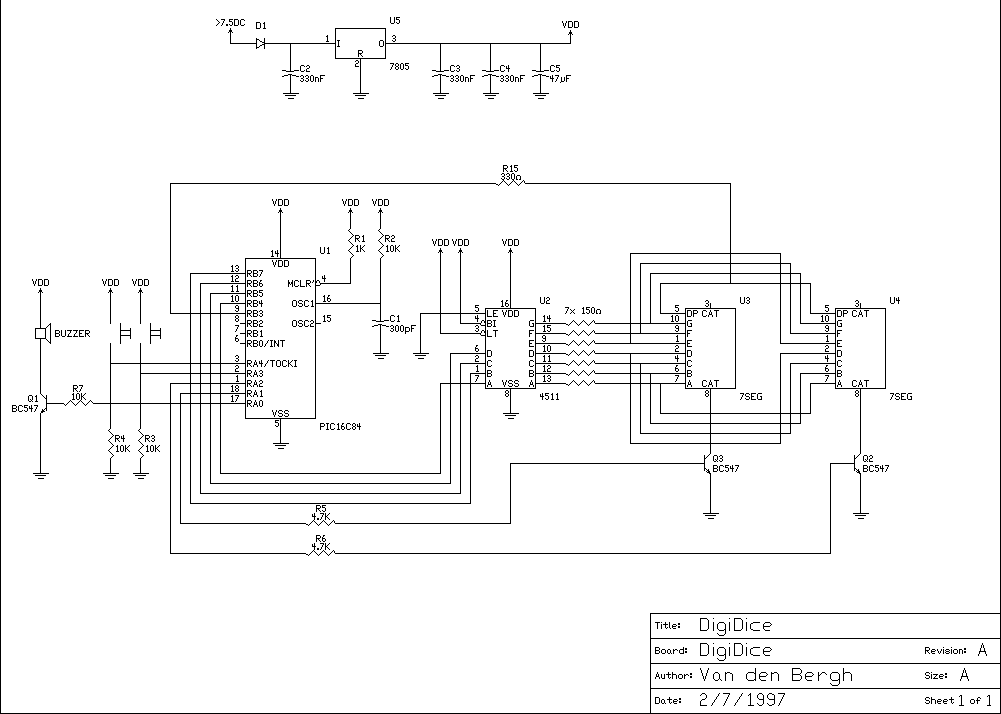
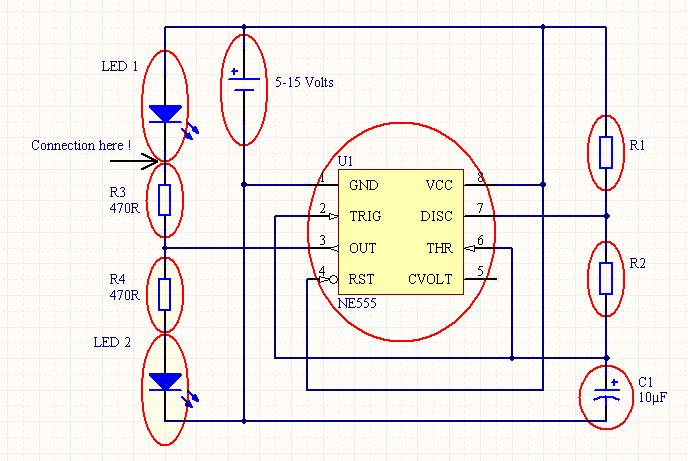
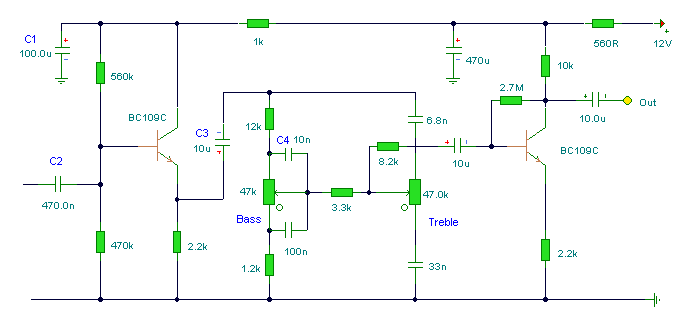
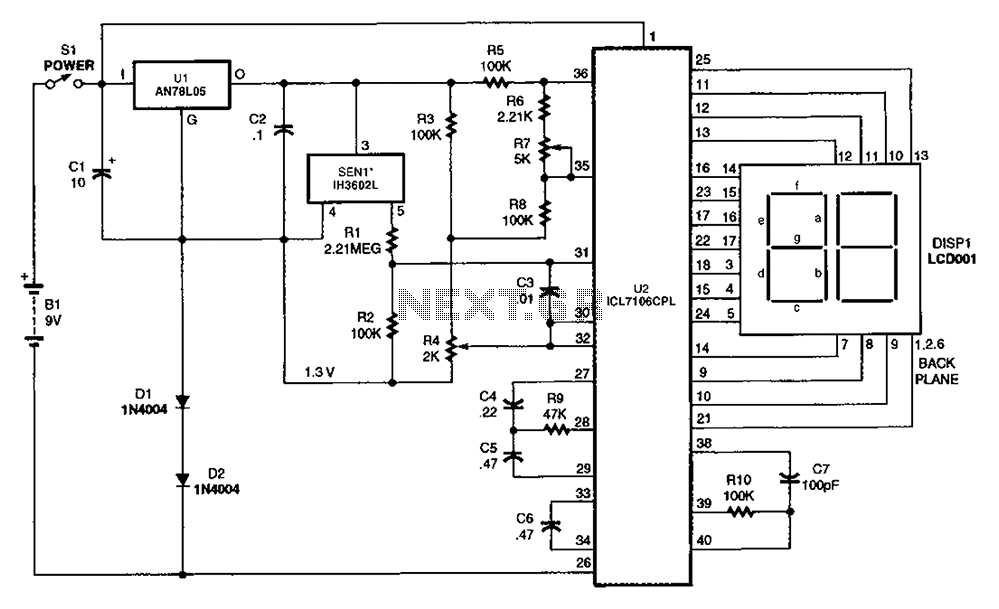
For differential drive circuit diagram of a voltage output DAC AD5620
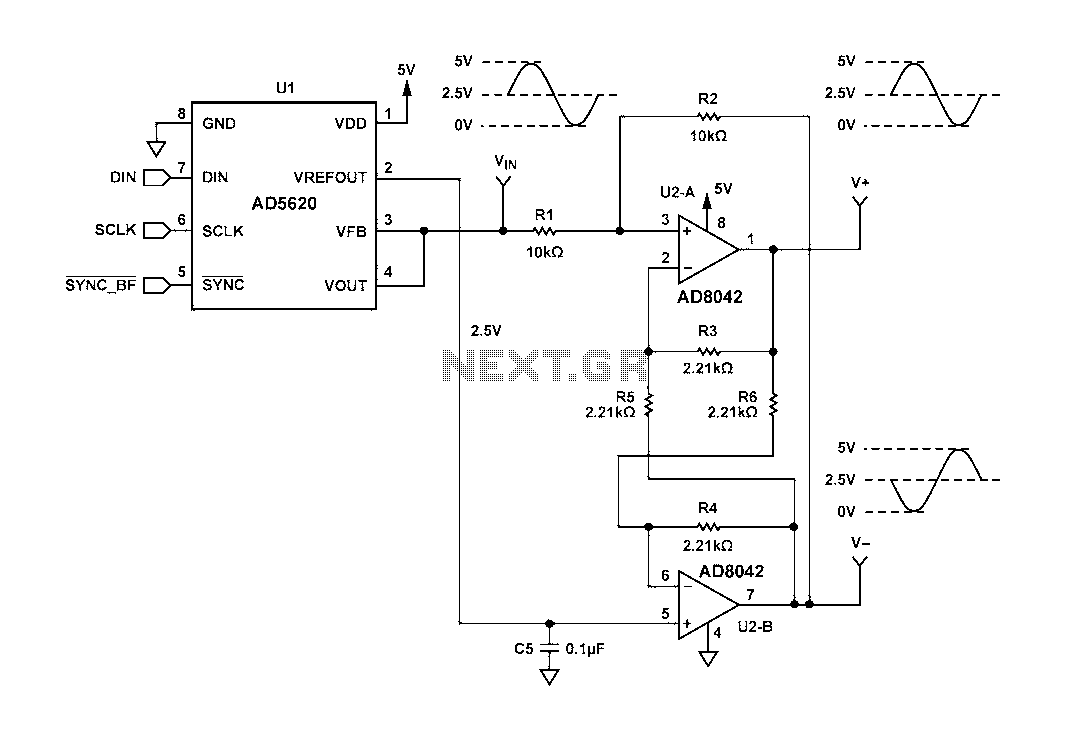
Figure 1 illustrates a circuit that utilizes a single +V power supply and a voltage output Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) known as the AD5620. The DAC is controlled via an SPI port, with its output ranging from 0 V to +5 V. The DAC chip employs a reference voltage source of +2.5 V to establish the common-mode voltage for the AD8042 differential driver circuit. The reference voltage source has a temperature coefficient of 5 ppm/°C. The common-mode voltage at the V-side output is +2.5 V, which is centered around the inverted DAC output. The feedback network in U2-B modifies the voltage at the V+ terminal, introducing a 180-degree phase shift to the terminal voltage.
