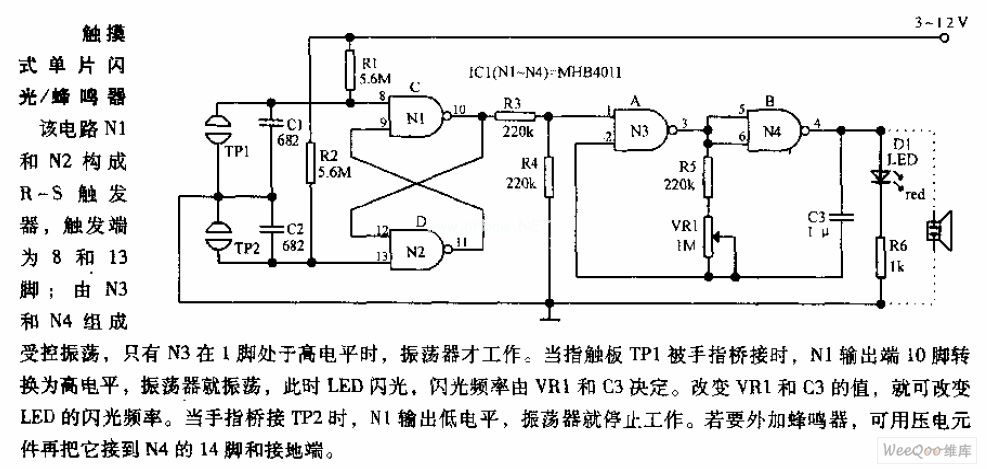
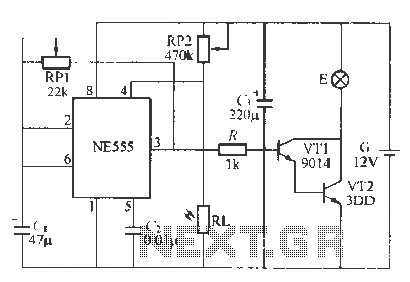
Flash ADC
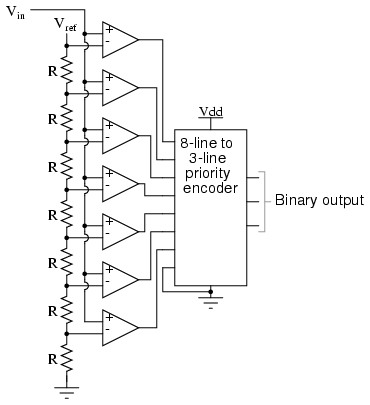
Also known as the parallel A/D converter, this circuit is the simplest to understand. It consists of a series of comparators, each comparing the input voltage to a reference voltage.
The parallel analog-to-digital (A/D) converter is a fundamental circuit in electronics, primarily utilized for converting continuous analog signals into discrete digital values. This type of converter employs multiple comparators, which operate simultaneously to evaluate the input voltage against a set of reference voltages. Each comparator corresponds to a specific bit in the digital output, allowing for a direct representation of the input signal.
In a typical configuration, the circuit includes a resistor ladder or a set of precision reference voltage sources that generate the necessary reference levels for comparison. The comparators output binary signals indicating whether the input voltage is higher or lower than the reference voltage. The outputs of these comparators are then combined to form a binary number, which represents the quantized value of the input signal.
The advantages of parallel A/D converters include high conversion speed due to simultaneous comparisons and straightforward implementation. However, they may require a considerable number of comparators for higher resolution, which can increase circuit complexity and power consumption. As a result, parallel A/D converters are often used in applications where speed is critical, such as in digital oscilloscopes or real-time signal processing systems.
In summary, the parallel A/D converter is a vital component in modern electronics, enabling rapid and efficient analog-to-digital conversion through its array of comparators and reference voltages.Also called the parallel A/D converter, this circuit is the simplest to understand. It is formed of a series of comparators, each one comparing the.. 🔗 External reference
The parallel analog-to-digital (A/D) converter is a fundamental circuit in electronics, primarily utilized for converting continuous analog signals into discrete digital values. This type of converter employs multiple comparators, which operate simultaneously to evaluate the input voltage against a set of reference voltages. Each comparator corresponds to a specific bit in the digital output, allowing for a direct representation of the input signal.
In a typical configuration, the circuit includes a resistor ladder or a set of precision reference voltage sources that generate the necessary reference levels for comparison. The comparators output binary signals indicating whether the input voltage is higher or lower than the reference voltage. The outputs of these comparators are then combined to form a binary number, which represents the quantized value of the input signal.
The advantages of parallel A/D converters include high conversion speed due to simultaneous comparisons and straightforward implementation. However, they may require a considerable number of comparators for higher resolution, which can increase circuit complexity and power consumption. As a result, parallel A/D converters are often used in applications where speed is critical, such as in digital oscilloscopes or real-time signal processing systems.
In summary, the parallel A/D converter is a vital component in modern electronics, enabling rapid and efficient analog-to-digital conversion through its array of comparators and reference voltages.Also called the parallel A/D converter, this circuit is the simplest to understand. It is formed of a series of comparators, each one comparing the.. 🔗 External reference