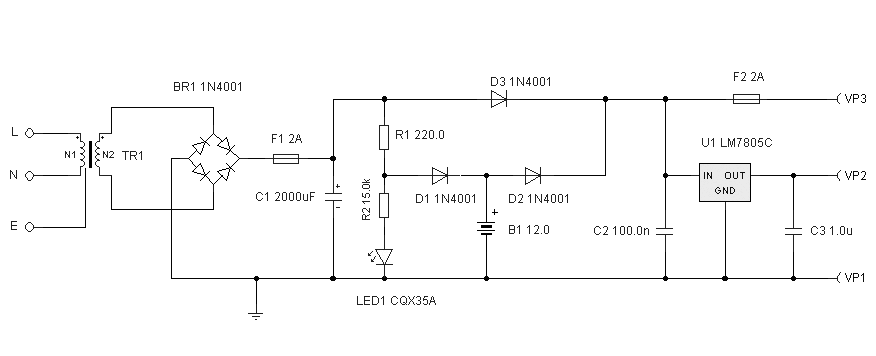
Multi Output Instrument Power Supply With 7805 IC
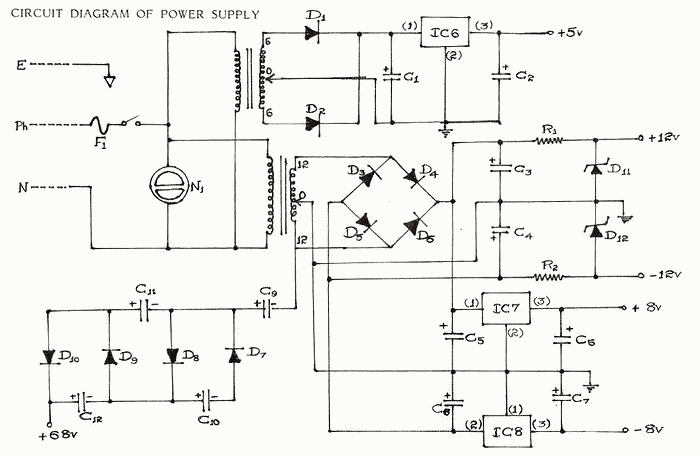
The following circuit illustrates a Multi Output Instrument Power Supply Circuit Diagram. Features include the ability to obtain multiple voltage values for cost reduction and basic functionality.
The Multi Output Instrument Power Supply Circuit is designed to provide various voltage outputs from a single power source, making it a cost-effective solution for powering multiple devices or instruments. The circuit typically consists of a main transformer, rectifier, voltage regulators, and filtering capacitors.
The transformer steps down the input AC voltage to a lower AC voltage suitable for the desired output levels. The output from the transformer is then fed into a rectifier circuit, which converts the AC voltage to DC voltage. This is often achieved using a bridge rectifier configuration, which allows for full-wave rectification, improving efficiency.
After rectification, the DC voltage may still contain ripples. To smooth this output, filtering capacitors are employed. These capacitors help to reduce voltage fluctuations, providing a more stable DC output.
Voltage regulators are then used to obtain specific voltage levels from the rectified DC. Common types of voltage regulators include linear regulators (such as the 7805 for +5V or 7812 for +12V outputs) and switching regulators, which are more efficient for higher currents. The output voltage can be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor values in the feedback network of adjustable regulators.
The circuit may also include additional features such as overcurrent protection, thermal shutdown, and short-circuit protection to enhance reliability and safety. By integrating these components, the Multi Output Instrument Power Supply Circuit can effectively serve various applications in laboratories, testing environments, or any scenario where multiple voltage levels are required from a single supply source.The following circuit shows about Multi Output Instrument Power Supply Circuit Diagram. Features: obtain multiple voltage values for cost reduction, basic .. 🔗 External reference
The Multi Output Instrument Power Supply Circuit is designed to provide various voltage outputs from a single power source, making it a cost-effective solution for powering multiple devices or instruments. The circuit typically consists of a main transformer, rectifier, voltage regulators, and filtering capacitors.
The transformer steps down the input AC voltage to a lower AC voltage suitable for the desired output levels. The output from the transformer is then fed into a rectifier circuit, which converts the AC voltage to DC voltage. This is often achieved using a bridge rectifier configuration, which allows for full-wave rectification, improving efficiency.
After rectification, the DC voltage may still contain ripples. To smooth this output, filtering capacitors are employed. These capacitors help to reduce voltage fluctuations, providing a more stable DC output.
Voltage regulators are then used to obtain specific voltage levels from the rectified DC. Common types of voltage regulators include linear regulators (such as the 7805 for +5V or 7812 for +12V outputs) and switching regulators, which are more efficient for higher currents. The output voltage can be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor values in the feedback network of adjustable regulators.
The circuit may also include additional features such as overcurrent protection, thermal shutdown, and short-circuit protection to enhance reliability and safety. By integrating these components, the Multi Output Instrument Power Supply Circuit can effectively serve various applications in laboratories, testing environments, or any scenario where multiple voltage levels are required from a single supply source.The following circuit shows about Multi Output Instrument Power Supply Circuit Diagram. Features: obtain multiple voltage values for cost reduction, basic .. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713