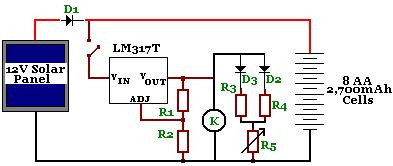
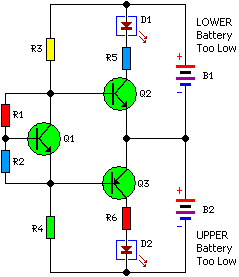
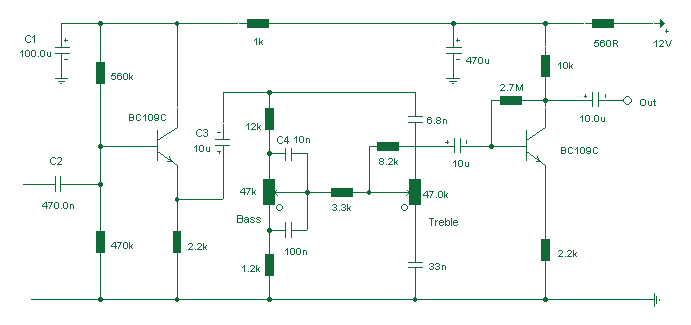
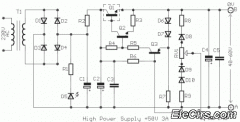
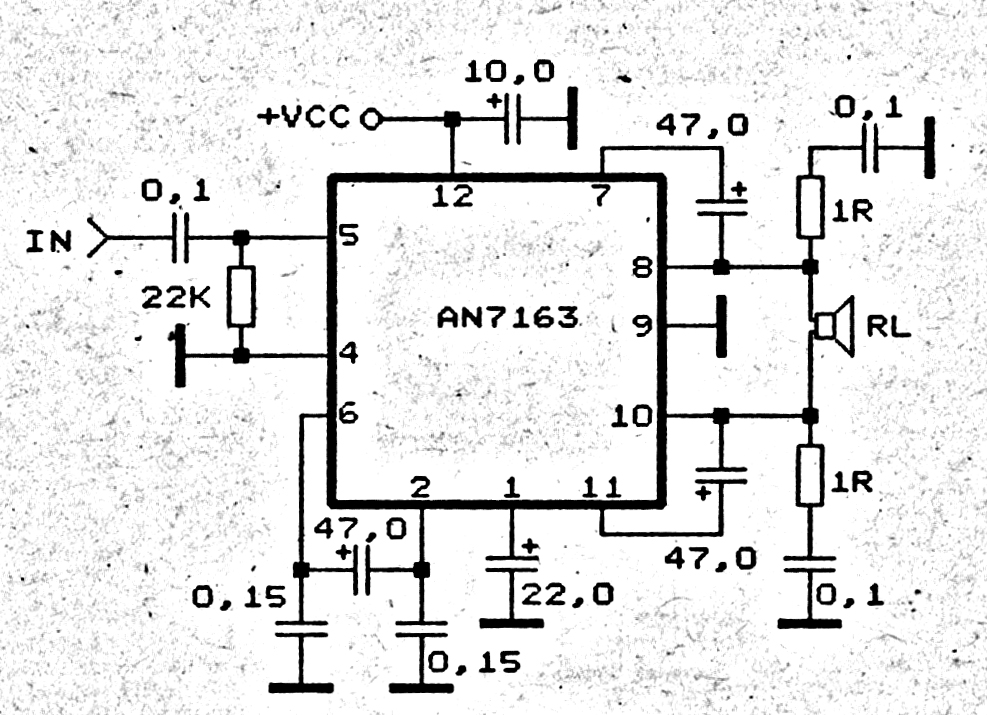
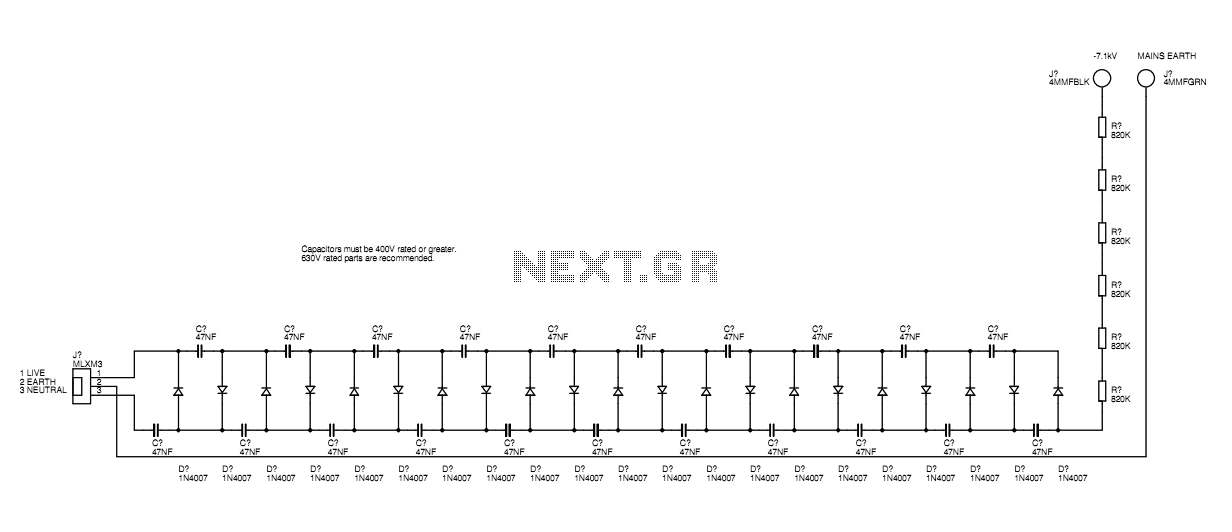
Four-way operation of the dynamic braking circuit
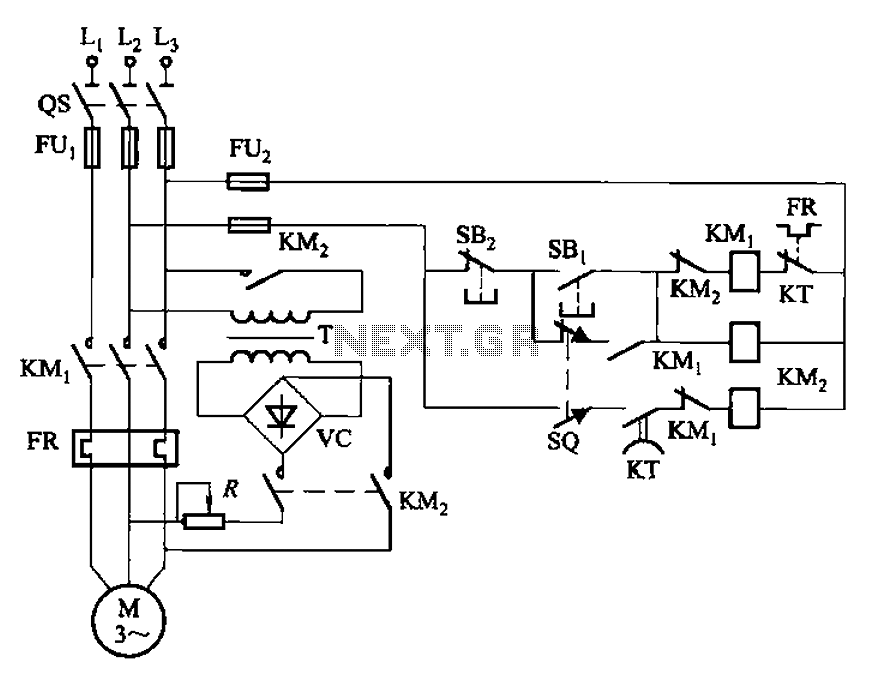
The circuit illustrated in Figure 3-136 incorporates a limit switch (SQ) that, when the motor operates a mechanical device to reach a predetermined position, cuts off the power and initiates dynamic braking for fast and accurate positioning. This configuration is commonly employed in machine circuits.
The circuit utilizes a limit switch to ensure precise control of motor operations. The limit switch (SQ) is strategically placed to detect when the mechanical device has reached its designated position. Upon activation, the limit switch interrupts the power supply to the motor, effectively stopping its operation. This is crucial in applications where overshooting the target position could lead to mechanical damage or operational inefficiencies.
In addition to power interruption, the circuit employs dynamic braking, a technique that utilizes the motor's own back EMF to rapidly decelerate the mechanical device. This is achieved by rerouting the motor's terminals to create a short circuit, allowing the motor to act as a generator. The generated current dissipates energy, leading to a swift stop. This feature is particularly beneficial in applications requiring quick response times and high precision, such as automated machinery, CNC machines, and robotic systems.
The integration of the limit switch and dynamic braking enhances the safety and reliability of the machine circuit. By ensuring that the motor ceases operation at the correct moment, the risk of mechanical wear and tear is minimized, thereby extending the lifespan of the equipment. Furthermore, this configuration allows for smooth transitions between operational states, reducing the likelihood of sudden jerks or movements that could compromise the integrity of the system or the safety of operators.
