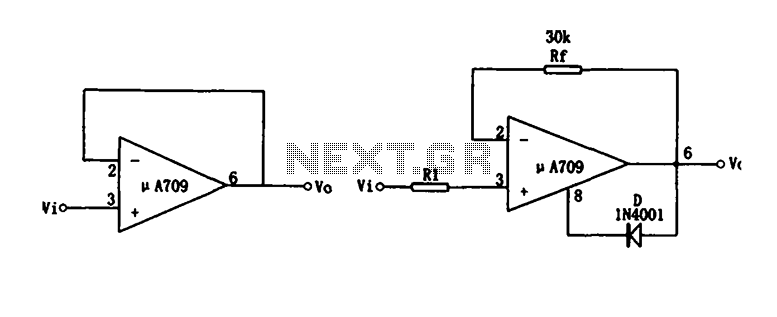
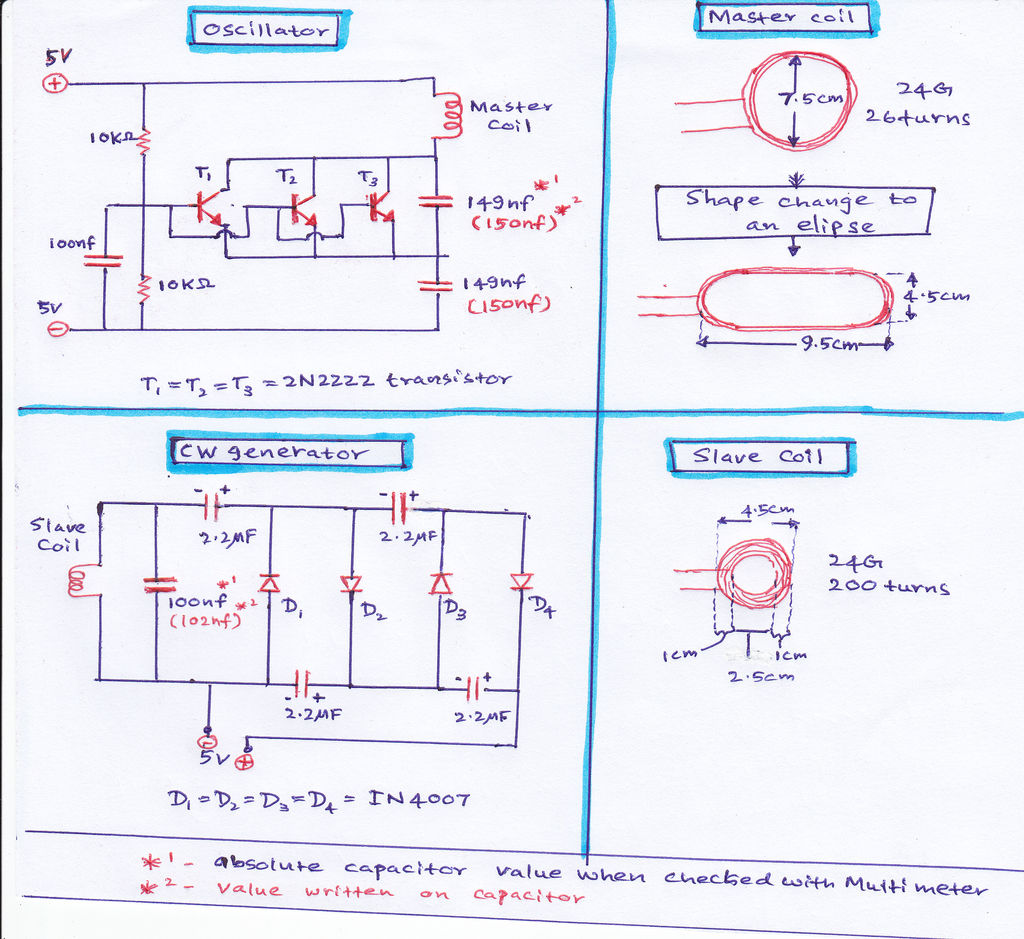
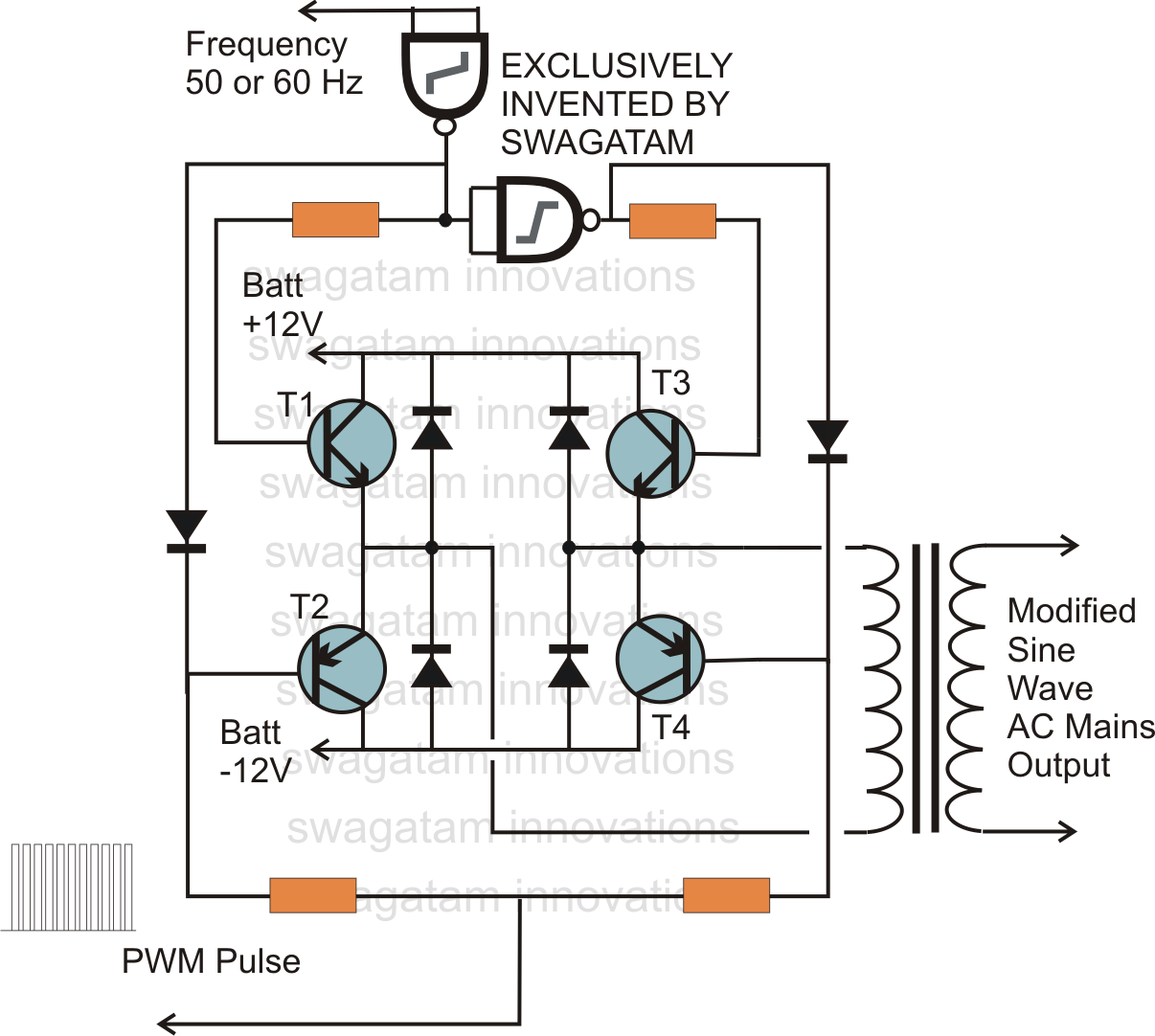
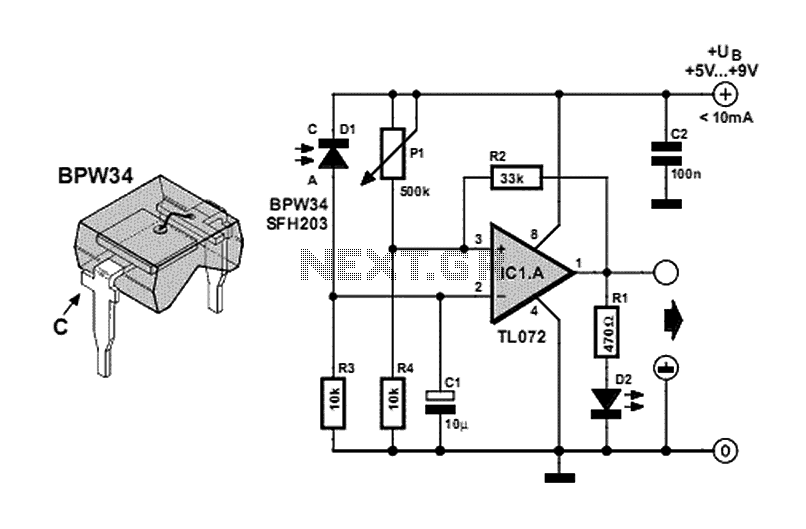
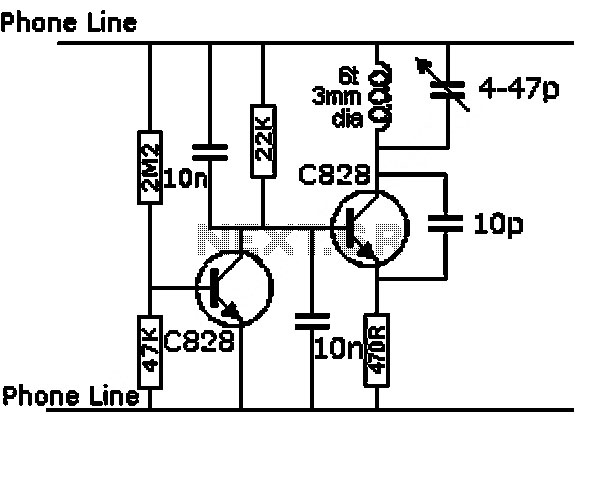
h bridge voltage multiplier at low voltage
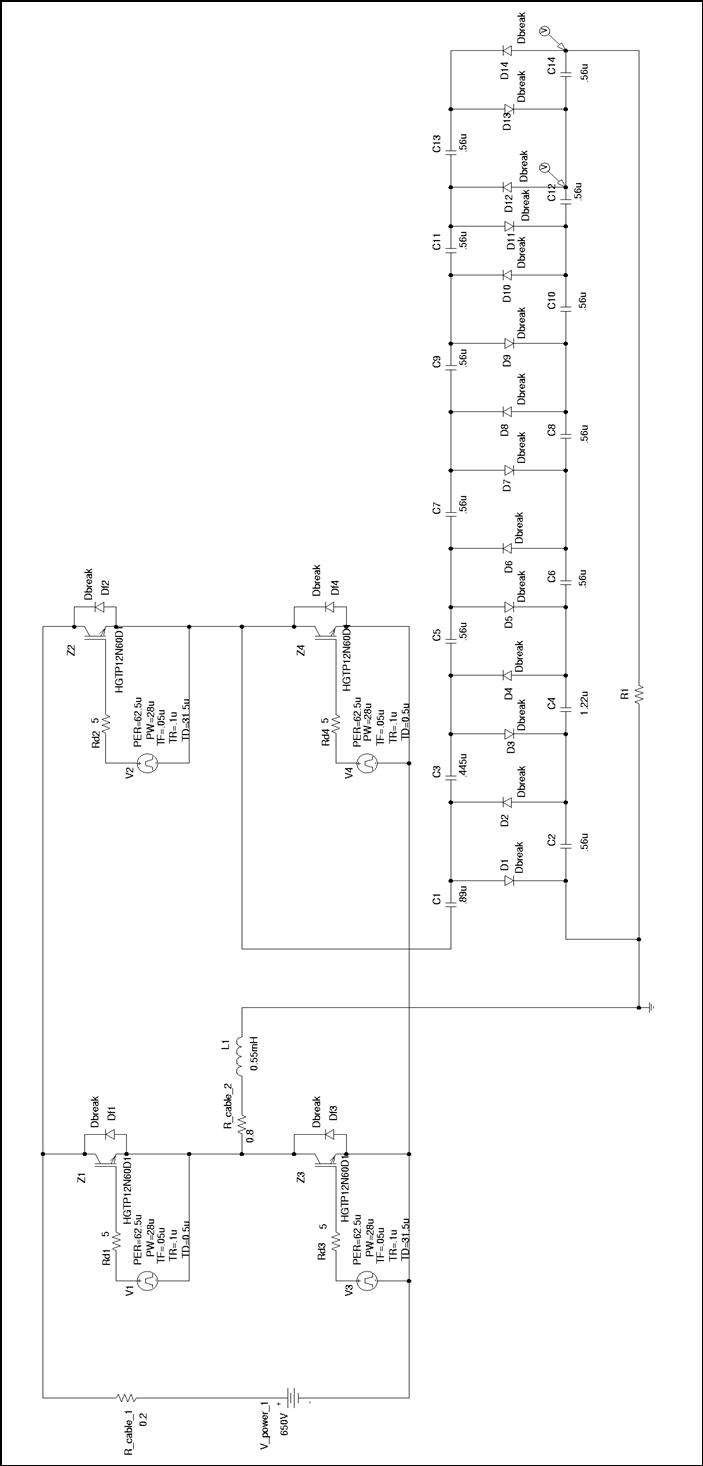
Thesis by Rafael Bräg at the University of Canterbury, New Zealand, in cooperation with the Universität Karlsruhe, Institut Elektrotechnik und Hochspannungstechnik.
The thesis presents a comprehensive study conducted by Rafael Bräg, focusing on advancements in the field of electrical engineering. The collaboration between the University of Canterbury and the Universität Karlsruhe, specifically the Institute of Electrical Engineering and High Voltage Technology, underscores the significance of international cooperation in academic research.
