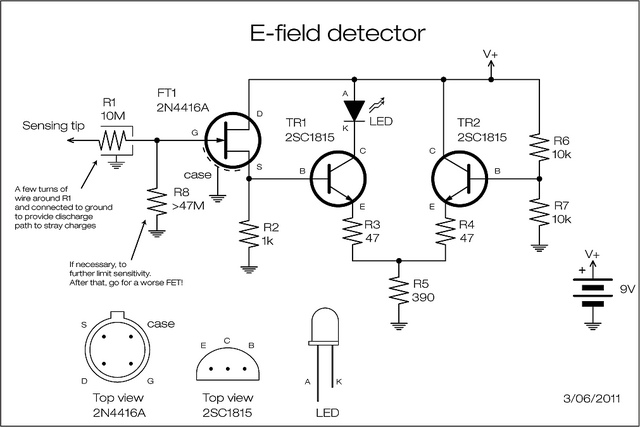
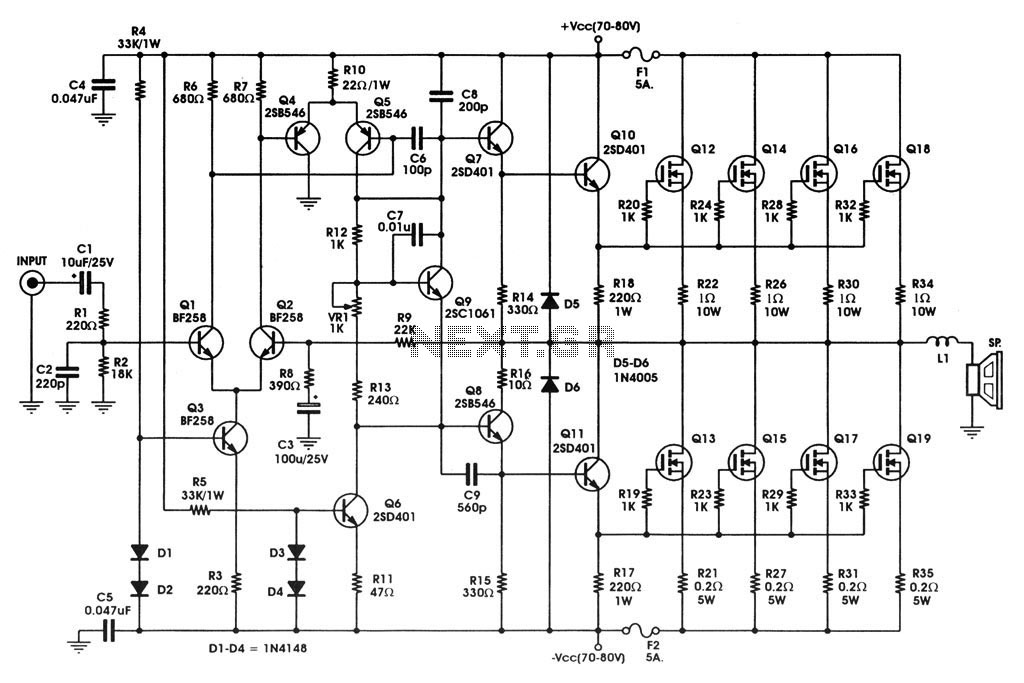
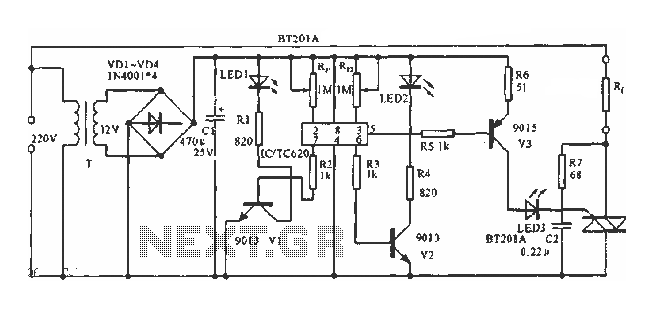
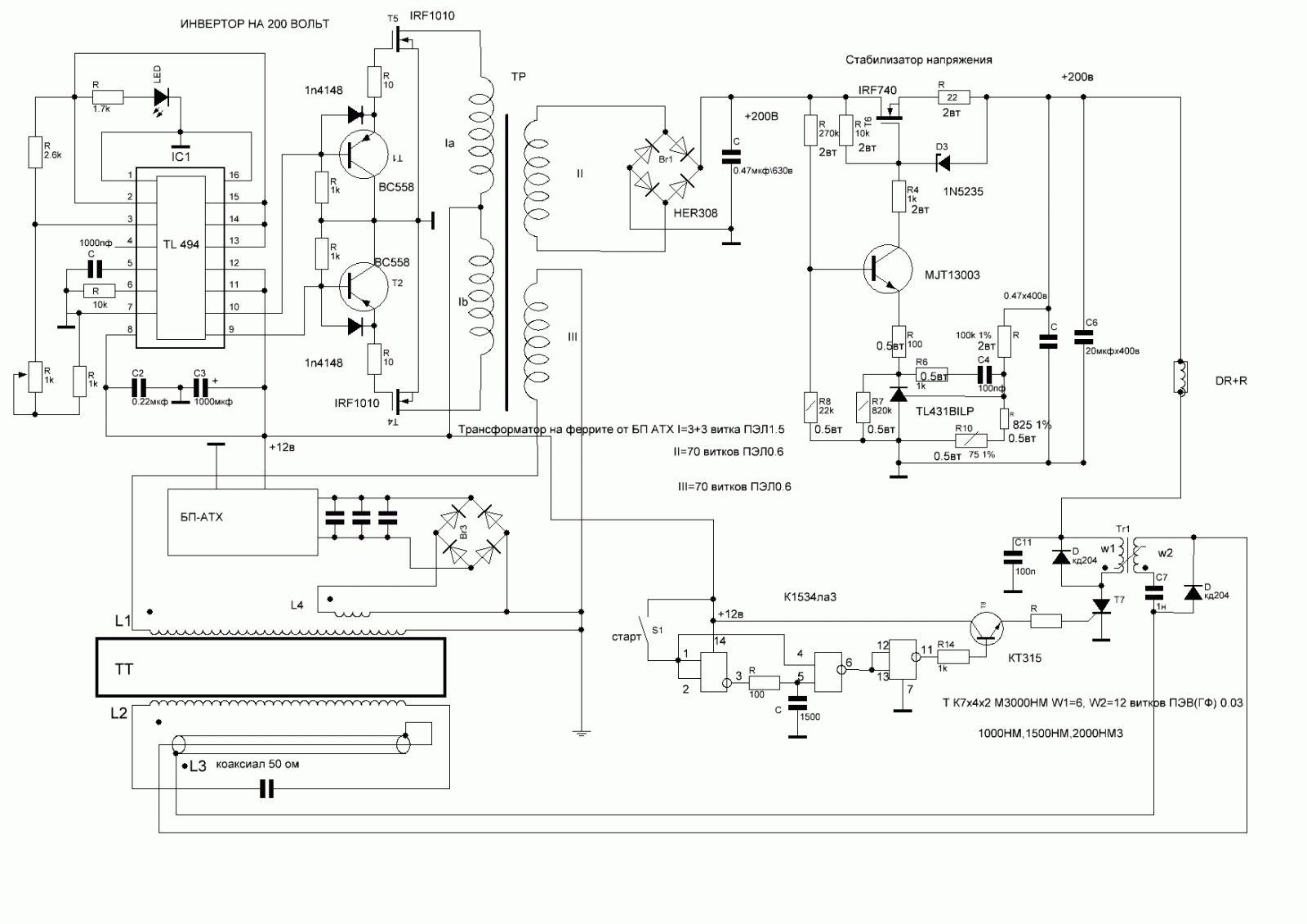
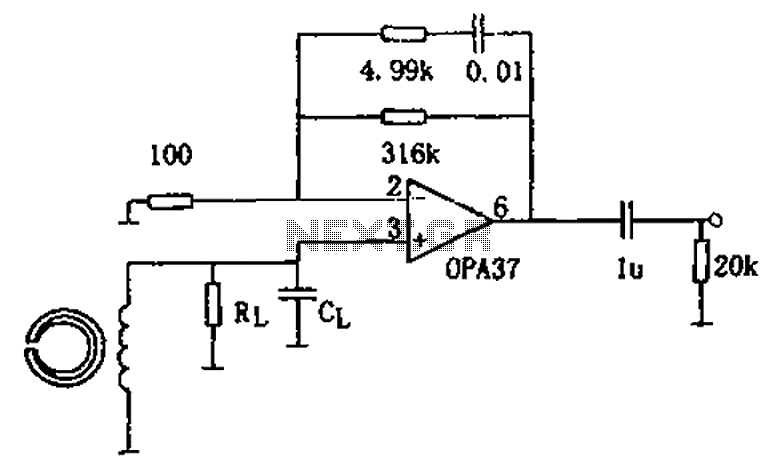
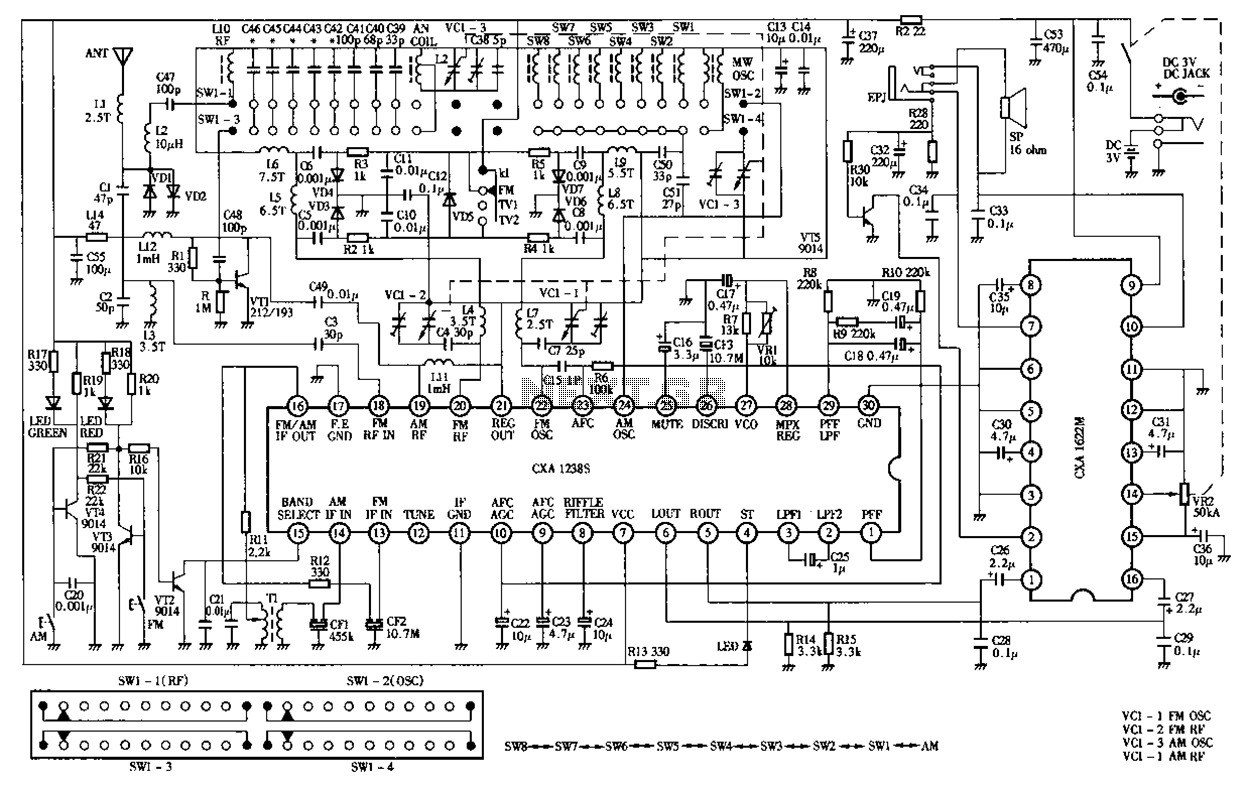
Heathkit Groundtrack GR-1290 metal detector schematic diagram
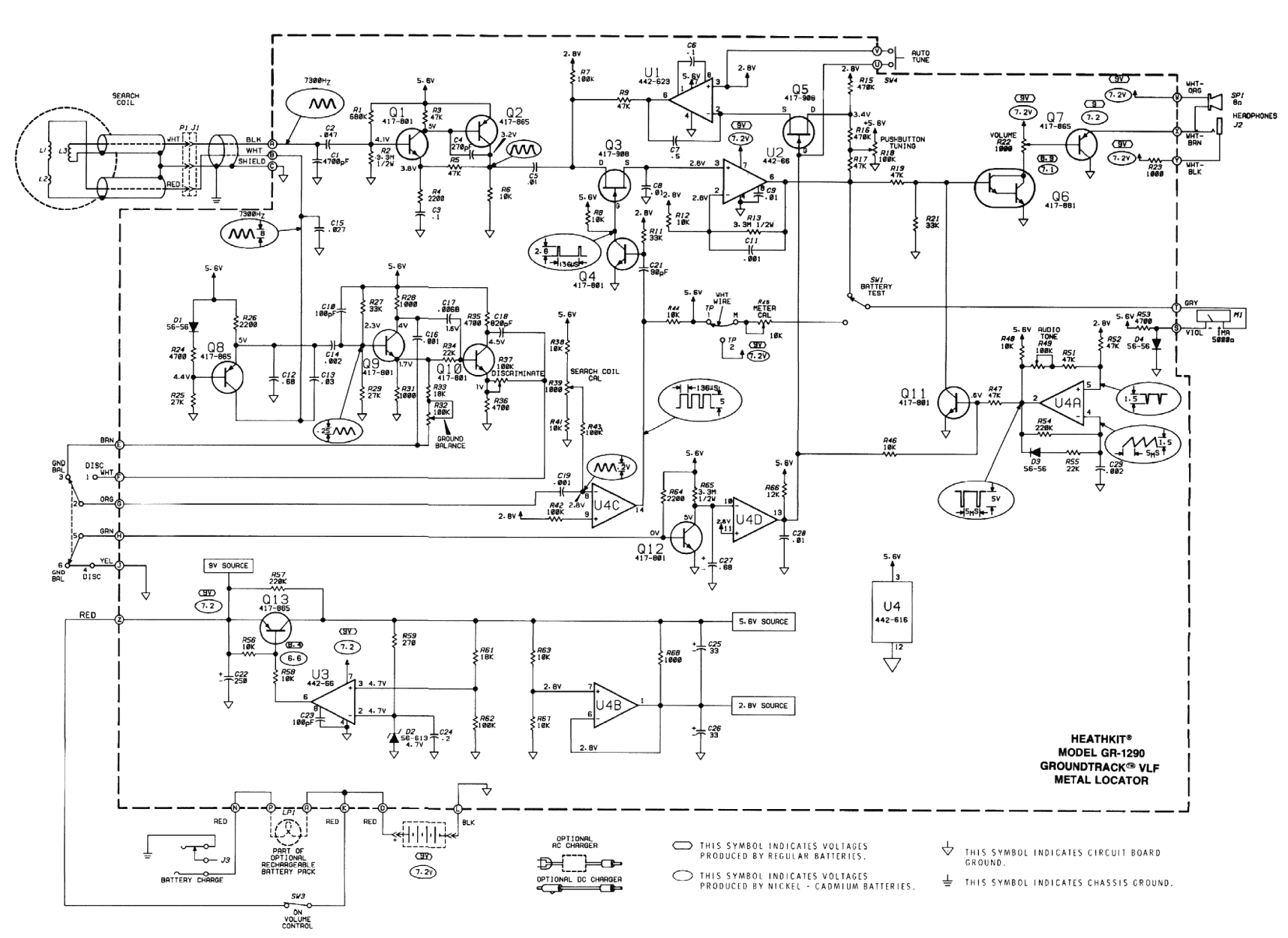
The original coil that came with the Heathkit project was preassembled at the factory. It had a diameter of around 15 cm (6 inches). A larger (30 cm, 12 inches) coil can be made using the following data.
The design of a larger coil, specifically one with a diameter of 30 cm (12 inches), requires careful consideration of various parameters to ensure optimal performance. The coil's dimensions directly influence its inductance, resistance, and overall efficiency in an electrical circuit.
To construct a 30 cm coil, the wire gauge must be selected based on the intended current capacity and the coil's resistance. A thicker wire will reduce resistance but may increase the weight