Overall, the circuit design exemplifies effective motor control through the combination of limit switches and dynamic braking, making it an essential component in modern automated systems. Circuit shown in Figure 3-136. The line adds a limit switch SQ, when the motor is running with a mechanical device to a predetermined position, turn off the power and dynamic b raking for fast, accurate positioning. Commonly used in the machine circuit.
The circuit utilizes a limit switch to ensure precise control of motor operations. The limit switch (SQ) is strategically placed to detect when the mechanical device has reached its designated position. Upon activation, the limit switch interrupts the power supply to the motor, effectively stopping its operation. This is crucial in applications where overshooting the target position could lead to mechanical damage or operational inefficiencies.
In addition to power interruption, the circuit employs dynamic braking, a technique that utilizes the motor's own back EMF to rapidly decelerate the mechanical device. This is achieved by rerouting the motor's terminals to create a short circuit, allowing the motor to act as a generator. The generated current dissipates energy, leading to a swift stop. This feature is particularly beneficial in applications requiring quick response times and high precision, such as automated machinery, CNC machines, and robotic systems.
The integration of the limit switch and dynamic braking enhances the safety and reliability of the machine circuit. By ensuring that the motor ceases operation at the correct moment, the risk of mechanical wear and tear is minimized, thereby extending the lifespan of the equipment. Furthermore, this configuration allows for smooth transitions between operational states, reducing the likelihood of sudden jerks or movements that could compromise the integrity of the system or the safety of operators.
Overall, the circuit design exemplifies effective motor control through the combination of limit switches and dynamic braking, making it an essential component in modern automated systems. Circuit shown in Figure 3-136. The line adds a limit switch SQ, when the motor is running with a mechanical device to a predetermined position, turn off the power and dynamic b raking for fast, accurate positioning. Commonly used in the machine circuit.