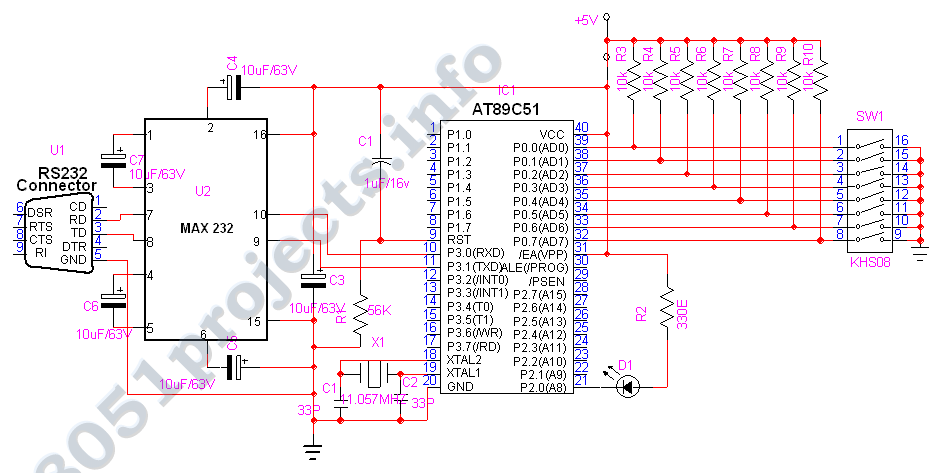
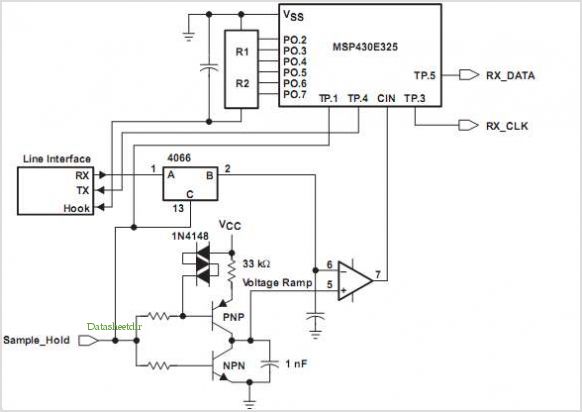
graphical LCDs with a microcontroller
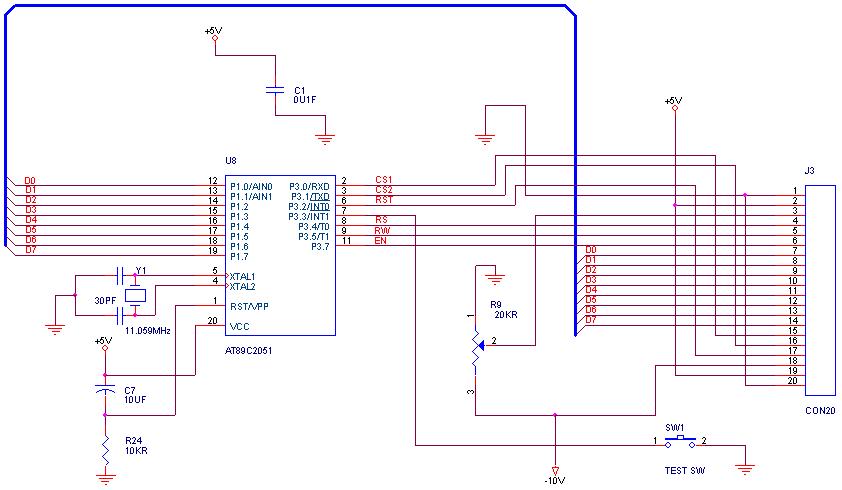
How can graphical LCDs be controlled using a microcontroller? Is there any datasheet available?
