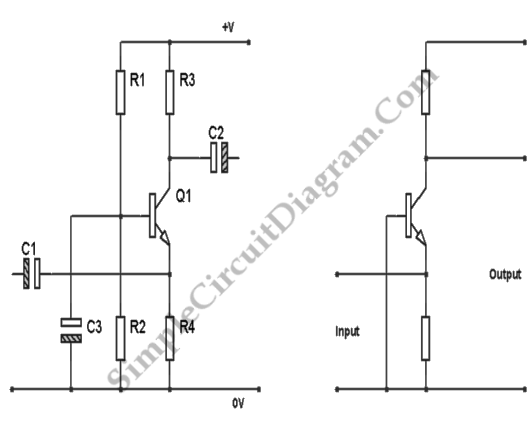
Gain-Controlled Op Amp
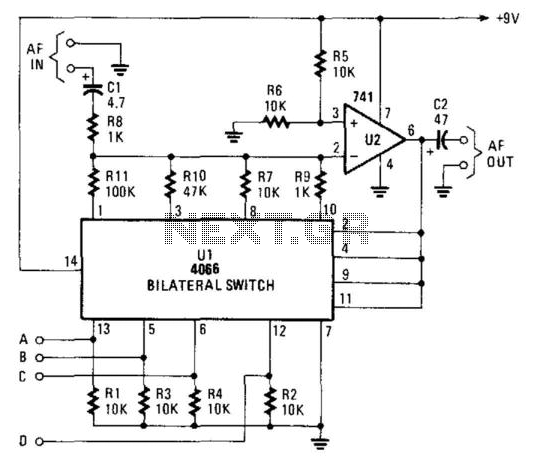
The gain controller utilizes a 4066 quad bilateral switch to electronically select a feedback resistor for the 741 operational amplifier. One or more switches can be activated simultaneously to achieve a stepped, variable-gain range from less than 1 to 100.
The circuit design incorporates the 4066 quad bilateral switch, which allows for the electronic selection of feedback resistors in conjunction with the 741 operational amplifier. This configuration enables the adjustment of gain levels by altering the feedback path through selected resistors. The operational amplifier is a critical component that amplifies the input signal, and the feedback resistor selection directly influences the gain factor.
In this setup, multiple switches can be activated at once, facilitating a range of gain settings. Each resistor corresponds to a specific gain value, and by combining different resistors through the switches, the circuit can produce a stepped gain that varies continuously from below 1 to as high as 100. This versatility is particularly useful in applications requiring precise control over signal amplification.
The implementation of the 4066 switch provides an efficient means of managing the feedback network without mechanical components, allowing for faster response times and reducing the potential for wear and tear associated with traditional potentiometers. The electronic nature of the switch also enhances the reliability of the gain control, making it suitable for various electronic applications, including audio processing, instrumentation, and signal conditioning.
In summary, the gain controller circuit leverages the capabilities of the 4066 quad bilateral switch and the 741 operational amplifier to create a flexible and reliable method for achieving variable gain, thereby enhancing the performance and adaptability of electronic systems. The gain controller uses a 4066 quad bilateral switch to electronically select a feedback resistor for the 741 op am p. One or more switches can be turned on at the same time to produce a stepped, variable-gain range from less than 1 to 100. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design incorporates the 4066 quad bilateral switch, which allows for the electronic selection of feedback resistors in conjunction with the 741 operational amplifier. This configuration enables the adjustment of gain levels by altering the feedback path through selected resistors. The operational amplifier is a critical component that amplifies the input signal, and the feedback resistor selection directly influences the gain factor.
In this setup, multiple switches can be activated at once, facilitating a range of gain settings. Each resistor corresponds to a specific gain value, and by combining different resistors through the switches, the circuit can produce a stepped gain that varies continuously from below 1 to as high as 100. This versatility is particularly useful in applications requiring precise control over signal amplification.
The implementation of the 4066 switch provides an efficient means of managing the feedback network without mechanical components, allowing for faster response times and reducing the potential for wear and tear associated with traditional potentiometers. The electronic nature of the switch also enhances the reliability of the gain control, making it suitable for various electronic applications, including audio processing, instrumentation, and signal conditioning.
In summary, the gain controller circuit leverages the capabilities of the 4066 quad bilateral switch and the 741 operational amplifier to create a flexible and reliable method for achieving variable gain, thereby enhancing the performance and adaptability of electronic systems. The gain controller uses a 4066 quad bilateral switch to electronically select a feedback resistor for the 741 op am p. One or more switches can be turned on at the same time to produce a stepped, variable-gain range from less than 1 to 100. 🔗 External reference