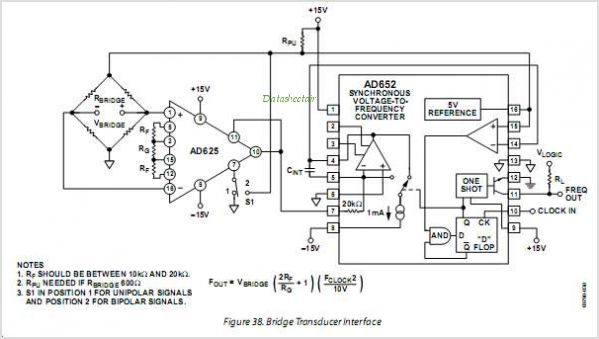
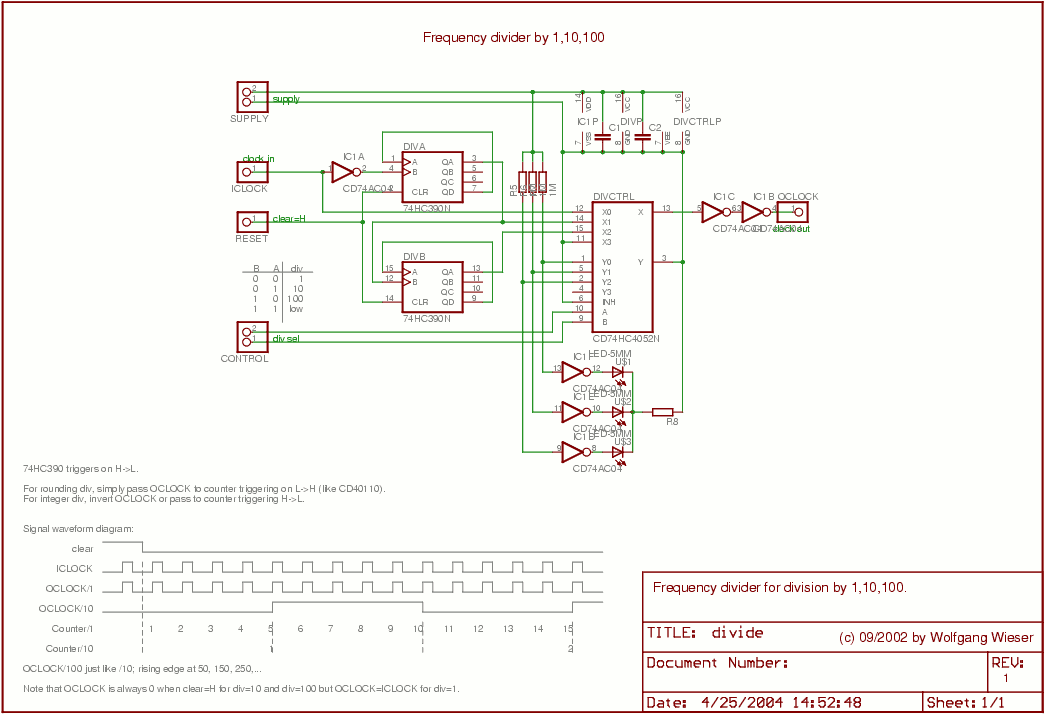
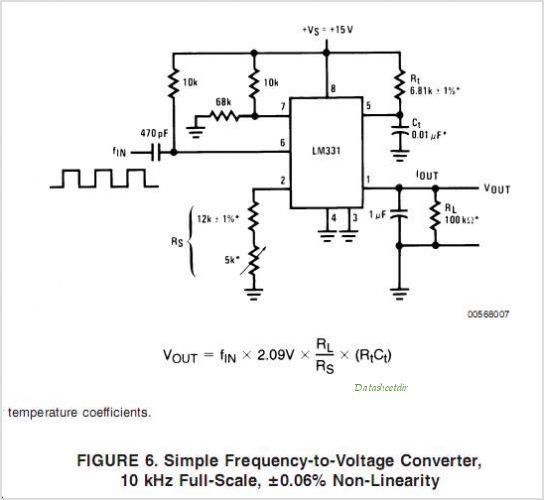
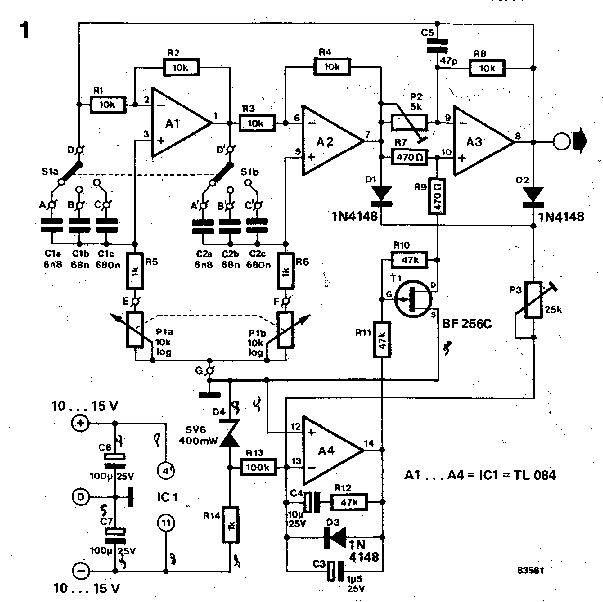
Frequency doubler
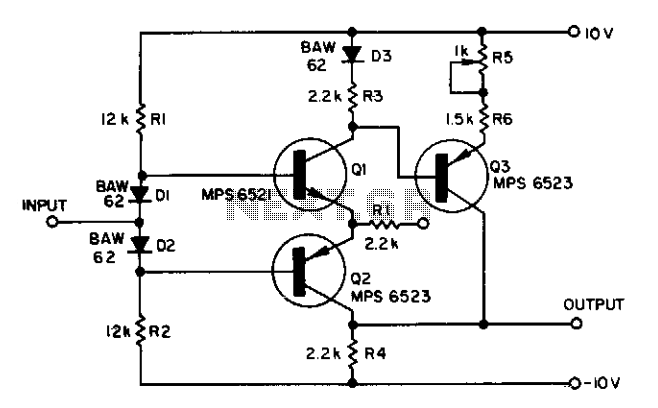
Adding components Q3, D3, and resistors R3 through R6 to a conventional complementary symmetry class AB buffer can double the frequency of an input sine wave. The circuit works at 1 MHz.
The proposed circuit modification involves integrating additional components into a standard complementary symmetry class AB buffer configuration, which is commonly used for audio amplification and signal buffering. The primary objective of this modification is to achieve frequency doubling of an input sine wave signal.
In this configuration, Q3 serves as an additional transistor that enhances the buffer's ability to handle higher frequencies. The inclusion of D3, a diode, plays a critical role in shaping the waveform and ensuring that the output maintains the integrity of the signal during the frequency doubling process. The resistors R3 through R6 are strategically placed to control the biasing and gain of the transistors, ensuring optimal performance at the designated frequency of 1 MHz.
The operation of this circuit can be understood through the principles of nonlinear mixing, where the input sine wave is subjected to a non-linear transfer characteristic introduced by the diode and the transistors. This interaction results in the generation of harmonics, with the second harmonic being the primary focus for frequency doubling.
The careful selection of resistor values is crucial to achieving the desired performance. R3 and R4 typically set the biasing conditions for Q3, while R5 and R6 may be used to stabilize the output and control the gain. The circuit's design must ensure that the transistors operate within their active regions to maintain linearity and prevent distortion.
In summary, the integration of Q3, D3, and resistors R3 through R6 into a conventional complementary symmetry class AB buffer enables the circuit to effectively double the frequency of an input sine wave, achieving operational effectiveness at 1 MHz. This configuration is beneficial in applications requiring frequency manipulation while maintaining signal fidelity.Adding components Q3, D3, and resistors R3 through R6 to a conventional complementary symmetry class AB buffer can double the frequency of an input sine wave. The circuit works at 1 MHz. 🔗 External reference
