High speed data switch circuit
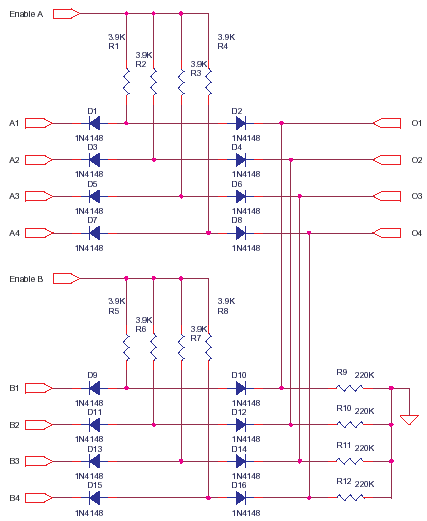
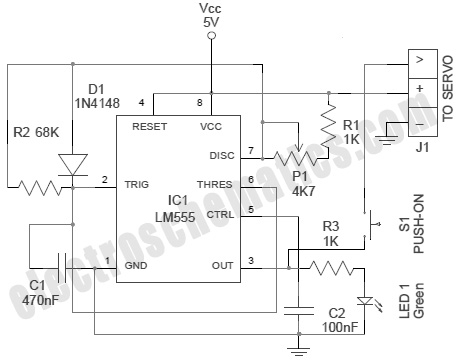
This circuit represents a low-cost printer sharing device that was developed some time ago. The product was encapsulated in epoxy with a black dye and had a limited commercial release. The output impedance of this circuit is high, with a sink impedance of 220K ohms and a source impedance of 3.9K ohms. It is recommended to use buffers or drivers at the output. When Enable A is in a floating state (high impedance) or low, the outputs O1 to O4 are unaffected by the inputs A1 to A4. Activating Enable A to a logic high (5V) allows the signals from A1 to A4 to be present at O1 to O4. By setting Enable A or Enable B to high, it is possible to route the data from A1 to A4 or B1 to B4 to the outputs O1 to O4. The circuit also supports data mixing and can be expanded to accommodate multiple input sets or increased data width. The use of a 1N4148 diode, which has a fast switching time of 4 nanoseconds, contributes to the rapid operation of this data switch. However, the circuit is not capable of driving long printer cables without additional drivers, as they will impose a load on the output.
This printer sharing circuit utilizes a simple architecture to facilitate the connection of multiple printers to a single output. The core functionality hinges on the Enable A and Enable B lines, which control the routing of data from the respective input sets (A1-A4 and B1-B4) to the output lines (O1-O4). The high output impedance necessitates the incorporation of buffers or drivers to ensure signal integrity, particularly over longer distances where capacitance and resistance in the cabling could degrade performance.
The circuit design allows for flexibility in the configuration of inputs and outputs. By employing logic gates or multiplexers, the system can be expanded to support additional input sets, making it adaptable for various applications. The fast switching capability of the 1N4148 diode ensures that data can be transmitted quickly, minimizing delay, which is critical in printer data communication.
In practical applications, care must be taken to avoid excessive loading on the output lines. The recommendation to use drivers is essential when interfacing with long printer cables, as the inherent capacitance and resistance of the cables can create signal degradation. Therefore, the implementation of suitable driver circuits will enhance the performance and reliability of the printer sharing device, ensuring that it can operate effectively in diverse environments.
Overall, this circuit serves as a foundational model for printer sharing solutions, demonstrating key principles of electronic design, including impedance matching, signal routing, and the importance of component selection in achieving desired performance characteristics.This circuit is a small representation of a very low cost printer sharer i made very long ago. This is as much i can remember of the basic ideas behind the product. I used to pot the product in epoxy with a black dye and sold a few, they sort of served the purpose. Output impedance of this circuit is high, sink is 220K source is 3.9K+ so use some buffers or drivers at Output. when Enable A is at float-high impedance or low the output O1-O4 is not influenced by A1-A4 inputs. If Enable A is made logic high or 5V then A1-A4 is available at O1-O4. By turning Enable A or Enable B high, you can route the data A1-A4 or B1-B4 to the output O1-O4, you can also mix data and you can expand to any number of input sets or data width.
1N4148 is fast, 4nS, that makes this data switch quite fast. This circuit cannot drive long printer cables without drivers. They will load the output. 🔗 External reference
This printer sharing circuit utilizes a simple architecture to facilitate the connection of multiple printers to a single output. The core functionality hinges on the Enable A and Enable B lines, which control the routing of data from the respective input sets (A1-A4 and B1-B4) to the output lines (O1-O4). The high output impedance necessitates the incorporation of buffers or drivers to ensure signal integrity, particularly over longer distances where capacitance and resistance in the cabling could degrade performance.
The circuit design allows for flexibility in the configuration of inputs and outputs. By employing logic gates or multiplexers, the system can be expanded to support additional input sets, making it adaptable for various applications. The fast switching capability of the 1N4148 diode ensures that data can be transmitted quickly, minimizing delay, which is critical in printer data communication.
In practical applications, care must be taken to avoid excessive loading on the output lines. The recommendation to use drivers is essential when interfacing with long printer cables, as the inherent capacitance and resistance of the cables can create signal degradation. Therefore, the implementation of suitable driver circuits will enhance the performance and reliability of the printer sharing device, ensuring that it can operate effectively in diverse environments.
Overall, this circuit serves as a foundational model for printer sharing solutions, demonstrating key principles of electronic design, including impedance matching, signal routing, and the importance of component selection in achieving desired performance characteristics.This circuit is a small representation of a very low cost printer sharer i made very long ago. This is as much i can remember of the basic ideas behind the product. I used to pot the product in epoxy with a black dye and sold a few, they sort of served the purpose. Output impedance of this circuit is high, sink is 220K source is 3.9K+ so use some buffers or drivers at Output. when Enable A is at float-high impedance or low the output O1-O4 is not influenced by A1-A4 inputs. If Enable A is made logic high or 5V then A1-A4 is available at O1-O4. By turning Enable A or Enable B high, you can route the data A1-A4 or B1-B4 to the output O1-O4, you can also mix data and you can expand to any number of input sets or data width.
1N4148 is fast, 4nS, that makes this data switch quite fast. This circuit cannot drive long printer cables without drivers. They will load the output. 🔗 External reference