High Impedance DC Voltmeter using MOS Op-Amp
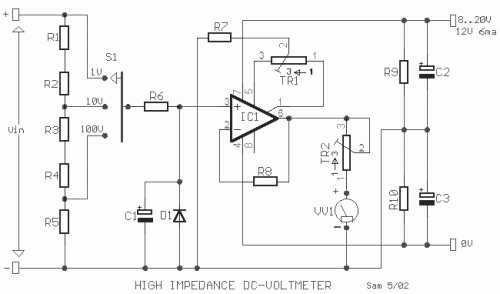
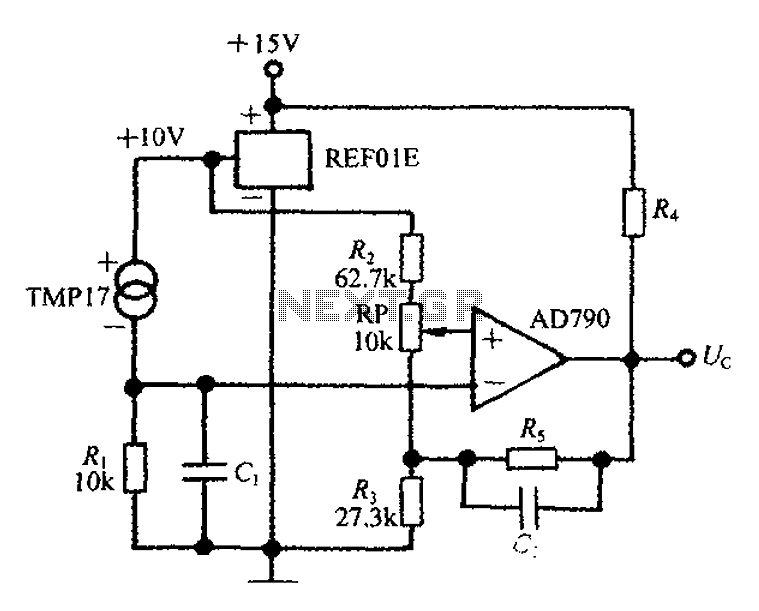
The circuit was designed to create a high-impedance voltmeter capable of measuring Direct Current (DC) voltages across various types of circuits.
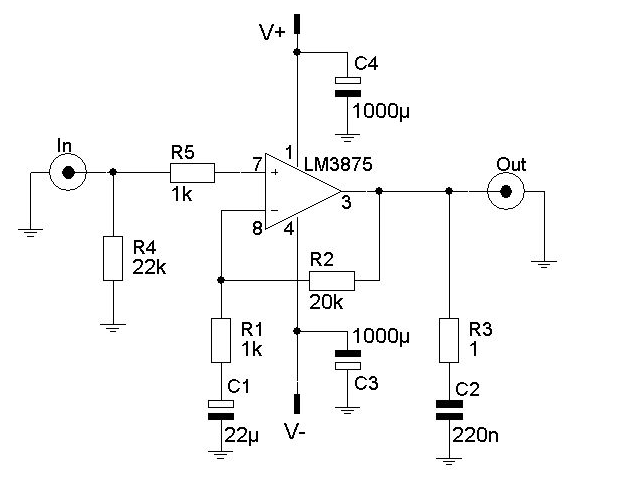
The high-impedance voltmeter circuit typically employs operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured in a non-inverting arrangement to ensure minimal loading on the circuit under test. This configuration is essential for accurately measuring the voltage without significantly affecting the circuit's operation.
The input stage of the voltmeter consists of a precision op-amp, which is chosen for its high input impedance, usually in the range of megaohms, and low offset voltage to enhance measurement accuracy. The op-amp's non-inverting input receives the voltage to be measured, while the inverting input is connected to a feedback resistor network that sets the gain of the amplifier.
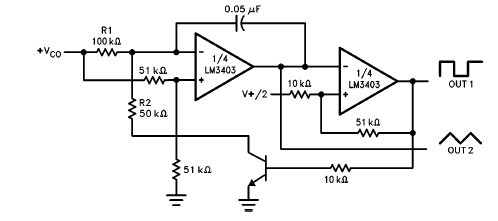
To convert the output voltage of the op-amp to a readable format, a digital voltmeter (DVM) or an analog display can be used. If a DVM is employed, an Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) may be integrated into the circuit, allowing for digital readouts of the measured voltage. The circuit may also include a reference voltage source to calibrate the measurement range, ensuring that the displayed voltage accurately corresponds to the input voltage.
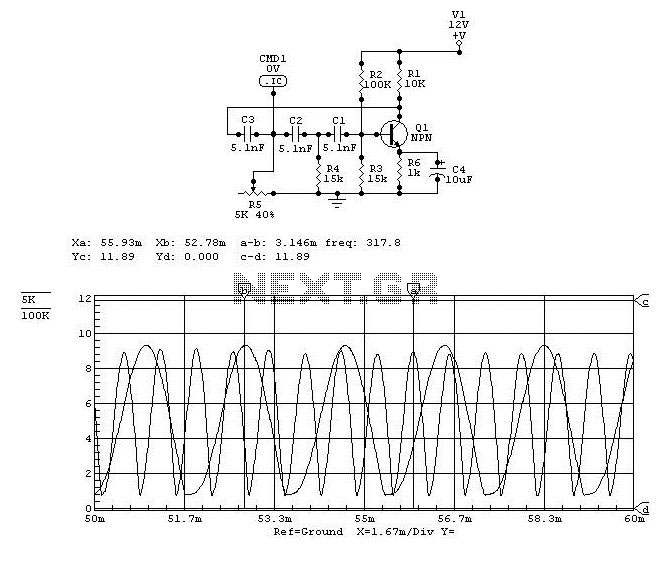
Additional components in the circuit may include protection diodes to prevent damage from overvoltage conditions, as well as filtering capacitors to minimize noise and stabilize the readings. The layout of the circuit should be carefully considered to reduce interference and ensure accurate measurements, particularly in environments with fluctuating electrical noise.
Overall, this high-impedance voltmeter design is suitable for applications where precise voltage measurements are required without impacting the performance of the circuit being tested.The circuit was designed for the purpose of creating a voltmeter with high impedance that would measure Direct Current voltages across any types of circui. 🔗 External reference
The high-impedance voltmeter circuit typically employs operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured in a non-inverting arrangement to ensure minimal loading on the circuit under test. This configuration is essential for accurately measuring the voltage without significantly affecting the circuit's operation.
The input stage of the voltmeter consists of a precision op-amp, which is chosen for its high input impedance, usually in the range of megaohms, and low offset voltage to enhance measurement accuracy. The op-amp's non-inverting input receives the voltage to be measured, while the inverting input is connected to a feedback resistor network that sets the gain of the amplifier.
To convert the output voltage of the op-amp to a readable format, a digital voltmeter (DVM) or an analog display can be used. If a DVM is employed, an Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) may be integrated into the circuit, allowing for digital readouts of the measured voltage. The circuit may also include a reference voltage source to calibrate the measurement range, ensuring that the displayed voltage accurately corresponds to the input voltage.
Additional components in the circuit may include protection diodes to prevent damage from overvoltage conditions, as well as filtering capacitors to minimize noise and stabilize the readings. The layout of the circuit should be carefully considered to reduce interference and ensure accurate measurements, particularly in environments with fluctuating electrical noise.
Overall, this high-impedance voltmeter design is suitable for applications where precise voltage measurements are required without impacting the performance of the circuit being tested.The circuit was designed for the purpose of creating a voltmeter with high impedance that would measure Direct Current voltages across any types of circui. 🔗 External reference