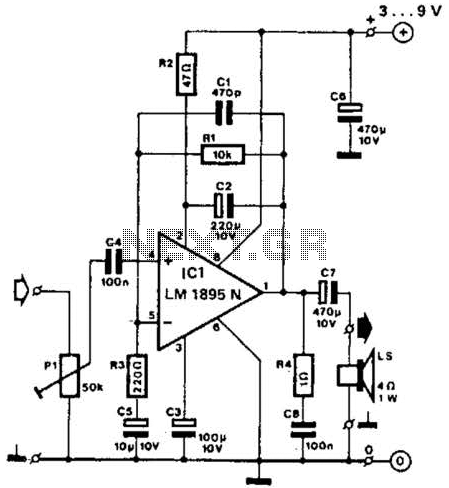
First POWER MOSFET Amplifier by K134+J49
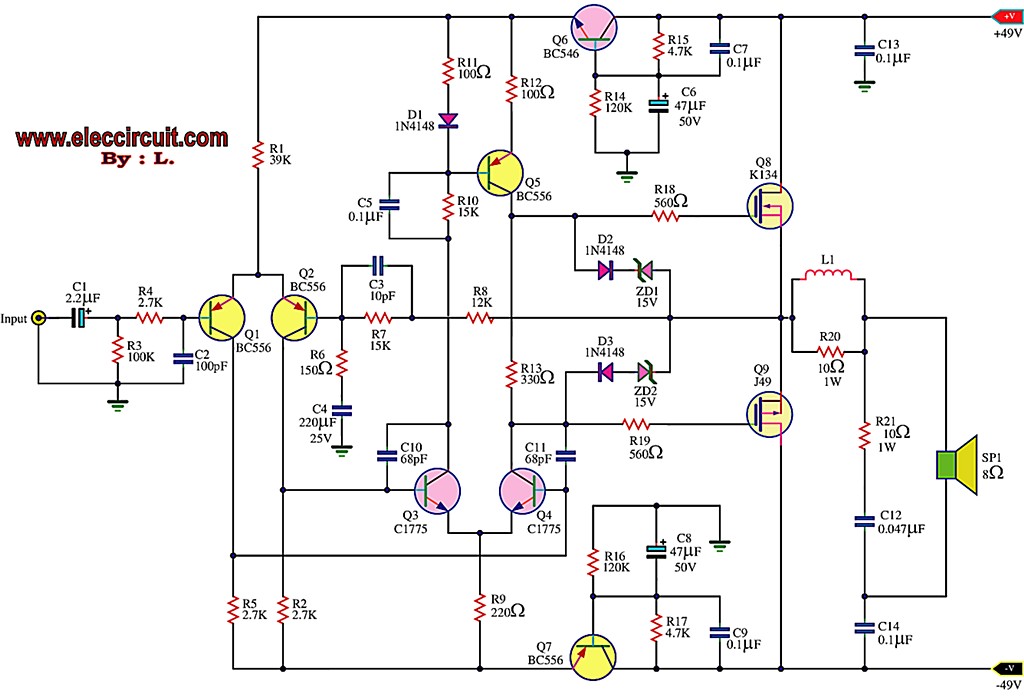
This is the first MOSFET power amplifier designed, featuring a comprehensive circuit. As a 60-watt power amplifier, it is adequate for typical usage.
The 60-watt MOSFET power amplifier circuit is designed to deliver high efficiency and robust performance for audio amplification applications. The circuit typically consists of several key components, including MOSFET transistors, resistors, capacitors, and a power supply unit.
The heart of the amplifier is the MOSFET transistor, chosen for its high input impedance and low output capacitance, which contribute to improved linearity and reduced distortion. The circuit configuration often employs a complementary push-pull arrangement, utilizing both N-channel and P-channel MOSFETs to enhance performance across the audio frequency spectrum.
The input stage of the amplifier usually includes a differential amplifier configuration to ensure high gain and minimal noise. This stage may be followed by a voltage gain stage that drives the output stage. Feedback mechanisms are often implemented to stabilize the gain and improve linearity, reducing the total harmonic distortion (THD) of the amplifier.
Power supply considerations are crucial for the performance of the amplifier. A regulated power supply is recommended to maintain consistent voltage levels, which helps in minimizing fluctuations that could affect audio quality. Additionally, decoupling capacitors are placed close to the MOSFETs to filter out high-frequency noise and ensure stable operation.
Thermal management is also an important aspect of the design. Adequate heatsinking is required to dissipate heat generated by the MOSFETs during operation, preventing thermal runaway and ensuring reliable performance over extended periods.
Overall, this 60-watt MOSFET power amplifier circuit is suitable for various applications, including home audio systems, musical instrument amplifiers, and other audio-related projects, providing a balance of power, efficiency, and sound quality.This has been the first Mosfet power amplifier of me, It is the most complete circuit. As a 60 watt power amplifier, this is sufficient for normal use in my.. 🔗 External reference
The 60-watt MOSFET power amplifier circuit is designed to deliver high efficiency and robust performance for audio amplification applications. The circuit typically consists of several key components, including MOSFET transistors, resistors, capacitors, and a power supply unit.
The heart of the amplifier is the MOSFET transistor, chosen for its high input impedance and low output capacitance, which contribute to improved linearity and reduced distortion. The circuit configuration often employs a complementary push-pull arrangement, utilizing both N-channel and P-channel MOSFETs to enhance performance across the audio frequency spectrum.
The input stage of the amplifier usually includes a differential amplifier configuration to ensure high gain and minimal noise. This stage may be followed by a voltage gain stage that drives the output stage. Feedback mechanisms are often implemented to stabilize the gain and improve linearity, reducing the total harmonic distortion (THD) of the amplifier.
Power supply considerations are crucial for the performance of the amplifier. A regulated power supply is recommended to maintain consistent voltage levels, which helps in minimizing fluctuations that could affect audio quality. Additionally, decoupling capacitors are placed close to the MOSFETs to filter out high-frequency noise and ensure stable operation.
Thermal management is also an important aspect of the design. Adequate heatsinking is required to dissipate heat generated by the MOSFETs during operation, preventing thermal runaway and ensuring reliable performance over extended periods.
Overall, this 60-watt MOSFET power amplifier circuit is suitable for various applications, including home audio systems, musical instrument amplifiers, and other audio-related projects, providing a balance of power, efficiency, and sound quality.This has been the first Mosfet power amplifier of me, It is the most complete circuit. As a 60 watt power amplifier, this is sufficient for normal use in my.. 🔗 External reference
%2BCircuit%2Bdiagram%2Busing%2BCD4047%2Band%2BIRFZ44%2Bpower%2BMOSFET.png)