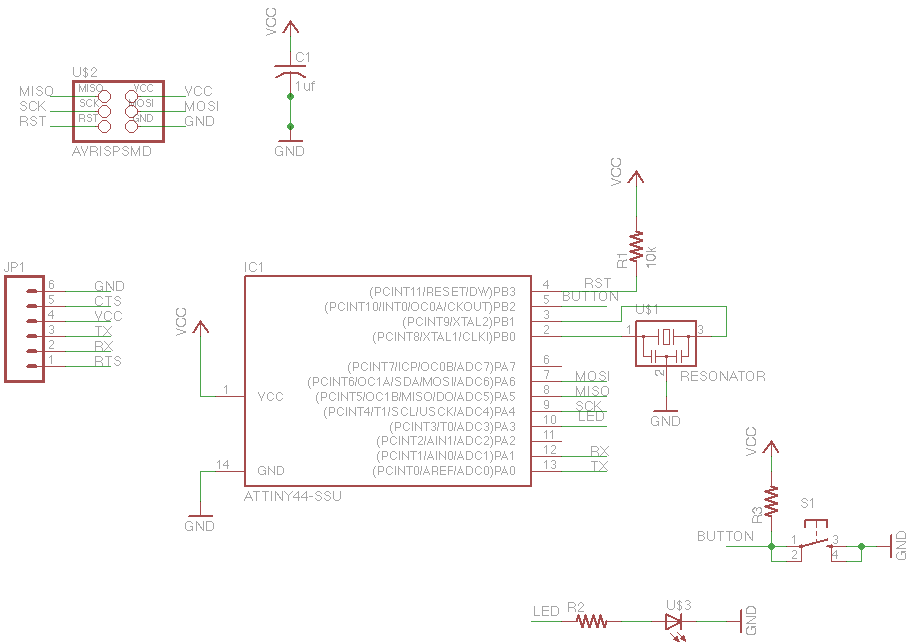
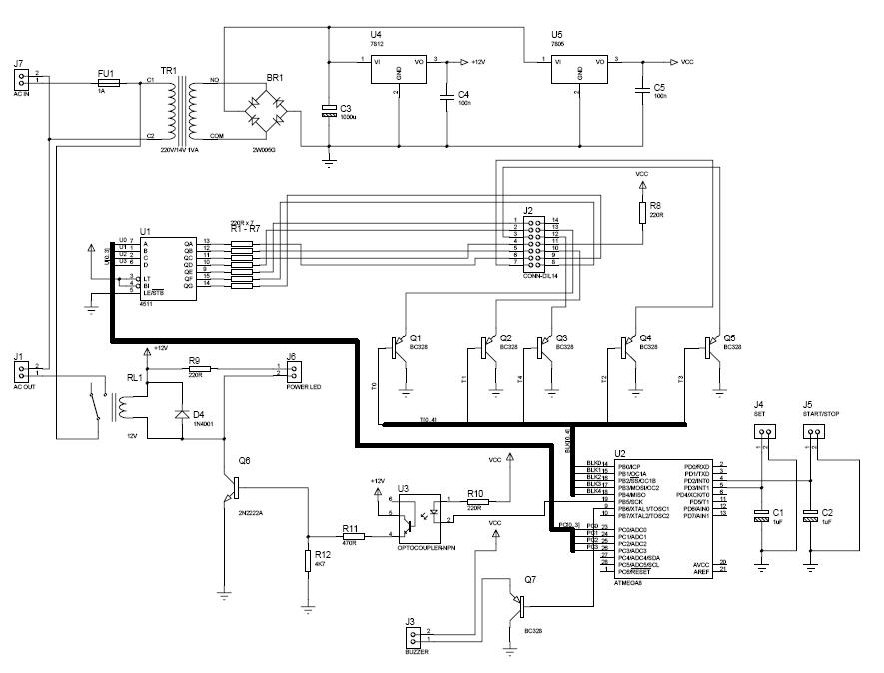
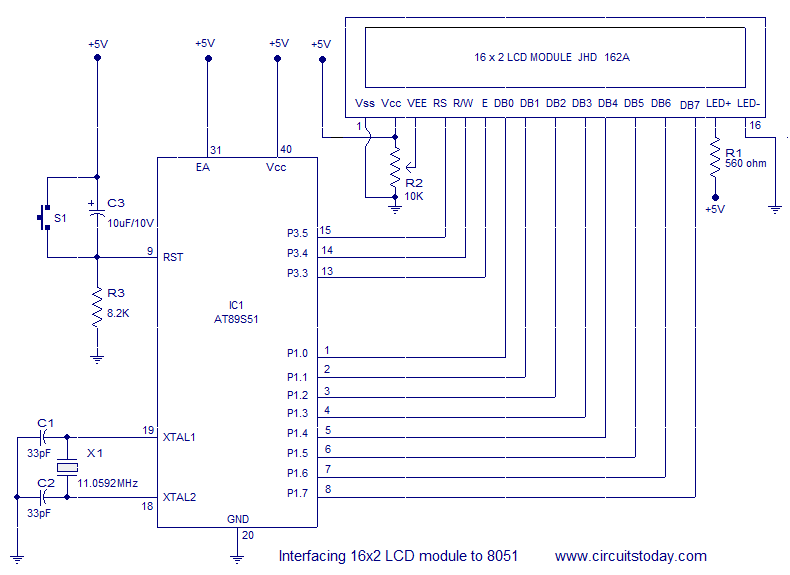
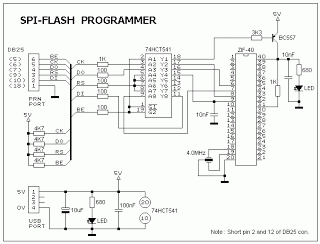
Graphical LCDs (Liquid Crystal Displays) are widely used in various electronic applications for displaying complex graphics and text. To control these displays with a microcontroller, several steps and considerations must be taken into account.
