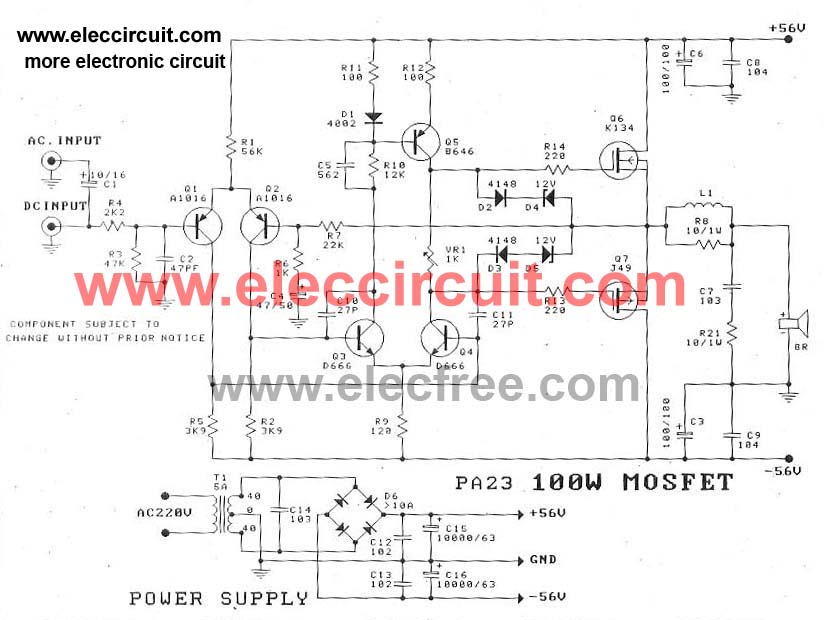
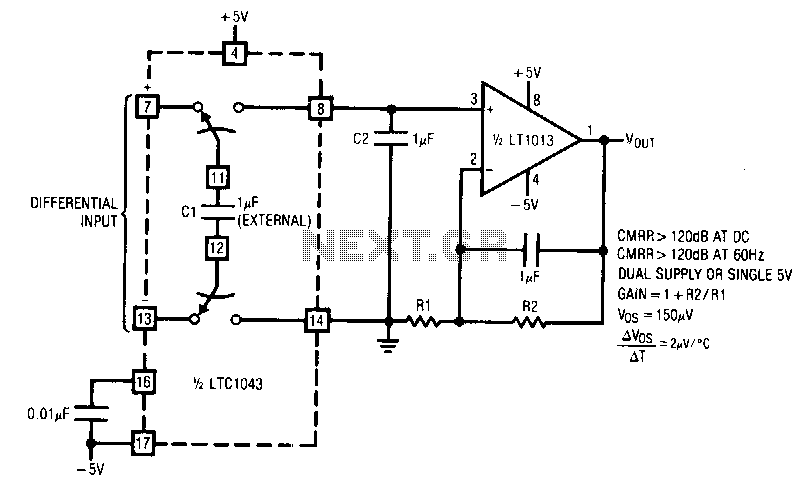
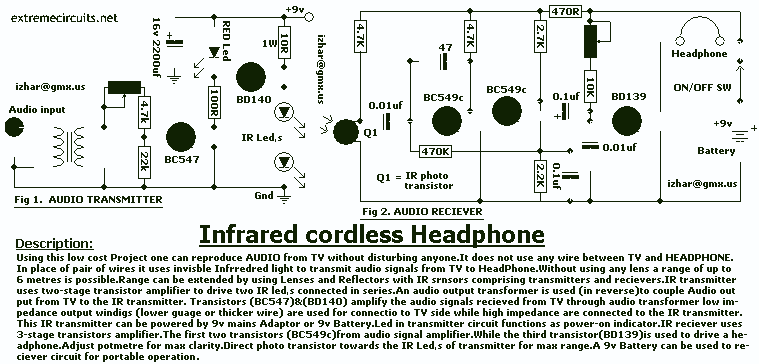
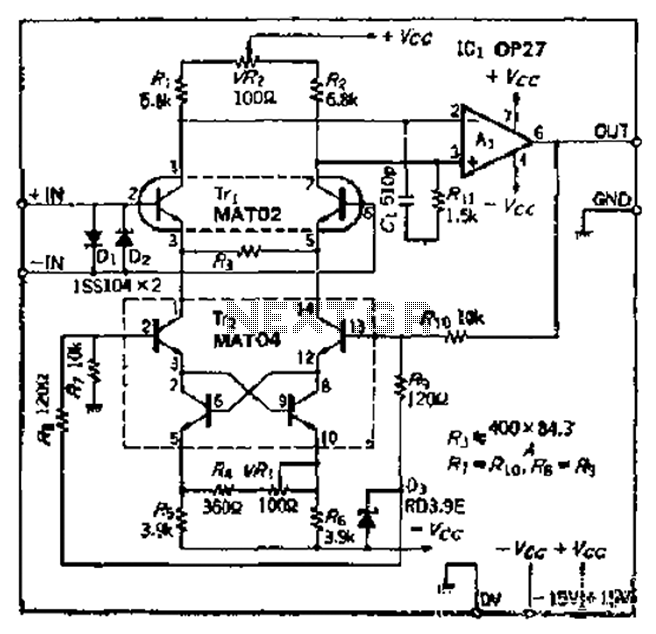
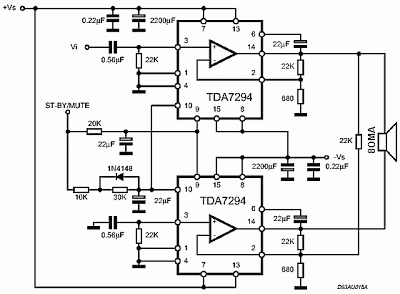
headphone amplifier class a
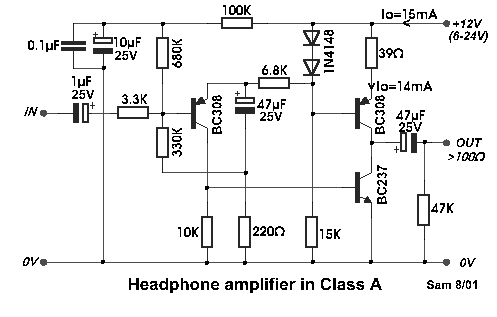
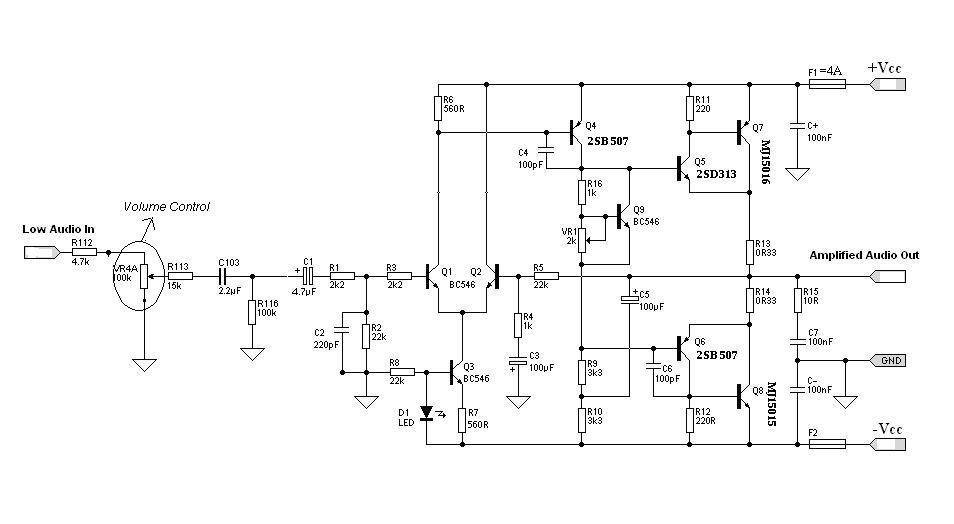
Even if simple, the circuit meets all conditions regarding distortion and frequency response. The input resistance is 250K ohms, and it can drive loads between 100 ohms and 2K ohms.
The described circuit is a basic signal processing circuit designed to handle audio or low-frequency signals while maintaining fidelity in terms of distortion and frequency response. The input resistance of 250K ohms indicates it is suitable for interfacing with high-impedance sources, ensuring minimal loading effect on the preceding stage. This high input resistance is advantageous in applications such as audio preamplifiers or sensor interfaces, where preserving the integrity of the original signal is critical.
The circuit is capable of driving loads ranging from 100 ohms to 2K ohms, making it versatile for various applications. The lower end of the load range (100 ohms) suggests it can interface with low-impedance devices, such as speakers or certain types of sensors, while the upper limit of 2K ohms allows compatibility with higher impedance loads, such as line-level inputs on mixers or amplifiers.
In terms of performance, the circuit is designed to minimize distortion across the frequency spectrum, which is crucial for applications in audio processing. The frequency response should be flat over the intended operating range, ensuring that all frequencies are amplified equally without coloration. This characteristic is essential for maintaining the quality of audio signals, making the circuit suitable for professional audio equipment.
