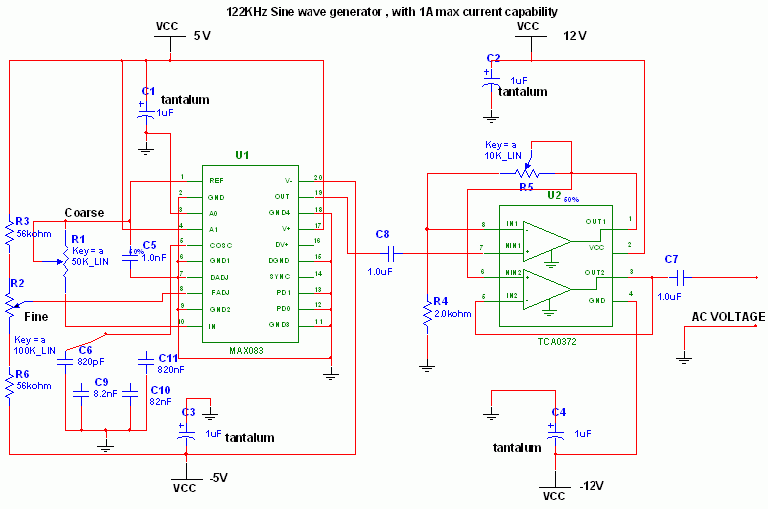
HIGH VOLTAGE PULSE SUPPLY
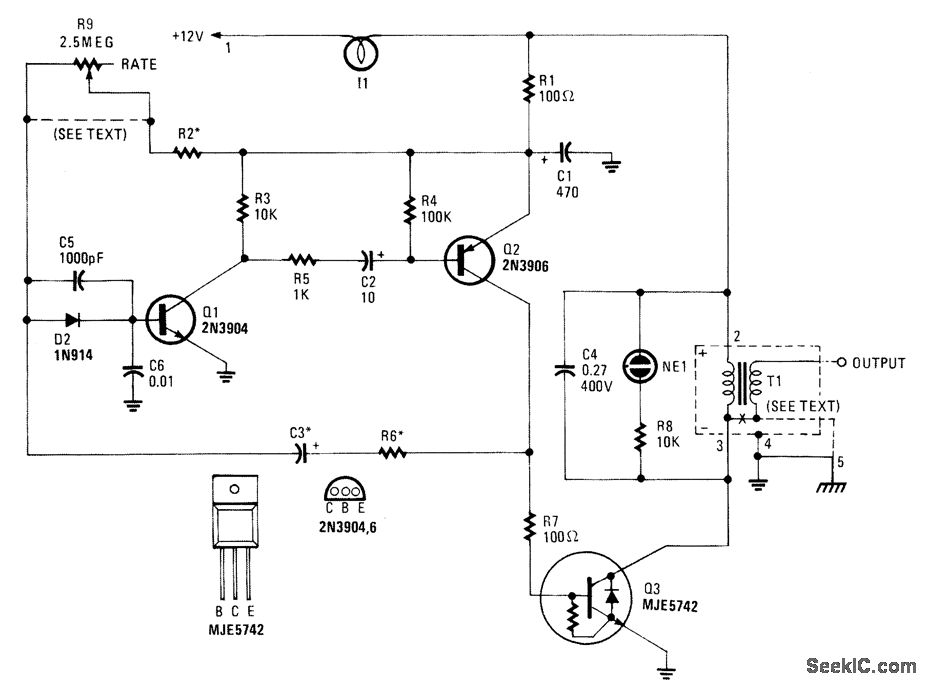
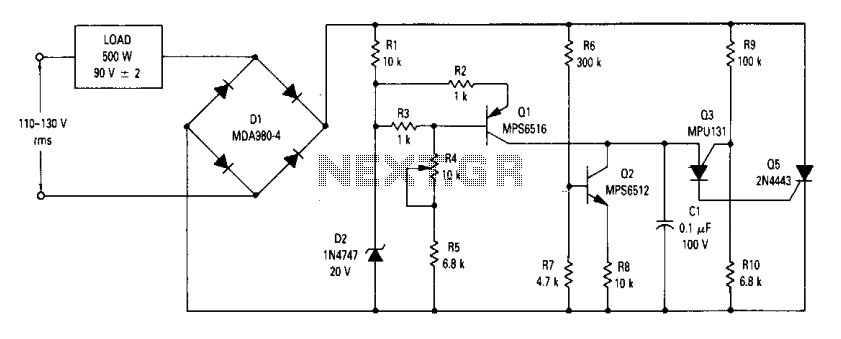
This high-voltage pulse supply generates pulses up to 30 kV. Transistors Q1 and Q2 create a multivibrator in conjunction with peripheral components R1 through R6 and capacitors C1, C2, C3, C5, C6, and diode D2. Resistor R9 adjusts the pulse repetition rate, while R2 should be chosen to limit the maximum repetition rate to 20 Hz. Lamp I1, a type 1156, functions as a current limiter. R9 may be omitted, and R2 can be selected to produce a fixed rate if desired. Transistor Q3 acts as a power amplifier and switch to drive transformer T1, which is an automotive ignition coil. NE1 serves as a pulse indicator, showing circuit operation. Due to the potential to develop up to 30 kV, appropriate construction techniques and safety precautions must be observed.
