HIGH VOLTAGE NEGATIVE ION GENERATOR
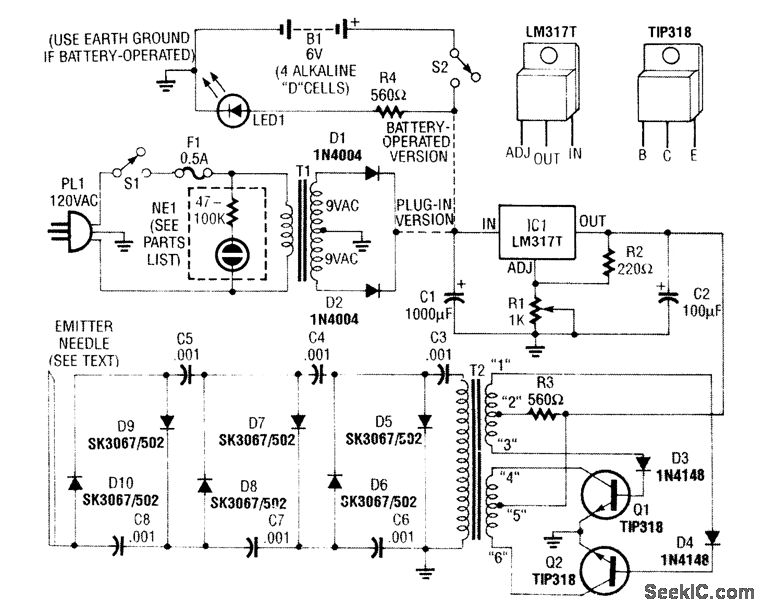
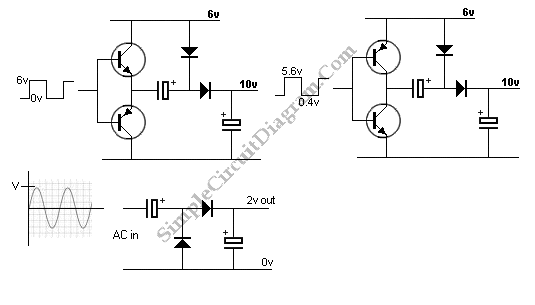
A modified black and white television flyback transformer is utilized in this circuit alongside a voltage multiplier to generate a negative voltage ranging from 9 kV to 14 kV. This high voltage is connected to a discharge needle to create negative ions.
The circuit employs a modified flyback transformer, which is known for its ability to generate high voltages efficiently. The flyback transformer operates by storing energy in its magnetic field during the flyback period of the horizontal scan in a television set. In this application, it is adapted to produce a higher output voltage than typical television applications.
The voltage multiplier is a crucial component in this circuit, as it steps up the voltage produced by the flyback transformer. This is typically achieved through a series of capacitors and diodes arranged in a configuration that allows for the accumulation of voltage. The diodes prevent backflow of current, while the capacitors store charge, effectively multiplying the voltage output.
The output voltage, which can vary between 9 kV and 14 kV, is then directed to a discharge needle. This needle serves as an ion emitter, where the high voltage creates a strong electric field that ionizes the surrounding air, resulting in the production of negative ions. These ions can have various applications, such as improving air quality or in certain industrial processes.
The design of the circuit must ensure that all components can handle the high voltages involved, particularly the voltage multiplier and the discharge needle. Proper insulation and safety measures should be implemented to prevent electrical hazards. Additionally, the circuit may require a suitable power supply to energize the flyback transformer, which must be capable of providing the necessary input voltage and current for stable operation.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies the use of high-voltage technology in generating negative ions, leveraging the principles of electromagnetic induction and voltage multiplication effectively.A modified B/W TV flyback transformer is used in this circuit with a voltage multiplier to produce 9- to 14-kV negative voltage. This is connected to a discharge needle to produce negative ions. 🔗 External reference
The circuit employs a modified flyback transformer, which is known for its ability to generate high voltages efficiently. The flyback transformer operates by storing energy in its magnetic field during the flyback period of the horizontal scan in a television set. In this application, it is adapted to produce a higher output voltage than typical television applications.
The voltage multiplier is a crucial component in this circuit, as it steps up the voltage produced by the flyback transformer. This is typically achieved through a series of capacitors and diodes arranged in a configuration that allows for the accumulation of voltage. The diodes prevent backflow of current, while the capacitors store charge, effectively multiplying the voltage output.
The output voltage, which can vary between 9 kV and 14 kV, is then directed to a discharge needle. This needle serves as an ion emitter, where the high voltage creates a strong electric field that ionizes the surrounding air, resulting in the production of negative ions. These ions can have various applications, such as improving air quality or in certain industrial processes.
The design of the circuit must ensure that all components can handle the high voltages involved, particularly the voltage multiplier and the discharge needle. Proper insulation and safety measures should be implemented to prevent electrical hazards. Additionally, the circuit may require a suitable power supply to energize the flyback transformer, which must be capable of providing the necessary input voltage and current for stable operation.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies the use of high-voltage technology in generating negative ions, leveraging the principles of electromagnetic induction and voltage multiplication effectively.A modified B/W TV flyback transformer is used in this circuit with a voltage multiplier to produce 9- to 14-kV negative voltage. This is connected to a discharge needle to produce negative ions. 🔗 External reference