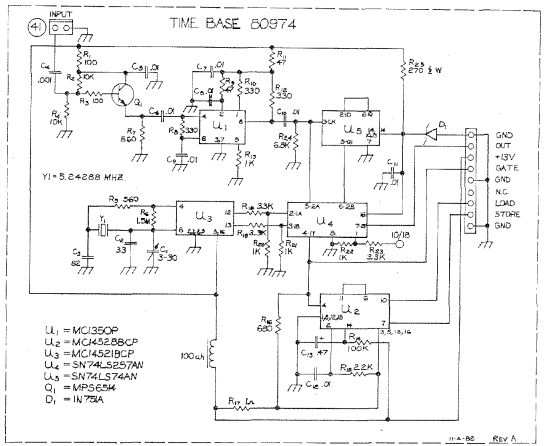
ANALOG TACHOMETER READOUT
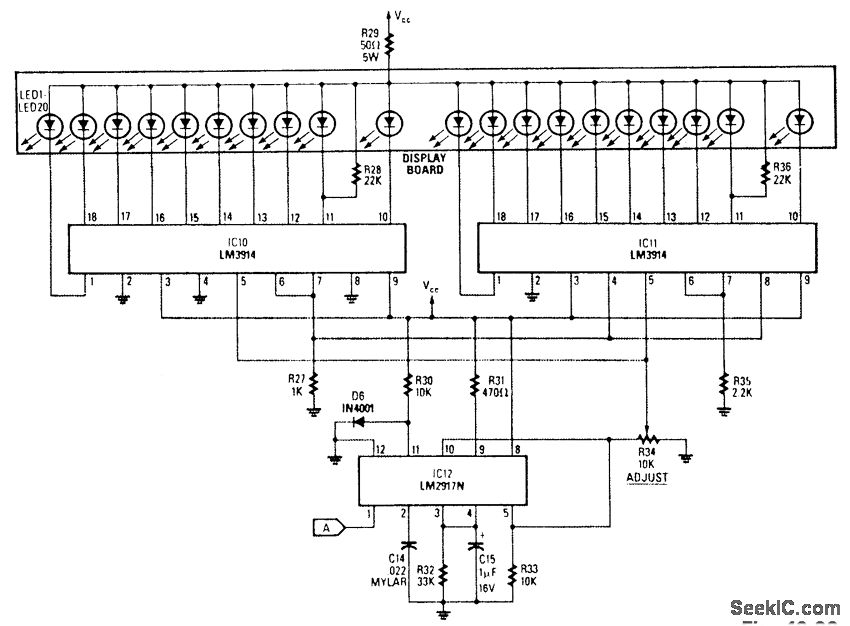
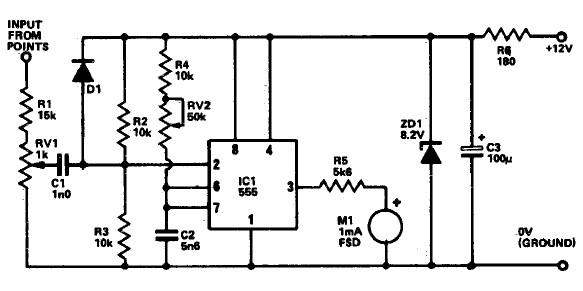
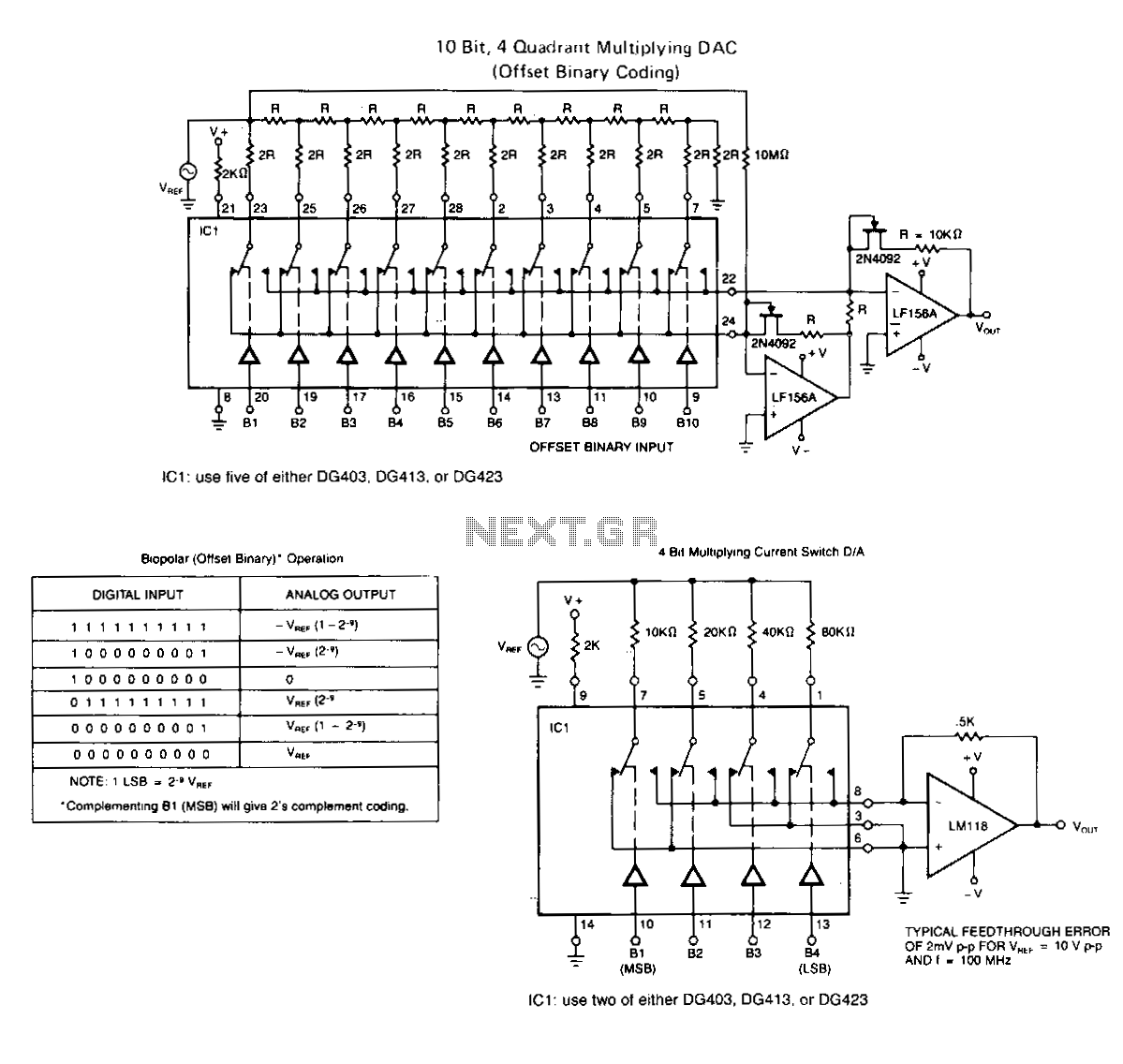
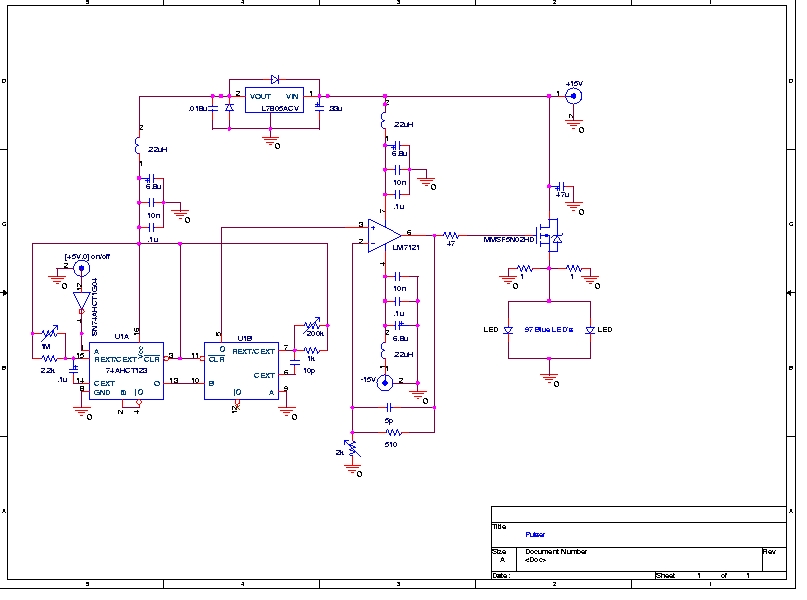
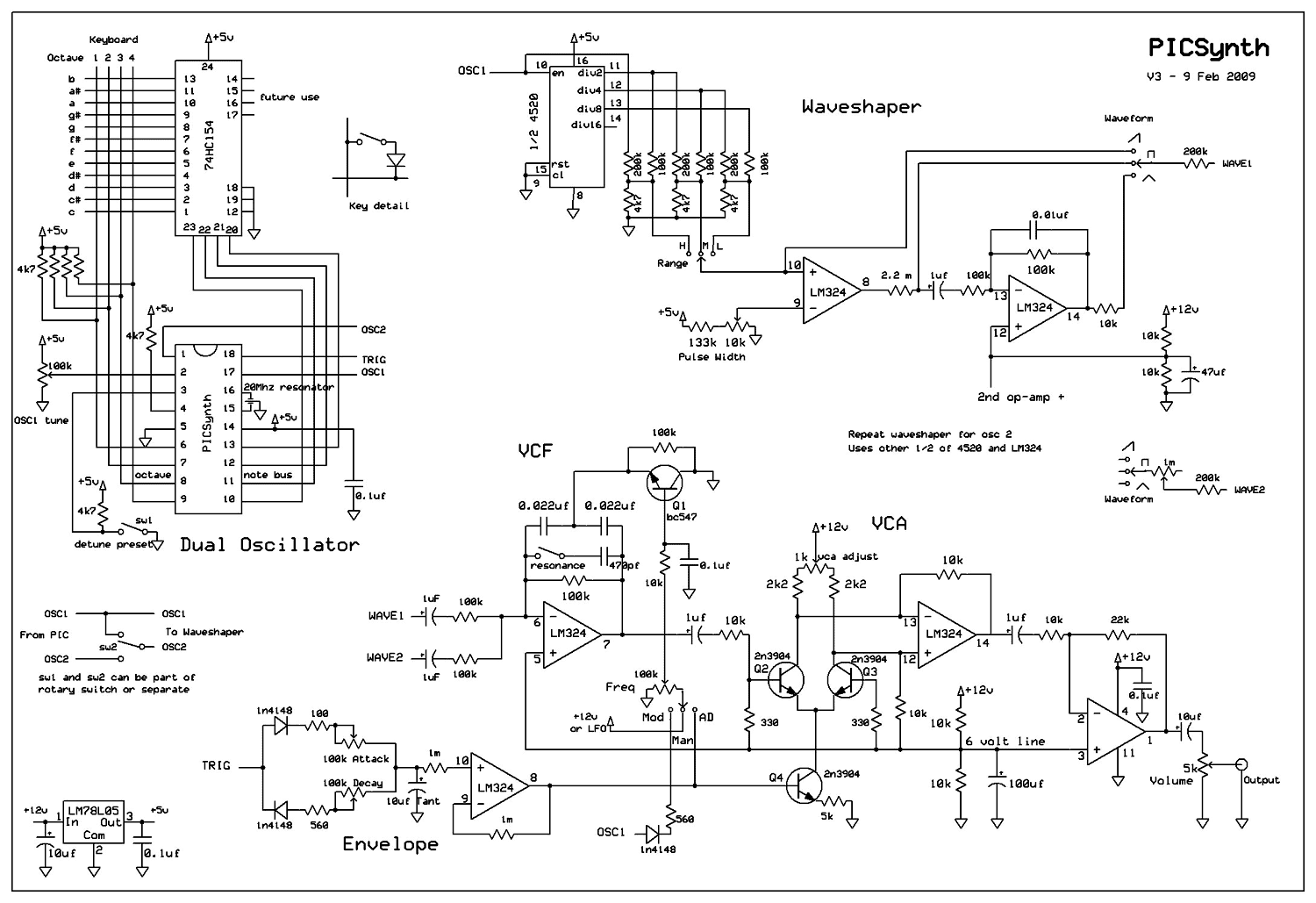
The analog display includes a frequency-to-voltage converter (IC12) along with bar-graph segment drivers IC10 and IC11. The calibration adjustment resistor R34 is configured to ensure that an engine speed of 5000 to 7000 rpm activates the first LED, which indicates the redline value.
The analog display circuit is designed to provide a visual representation of engine speed through a bar graph format. The core component, the frequency-to-voltage converter (IC12), receives a frequency input from the engine's ignition system, which correlates to the engine's RPM. This IC converts the frequency signal into a proportional voltage level, which is then fed into the bar-graph segment drivers (IC10 and IC11).
