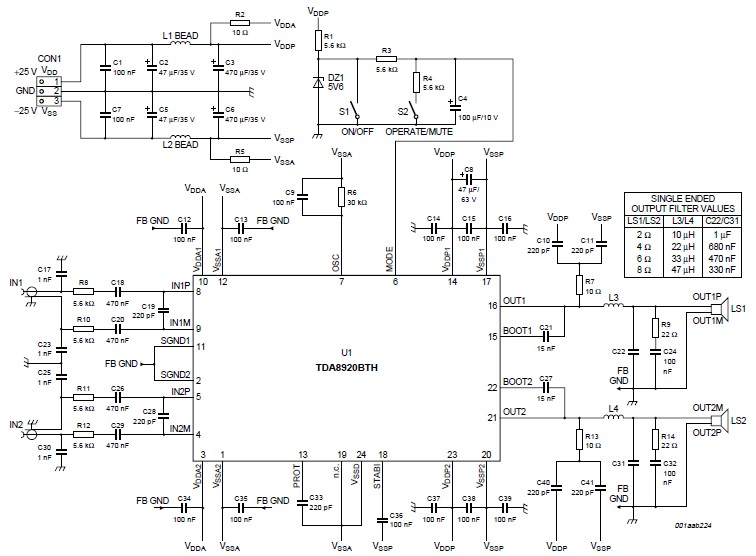
High-frequency characteristics are improved power MOSFET amplifier
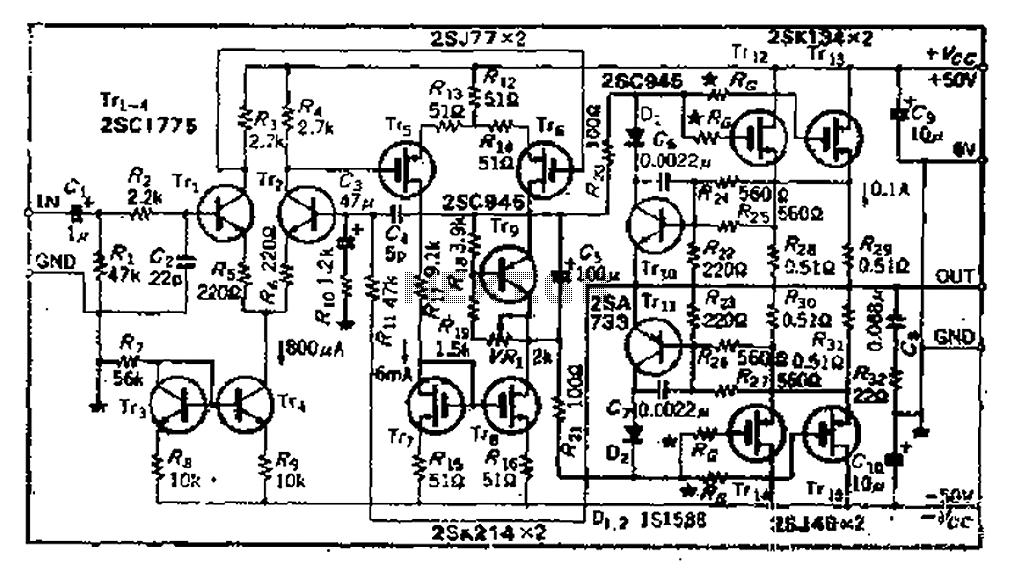
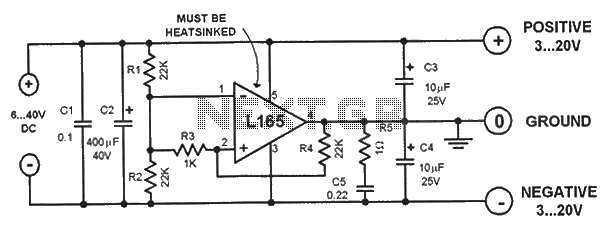
The circuit consists of three identical basic stages, with the second stage featuring a differential output from the power MOSFET, 2SJ77. A current mirror circuit utilizing 2SK214 is implemented. The operating current is 6mA; however, due to the power supply voltage reaching 50V, the transistor may generate significant heat, necessitating the installation of a small heat sink. The output stage operates in direct drive mode, as it lacks an emitter follower buffer to enhance the load driving capability. To improve the conversion rate, increasing the Tri- within the permissible loss range of the drain current may be considered. Power MOSFETs often exhibit high oscillation, which can be challenging to suppress. A straightforward method to mitigate this is to place a series resistance (marked as Ro) close to the gate, although this may compromise some high-frequency performance. The resistance Ra varies depending on the component, typically ranging from 50Ω to 500Ω.
