 should be adjusted until the maximum reading is observed on meter M1. To optimize the transmitter for maximum range, the meter circuit should be placed near the transmitter while adjusting the transmitter's tuning components. The maximum range setting is achieved when the meter shows full deflection. Switch S1 serves as the power switch; it should be turned off when the circuit is not in use to conserve battery life.
The field strength meter circuit consists of a few key components that work in unison to provide an accurate measurement of AM signal strength. The tuned circuit, formed by capacitor C3 and inductor L1, is critical for filtering and selecting the desired frequency from the incoming radio signals. The choice of inductor and capacitor values will determine the resonant frequency of the circuit, which should be aligned with the transmitter frequency for optimal performance.
The diode D1, typically a small signal diode, is responsible for rectifying the detected radio frequency signal, converting it into a direct current (DC) signal that can be processed by the transistor Q1. The MPSA 18 transistor amplifies this signal, and its collector current provides a measurable output that corresponds to the strength of the incoming signal. The meter M1, usually an analog or digital voltmeter, displays this current, allowing the user to visualize the signal strength.
The tuning process involves careful adjustment of C3 while monitoring the meter reading to achieve maximum deflection, indicating the strongest signal reception. This process is crucial for ensuring that the transmitter operates efficiently and effectively at its designated frequency. By placing the field strength meter near the transmitter and adjusting its tuning elements, the user can determine the optimal settings for maximum range.
The power switch S1 is an essential feature, allowing the user to control the circuit's power consumption. When the circuit is not in use, turning off S1 prevents unnecessary battery drain, extending the life of the power source. This consideration is particularly important in portable applications where battery life is critical.
Overall, this field strength meter serves as a valuable tool for amateur radio enthusiasts and professionals alike, facilitating the tuning and optimization of AM radio transmitters for enhanced performance.Here is a handy field strength meter that can be used to check the strength of AM radio signals. The circuit is a very useful for those who assemble radio transmitters(especially in the tuning of the final stage for maximum range). The circuit is essentially some sort of a AM receiver it self. The capacitor C3 and inductor L1 forms a tuned circuit to receive a particular frequency(the frequency of your transmitter). The diode D1 detects the signal and applies to the base of transistor Q1 (MPSA 18). The collector current of the Q1 will be proportional to the strength of this signal and will be shown in the meter M1. In result the meter reading will be a measure of the strength of the signal (of the tuned frequency) falling on the antenna.
The C3 must be varied to tune in to the frequency of your transmitter. For that, keep the antenna of meter circuit close to the antenna of your transmitter and adjust C3 to get a maximum reading on meter M1. In order to tune your transmitter for a maximum range, place the meter circuit some place near to the transmitter and adjust the transmitters tuning elements.
Maximum range setting will at the point where the meter shows full deflection. Switch S1 is used as a power switch. Keep this switch OFF when circuit is not in use to save battery life. Do you know Why. If you know then please add it as a comment here. The correct answers will be rewarded. A small contest for you!. 🔗 External reference
The field strength meter circuit consists of a few key components that work in unison to provide an accurate measurement of AM signal strength. The tuned circuit, formed by capacitor C3 and inductor L1, is critical for filtering and selecting the desired frequency from the incoming radio signals. The choice of inductor and capacitor values will determine the resonant frequency of the circuit, which should be aligned with the transmitter frequency for optimal performance.
The diode D1, typically a small signal diode, is responsible for rectifying the detected radio frequency signal, converting it into a direct current (DC) signal that can be processed by the transistor Q1. The MPSA 18 transistor amplifies this signal, and its collector current provides a measurable output that corresponds to the strength of the incoming signal. The meter M1, usually an analog or digital voltmeter, displays this current, allowing the user to visualize the signal strength.
The tuning process involves careful adjustment of C3 while monitoring the meter reading to achieve maximum deflection, indicating the strongest signal reception. This process is crucial for ensuring that the transmitter operates efficiently and effectively at its designated frequency. By placing the field strength meter near the transmitter and adjusting its tuning elements, the user can determine the optimal settings for maximum range.
The power switch S1 is an essential feature, allowing the user to control the circuit's power consumption. When the circuit is not in use, turning off S1 prevents unnecessary battery drain, extending the life of the power source. This consideration is particularly important in portable applications where battery life is critical.
Overall, this field strength meter serves as a valuable tool for amateur radio enthusiasts and professionals alike, facilitating the tuning and optimization of AM radio transmitters for enhanced performance.Here is a handy field strength meter that can be used to check the strength of AM radio signals. The circuit is a very useful for those who assemble radio transmitters(especially in the tuning of the final stage for maximum range). The circuit is essentially some sort of a AM receiver it self. The capacitor C3 and inductor L1 forms a tuned circuit to receive a particular frequency(the frequency of your transmitter). The diode D1 detects the signal and applies to the base of transistor Q1 (MPSA 18). The collector current of the Q1 will be proportional to the strength of this signal and will be shown in the meter M1. In result the meter reading will be a measure of the strength of the signal (of the tuned frequency) falling on the antenna.
The C3 must be varied to tune in to the frequency of your transmitter. For that, keep the antenna of meter circuit close to the antenna of your transmitter and adjust C3 to get a maximum reading on meter M1. In order to tune your transmitter for a maximum range, place the meter circuit some place near to the transmitter and adjust the transmitters tuning elements.
Maximum range setting will at the point where the meter shows full deflection. Switch S1 is used as a power switch. Keep this switch OFF when circuit is not in use to save battery life. Do you know Why. If you know then please add it as a comment here. The correct answers will be rewarded. A small contest for you!. 🔗 External reference