IC10 and IC11 are responsible for controlling the individual segments of the bar graph display. Each segment corresponds to a specific voltage range, allowing for a clear visual indication of the engine's RPM. The output voltage from IC12 is calibrated using the resistor R34, which adjusts the sensitivity of the display. By setting R34 appropriately, the first LED in the bar graph will illuminate at an engine speed of 5000 to 7000 RPM, serving as a warning for the driver when approaching the redline.
This configuration ensures that the driver receives timely feedback on engine performance, promoting safe operation and preventing engine damage due to over-revving. The use of an analog display allows for quick visual assessment, which can be more intuitive than digital readouts in certain driving conditions. Overall, this circuit effectively integrates frequency conversion and visual signaling to enhance engine monitoring.The analog display consists of a frequency/voltage converter (IC12) and bar-graph segment drivers IC10 and IC11. R34 is the calibration adjustment and is set so that an engine rpm of 5000 to 7000 rpm lights the first LED (redline value).
🔗 External reference
The analog display circuit is designed to provide a visual representation of engine speed through a bar graph format. The core component, the frequency-to-voltage converter (IC12), receives a frequency input from the engine's ignition system, which correlates to the engine's RPM. This IC converts the frequency signal into a proportional voltage level, which is then fed into the bar-graph segment drivers (IC10 and IC11).
IC10 and IC11 are responsible for controlling the individual segments of the bar graph display. Each segment corresponds to a specific voltage range, allowing for a clear visual indication of the engine's RPM. The output voltage from IC12 is calibrated using the resistor R34, which adjusts the sensitivity of the display. By setting R34 appropriately, the first LED in the bar graph will illuminate at an engine speed of 5000 to 7000 RPM, serving as a warning for the driver when approaching the redline.
This configuration ensures that the driver receives timely feedback on engine performance, promoting safe operation and preventing engine damage due to over-revving. The use of an analog display allows for quick visual assessment, which can be more intuitive than digital readouts in certain driving conditions. Overall, this circuit effectively integrates frequency conversion and visual signaling to enhance engine monitoring.The analog display consists of a frequency/voltage converter (IC12) and bar-graph segment drivers IC10 and IC11. R34 is the calibration adjustment and is set so that an engine rpm of 5000 to 7000 rpm lights the first LED (redline value).
🔗 External reference