Overall, this circuit represents a fundamental building block in electronic design, emphasizing the importance of input impedance, load driving capability, and fidelity in frequency response and distortion.Even if simple the circuit, plirej` all condition, regarding the distortion and the response of frequency. The resistance of entry is 250K and the load that can drive is between 100R and 2K.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is a basic signal processing circuit designed to handle audio or low-frequency signals while maintaining fidelity in terms of distortion and frequency response. The input resistance of 250K ohms indicates it is suitable for interfacing with high-impedance sources, ensuring minimal loading effect on the preceding stage. This high input resistance is advantageous in applications such as audio preamplifiers or sensor interfaces, where preserving the integrity of the original signal is critical.
The circuit is capable of driving loads ranging from 100 ohms to 2K ohms, making it versatile for various applications. The lower end of the load range (100 ohms) suggests it can interface with low-impedance devices, such as speakers or certain types of sensors, while the upper limit of 2K ohms allows compatibility with higher impedance loads, such as line-level inputs on mixers or amplifiers.
In terms of performance, the circuit is designed to minimize distortion across the frequency spectrum, which is crucial for applications in audio processing. The frequency response should be flat over the intended operating range, ensuring that all frequencies are amplified equally without coloration. This characteristic is essential for maintaining the quality of audio signals, making the circuit suitable for professional audio equipment.
Overall, this circuit represents a fundamental building block in electronic design, emphasizing the importance of input impedance, load driving capability, and fidelity in frequency response and distortion.Even if simple the circuit, plirej` all condition, regarding the distortion and the response of frequency. The resistance of entry is 250K and the load that can drive is between 100R and 2K.. 🔗 External reference