The proposed circuit modification involves integrating additional components into a standard complementary symmetry class AB buffer configuration, which is commonly used for audio amplification and signal buffering. The primary objective of this modification is to achieve frequency doubling of an input sine wave signal.
In this configuration, Q3 serves as an additional transistor that enhances the buffer's ability to handle higher frequencies. The inclusion of D3, a diode, plays a critical role in shaping the waveform and ensuring that the output maintains the integrity of the signal during the frequency doubling process. The resistors R3 through R6 are strategically placed to control the biasing and gain of the transistors, ensuring optimal performance at the designated frequency of 1 MHz.
The operation of this circuit can be understood through the principles of nonlinear mixing, where the input sine wave is subjected to a non-linear transfer characteristic introduced by the diode and the transistors. This interaction results in the generation of harmonics, with the second harmonic being the primary focus for frequency doubling.
The careful selection of resistor values is crucial to achieving the desired performance. R3 and R4 typically set the biasing conditions for Q3, while R5 and R6 may be used to stabilize the output and control the gain. The circuit's design must ensure that the transistors operate within their active regions to maintain linearity and prevent distortion.
In summary, the integration of Q3, D3, and resistors R3 through R6 into a conventional complementary symmetry class AB buffer enables the circuit to effectively double the frequency of an input sine wave, achieving operational effectiveness at 1 MHz. This configuration is beneficial in applications requiring frequency manipulation while maintaining signal fidelity.Adding components Q3, D3, and resistors R3 through R6 to a conventional complementary symmetry class AB buffer can double the frequency of an input sine wave. The circuit works at 1 MHz. 🔗 External reference