The research encompasses various aspects of electrical engineering, including the design, analysis, and implementation of high-voltage systems. It may involve the exploration of new materials, innovative circuit designs, and the application of advanced simulation techniques to enhance the efficiency and reliability of electrical systems.
In particular, the thesis likely addresses critical topics such as insulation technology, power system stability, and the integration of renewable energy sources into existing electrical grids. The findings and methodologies outlined in this work could provide valuable insights for both academic researchers and industry professionals seeking to improve electrical system performance and safety.
Overall, the thesis serves as a substantial contribution to the field of electrical engineering, reflecting the collaborative efforts and expertise of both institutions involved in the research.Thesis by Rafael Bräg at the University of Canterbury, New Zealand in cooperation with the Universität Karlsruhe, Institut Elektrotechnik und Hochspannungstechnik.. 🔗 External reference
The thesis presents a comprehensive study conducted by Rafael Bräg, focusing on advancements in the field of electrical engineering. The collaboration between the University of Canterbury and the Universität Karlsruhe, specifically the Institute of Electrical Engineering and High Voltage Technology, underscores the significance of international cooperation in academic research.
The research encompasses various aspects of electrical engineering, including the design, analysis, and implementation of high-voltage systems. It may involve the exploration of new materials, innovative circuit designs, and the application of advanced simulation techniques to enhance the efficiency and reliability of electrical systems.
In particular, the thesis likely addresses critical topics such as insulation technology, power system stability, and the integration of renewable energy sources into existing electrical grids. The findings and methodologies outlined in this work could provide valuable insights for both academic researchers and industry professionals seeking to improve electrical system performance and safety.
Overall, the thesis serves as a substantial contribution to the field of electrical engineering, reflecting the collaborative efforts and expertise of both institutions involved in the research.Thesis by Rafael Bräg at the University of Canterbury, New Zealand in cooperation with the Universität Karlsruhe, Institut Elektrotechnik und Hochspannungstechnik.. 🔗 External reference