The described circuit is a multi-stage amplifier featuring a differential output stage, which is critical for achieving high fidelity in audio applications or precision in signal processing. The use of the 2SJ77 power MOSFET allows for efficient amplification of the input signal, while the 2SK214 current mirror ensures stable biasing, maintaining consistent operation across varying conditions.
The operating current of 6mA is relatively low, which is advantageous for minimizing power consumption; however, the high supply voltage of 50V poses thermal challenges. The inclusion of a heat sink is essential to prevent thermal runaway and ensure reliable operation over extended periods. The direct drive output stage is particularly beneficial in applications where low output impedance is desired, allowing for better load driving capabilities without the added complexity of an emitter follower buffer.
To address the potential for oscillations, which are common in high-frequency applications, the design incorporates a series gate resistor (Ro) to dampen these effects. The choice of resistance value is crucial; while a lower resistance may enhance high-frequency response, it can also lead to increased susceptibility to oscillation. Therefore, selecting an appropriate value for Ra—considering the specific characteristics of the components used—is vital for maintaining performance integrity.
In summary, the circuit design effectively balances the need for power efficiency, thermal management, and signal integrity, making it suitable for various electronic applications that require robust performance with minimal distortion.And 3 gn same basic circuit, and the second stage is a differential output of the power MOSFET, 2SJ77, a current mirror circuit uses 2SK214. While the operating current is only 6mA, however, because the power supply voltage up to sov, the transistor may have a fever, so install a small heat sink. the output stage chestnut direct drive mode, since without emitter follower buffer, to increase the load driving circuit, and if the need to improve the conversion rate, may try to increase the Tri- * within the range of allowable loss drain on current initiatives.
power MOSFET often have high oscillation, the oscillation to be suppressed relatively sleepy difficult, simple measures are (as close to the gate position) at the gate series resistance ( mark Ro, but want to sacrifice some high frequency characteristics, Ra resistance varies with element member varies, usually between 50Q ~ 500Q.
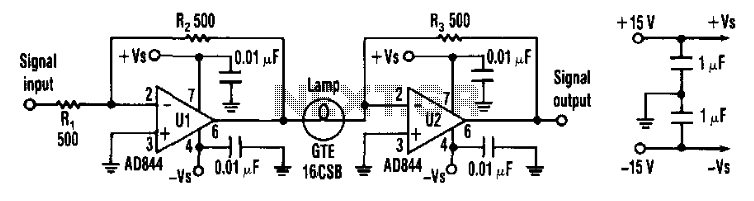
The described circuit is a multi-stage amplifier featuring a differential output stage, which is critical for achieving high fidelity in audio applications or precision in signal processing. The use of the 2SJ77 power MOSFET allows for efficient amplification of the input signal, while the 2SK214 current mirror ensures stable biasing, maintaining consistent operation across varying conditions.
The operating current of 6mA is relatively low, which is advantageous for minimizing power consumption; however, the high supply voltage of 50V poses thermal challenges. The inclusion of a heat sink is essential to prevent thermal runaway and ensure reliable operation over extended periods. The direct drive output stage is particularly beneficial in applications where low output impedance is desired, allowing for better load driving capabilities without the added complexity of an emitter follower buffer.
To address the potential for oscillations, which are common in high-frequency applications, the design incorporates a series gate resistor (Ro) to dampen these effects. The choice of resistance value is crucial; while a lower resistance may enhance high-frequency response, it can also lead to increased susceptibility to oscillation. Therefore, selecting an appropriate value for Ra—considering the specific characteristics of the components used—is vital for maintaining performance integrity.
In summary, the circuit design effectively balances the need for power efficiency, thermal management, and signal integrity, making it suitable for various electronic applications that require robust performance with minimal distortion.And 3 gn same basic circuit, and the second stage is a differential output of the power MOSFET, 2SJ77, a current mirror circuit uses 2SK214. While the operating current is only 6mA, however, because the power supply voltage up to sov, the transistor may have a fever, so install a small heat sink. the output stage chestnut direct drive mode, since without emitter follower buffer, to increase the load driving circuit, and if the need to improve the conversion rate, may try to increase the Tri- * within the range of allowable loss drain on current initiatives.
power MOSFET often have high oscillation, the oscillation to be suppressed relatively sleepy difficult, simple measures are (as close to the gate position) at the gate series resistance ( mark Ro, but want to sacrifice some high frequency characteristics, Ra resistance varies with element member varies, usually between 50Q ~ 500Q.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713