and cost of the coil. The number of turns is another critical factor; increasing the number of turns can enhance the inductance but may require more space and careful winding techniques to maintain uniformity and prevent overlapping.
The coil's core material also plays a significant role in its performance. A ferromagnetic core can significantly increase the inductance compared to an air core, but it also introduces losses due to hysteresis and eddy currents. If a ferromagnetic core is used, the type of material and its permeability must be chosen based on the frequency of operation and the desired inductance.
Additionally, the coil's layout should be designed to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance. This can be achieved by maintaining proper spacing between turns and using appropriate insulation materials.
In summary, constructing a larger coil involves careful planning regarding wire gauge, number of turns, core material, and layout to achieve the desired electrical characteristics while ensuring efficiency and reliability in the overall circuit design.The original coil that came with the Heathkit project was preassembled at the factory. It had a diameter of around 15cm (6 inch). A larger (30cm, 12inch) coil can be made using the following data: 🔗 External reference
The design of a larger coil, specifically one with a diameter of 30 cm (12 inches), requires careful consideration of various parameters to ensure optimal performance. The coil's dimensions directly influence its inductance, resistance, and overall efficiency in an electrical circuit.
To construct a 30 cm coil, the wire gauge must be selected based on the intended current capacity and the coil's resistance. A thicker wire will reduce resistance but may increase the weight and cost of the coil. The number of turns is another critical factor; increasing the number of turns can enhance the inductance but may require more space and careful winding techniques to maintain uniformity and prevent overlapping.
The coil's core material also plays a significant role in its performance. A ferromagnetic core can significantly increase the inductance compared to an air core, but it also introduces losses due to hysteresis and eddy currents. If a ferromagnetic core is used, the type of material and its permeability must be chosen based on the frequency of operation and the desired inductance.
Additionally, the coil's layout should be designed to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance. This can be achieved by maintaining proper spacing between turns and using appropriate insulation materials.
In summary, constructing a larger coil involves careful planning regarding wire gauge, number of turns, core material, and layout to achieve the desired electrical characteristics while ensuring efficiency and reliability in the overall circuit design.The original coil that came with the Heathkit project was preassembled at the factory. It had a diameter of around 15cm (6 inch). A larger (30cm, 12inch) coil can be made using the following data: 🔗 External reference