High Voltage Substations Overview
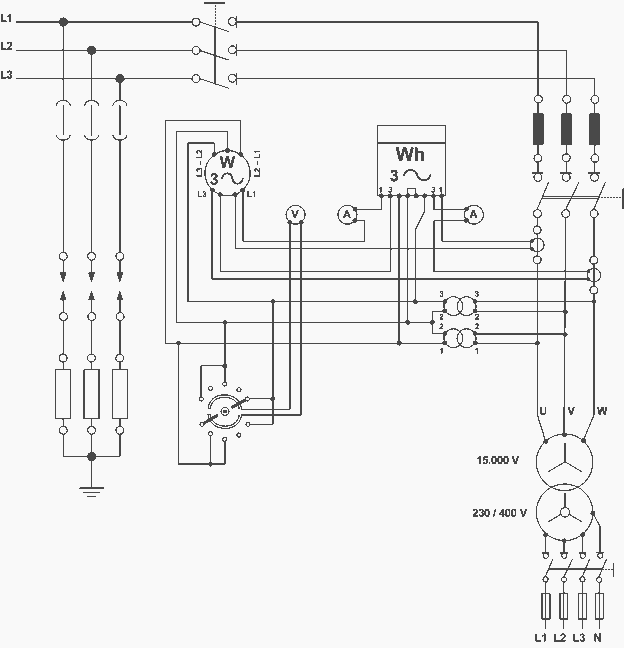
A distribution substation is defined by the apparent power of the transformer and its configuration, which can be aerial, terrestrial, or underground.
A distribution substation plays a critical role in the electrical power distribution network. It serves as a point where electrical energy is transformed from high voltage to a lower voltage suitable for distribution to end users. The apparent power of the transformer, typically measured in kilovolt-amperes (kVA), is a key specification that indicates the maximum load the transformer can handle without overheating.
The configuration of the substation can vary based on geographical and environmental considerations. Aerial substations are often mounted on poles or towers, making them easier to access for maintenance but potentially more vulnerable to weather-related damage. Terrestrial substations are located on the ground and can be integrated into existing infrastructure, providing a balance between accessibility and protection from environmental factors. Underground substations offer additional protection from external elements and can be less visually intrusive, but they may have higher installation and maintenance costs due to the complexity of underground work.
Overall, the design and configuration of a distribution substation must take into account factors such as load requirements, environmental conditions, safety regulations, and future expansion possibilities to ensure efficient and reliable power distribution.A distribution substation, is characterized by the apparent power of the transformer and whether it is aerial, terrestrial or underground 🔗 External reference
A distribution substation plays a critical role in the electrical power distribution network. It serves as a point where electrical energy is transformed from high voltage to a lower voltage suitable for distribution to end users. The apparent power of the transformer, typically measured in kilovolt-amperes (kVA), is a key specification that indicates the maximum load the transformer can handle without overheating.
The configuration of the substation can vary based on geographical and environmental considerations. Aerial substations are often mounted on poles or towers, making them easier to access for maintenance but potentially more vulnerable to weather-related damage. Terrestrial substations are located on the ground and can be integrated into existing infrastructure, providing a balance between accessibility and protection from environmental factors. Underground substations offer additional protection from external elements and can be less visually intrusive, but they may have higher installation and maintenance costs due to the complexity of underground work.
Overall, the design and configuration of a distribution substation must take into account factors such as load requirements, environmental conditions, safety regulations, and future expansion possibilities to ensure efficient and reliable power distribution.A distribution substation, is characterized by the apparent power of the transformer and whether it is aerial, terrestrial or underground 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713