The high-voltage pulse supply circuit is designed to generate high-voltage pulses suitable for various applications, including ignition systems and testing equipment. The core of the circuit is a multivibrator configuration formed by transistors Q1 and Q2, which alternately turn on and off, creating a square wave signal. This signal is shaped by the resistors R1 to R6 and the capacitors C1, C2, C3, C5, and C6, which determine the timing characteristics and stability of the multivibrator.
Resistor R9 plays a crucial role in adjusting the frequency of the output pulses. By varying the resistance, the pulse repetition rate can be fine-tuned to meet specific operational requirements. R2 is selected to limit the maximum frequency to 20 Hz, ensuring that the circuit operates within safe limits while still providing sufficient pulse output for the intended application.
The inclusion of lamp I1 as a current limiter is a critical safety feature. It prevents excessive current from flowing through the circuit, protecting sensitive components from damage. In scenarios where a fixed pulse rate is required, R9 can be omitted, and R2 adjusted accordingly to establish a stable output.
Transistor Q3 acts as an amplifier and switch, providing the necessary power to drive T1, the automotive ignition coil. This coil is responsible for stepping up the voltage to the desired 30 kV output. The high voltage generated can be utilized for various applications, including ignition systems in internal combustion engines or high-voltage testing.
The NE1 component serves as a pulse indicator, providing visual feedback on the circuit's operation. This feature is particularly useful for troubleshooting and ensuring that the circuit is functioning as intended.
Given the high voltage capabilities of this circuit, it is imperative to adhere to strict construction techniques and safety protocols. Proper insulation, secure connections, and protective enclosures should be employed to mitigate the risks associated with high-voltage operation. Users must be trained and equipped with the necessary safety gear when working with or around this circuit to prevent electrical hazards.This high-voltage pulse supply will generate pulses up to 30 kV. Q1 and Q2 form a multivibrator in conjunction with peripheral components R1 through R6 and C1, C2, C3, C5, C6, and D2. R9 adjusts the pulse repetition rate. R2 should be selected to limit the maximum repetition rate to 20 Hz. I1 is a type 1156 lamp used as a current limiter. R9 can b e left out and R2 selected to produce a fixed rate, if desired. Q3 serves as a power amplifier and switch to drive T1 (an automotive ignition coil). NE1 is used as a pulse indicator and indicates circuit operation. Because this circuit can develop up to 30 kV, suitable construction techniques and safety precautions should be observed. 🔗 External reference
The high-voltage pulse supply circuit is designed to generate high-voltage pulses suitable for various applications, including ignition systems and testing equipment. The core of the circuit is a multivibrator configuration formed by transistors Q1 and Q2, which alternately turn on and off, creating a square wave signal. This signal is shaped by the resistors R1 to R6 and the capacitors C1, C2, C3, C5, and C6, which determine the timing characteristics and stability of the multivibrator.
Resistor R9 plays a crucial role in adjusting the frequency of the output pulses. By varying the resistance, the pulse repetition rate can be fine-tuned to meet specific operational requirements. R2 is selected to limit the maximum frequency to 20 Hz, ensuring that the circuit operates within safe limits while still providing sufficient pulse output for the intended application.
The inclusion of lamp I1 as a current limiter is a critical safety feature. It prevents excessive current from flowing through the circuit, protecting sensitive components from damage. In scenarios where a fixed pulse rate is required, R9 can be omitted, and R2 adjusted accordingly to establish a stable output.
Transistor Q3 acts as an amplifier and switch, providing the necessary power to drive T1, the automotive ignition coil. This coil is responsible for stepping up the voltage to the desired 30 kV output. The high voltage generated can be utilized for various applications, including ignition systems in internal combustion engines or high-voltage testing.
The NE1 component serves as a pulse indicator, providing visual feedback on the circuit's operation. This feature is particularly useful for troubleshooting and ensuring that the circuit is functioning as intended.
Given the high voltage capabilities of this circuit, it is imperative to adhere to strict construction techniques and safety protocols. Proper insulation, secure connections, and protective enclosures should be employed to mitigate the risks associated with high-voltage operation. Users must be trained and equipped with the necessary safety gear when working with or around this circuit to prevent electrical hazards.This high-voltage pulse supply will generate pulses up to 30 kV. Q1 and Q2 form a multivibrator in conjunction with peripheral components R1 through R6 and C1, C2, C3, C5, C6, and D2. R9 adjusts the pulse repetition rate. R2 should be selected to limit the maximum repetition rate to 20 Hz. I1 is a type 1156 lamp used as a current limiter. R9 can b e left out and R2 selected to produce a fixed rate, if desired. Q3 serves as a power amplifier and switch to drive T1 (an automotive ignition coil). NE1 is used as a pulse indicator and indicates circuit operation. Because this circuit can develop up to 30 kV, suitable construction techniques and safety precautions should be observed. 🔗 External reference