The circuit configuration in Figure 1 is designed to convert digital signals into analog voltages with precision and stability. The use of the AD5620 DAC allows for a high-resolution output, which is essential for applications requiring accurate signal representation. The control of the DAC through an SPI interface facilitates straightforward integration with microcontrollers or digital signal processors, enabling efficient data transfer and command execution.
The reference voltage of +2.5 V plays a critical role in maintaining the accuracy of the output signal. With a temperature coefficient of 5 ppm/°C, the reference voltage source ensures minimal drift over temperature variations, which is vital for applications in environments with fluctuating temperatures. The common-mode voltage of +2.5 V at the V-side output allows for optimal operation of the AD8042 differential driver, which is designed to amplify the differential signal while rejecting common-mode noise.
The feedback network associated with U2-B is crucial in determining the gain and phase characteristics of the circuit. By forcing a 180-degree phase shift at the V+ terminal, the circuit can effectively manage the output characteristics, ensuring that the signal integrity is preserved. This phase manipulation is particularly important in differential signaling applications, where maintaining the correct timing and phase relationships between signals is critical for performance.
Overall, the circuit depicted in Figure 1 represents a robust solution for generating precise analog outputs from digital inputs, suitable for a wide range of electronic applications. The careful selection of components and configuration ensures high performance and reliability in signal processing tasks.Figure 1 circuit uses a single +V power supply, and a voltage output DAC AD5620. DAC input by an SPI port control. DAC output swing from V to +5 V. Within the DAC chip referenc e voltage source (+2.5 V) to set the AD8042 differential driver circuit common-mode voltage. The temperature coefficient of the reference voltage source is 5 ppm/C. V -Side output common-mode voltage of +2.V is centered inverted DAC output. U2-B feedback network and forcing V + terminal voltage V Terminal voltage phase by 180. Figure 1. Voltage Output DAC AD5620 differential driver
The circuit configuration in Figure 1 is designed to convert digital signals into analog voltages with precision and stability. The use of the AD5620 DAC allows for a high-resolution output, which is essential for applications requiring accurate signal representation. The control of the DAC through an SPI interface facilitates straightforward integration with microcontrollers or digital signal processors, enabling efficient data transfer and command execution.
The reference voltage of +2.5 V plays a critical role in maintaining the accuracy of the output signal. With a temperature coefficient of 5 ppm/°C, the reference voltage source ensures minimal drift over temperature variations, which is vital for applications in environments with fluctuating temperatures. The common-mode voltage of +2.5 V at the V-side output allows for optimal operation of the AD8042 differential driver, which is designed to amplify the differential signal while rejecting common-mode noise.
The feedback network associated with U2-B is crucial in determining the gain and phase characteristics of the circuit. By forcing a 180-degree phase shift at the V+ terminal, the circuit can effectively manage the output characteristics, ensuring that the signal integrity is preserved. This phase manipulation is particularly important in differential signaling applications, where maintaining the correct timing and phase relationships between signals is critical for performance.
Overall, the circuit depicted in Figure 1 represents a robust solution for generating precise analog outputs from digital inputs, suitable for a wide range of electronic applications. The careful selection of components and configuration ensures high performance and reliability in signal processing tasks.Figure 1 circuit uses a single +V power supply, and a voltage output DAC AD5620. DAC input by an SPI port control. DAC output swing from V to +5 V. Within the DAC chip referenc e voltage source (+2.5 V) to set the AD8042 differential driver circuit common-mode voltage. The temperature coefficient of the reference voltage source is 5 ppm/C. V -Side output common-mode voltage of +2.V is centered inverted DAC output. U2-B feedback network and forcing V + terminal voltage V Terminal voltage phase by 180. Figure 1. Voltage Output DAC AD5620 differential driver