First, it is essential to identify the specific model of the graphical LCD in use, as different models may have varying control interfaces and requirements. Most graphical LCDs utilize either parallel or serial communication protocols. Common interfaces include SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) and I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) for serial communication, while parallel interfaces often require multiple data lines for communication.
The microcontroller must be programmed to send commands and data to the graphical LCD according to its specific instruction set, which is typically detailed in the LCD’s datasheet. The datasheet provides crucial information regarding pin configurations, voltage levels, timing requirements, and command sequences necessary for initializing the display, drawing graphics, and updating text.
To establish communication, the microcontroller must be connected to the graphical LCD using appropriate pins. For parallel interfaces, multiple GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) pins are allocated for data and control signals. In contrast, serial interfaces will require fewer pins, simplifying the hardware connections.
Once the physical connections are established, the microcontroller firmware must implement the communication protocol. This involves setting up the appropriate clock speeds for SPI or configuring the I2C address for I2C communication. The firmware should also include functions for sending commands to clear the display, set the cursor position, and draw pixels or shapes.
In addition to the basic control functions, advanced features such as image rendering and font management can be implemented to enhance the display's capabilities. Libraries and existing code repositories are often available for popular microcontrollers, which can facilitate the development process and provide examples of how to interact with the graphical LCD effectively.
In summary, controlling graphical LCDs with a microcontroller involves understanding the specific display model, establishing the correct communication interface, and programming the microcontroller to send the appropriate commands as outlined in the datasheet.Hello to everyone! How I can control these graphical LCDs with a microcontroller? Is there any datasheet?.. 🔗 External reference
Graphical LCDs (Liquid Crystal Displays) are widely used in various electronic applications for displaying complex graphics and text. To control these displays with a microcontroller, several steps and considerations must be taken into account.
First, it is essential to identify the specific model of the graphical LCD in use, as different models may have varying control interfaces and requirements. Most graphical LCDs utilize either parallel or serial communication protocols. Common interfaces include SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) and I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) for serial communication, while parallel interfaces often require multiple data lines for communication.
The microcontroller must be programmed to send commands and data to the graphical LCD according to its specific instruction set, which is typically detailed in the LCD’s datasheet. The datasheet provides crucial information regarding pin configurations, voltage levels, timing requirements, and command sequences necessary for initializing the display, drawing graphics, and updating text.
To establish communication, the microcontroller must be connected to the graphical LCD using appropriate pins. For parallel interfaces, multiple GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) pins are allocated for data and control signals. In contrast, serial interfaces will require fewer pins, simplifying the hardware connections.
Once the physical connections are established, the microcontroller firmware must implement the communication protocol. This involves setting up the appropriate clock speeds for SPI or configuring the I2C address for I2C communication. The firmware should also include functions for sending commands to clear the display, set the cursor position, and draw pixels or shapes.
In addition to the basic control functions, advanced features such as image rendering and font management can be implemented to enhance the display's capabilities. Libraries and existing code repositories are often available for popular microcontrollers, which can facilitate the development process and provide examples of how to interact with the graphical LCD effectively.
In summary, controlling graphical LCDs with a microcontroller involves understanding the specific display model, establishing the correct communication interface, and programming the microcontroller to send the appropriate commands as outlined in the datasheet.Hello to everyone! How I can control these graphical LCDs with a microcontroller? Is there any datasheet?.. 🔗 External reference