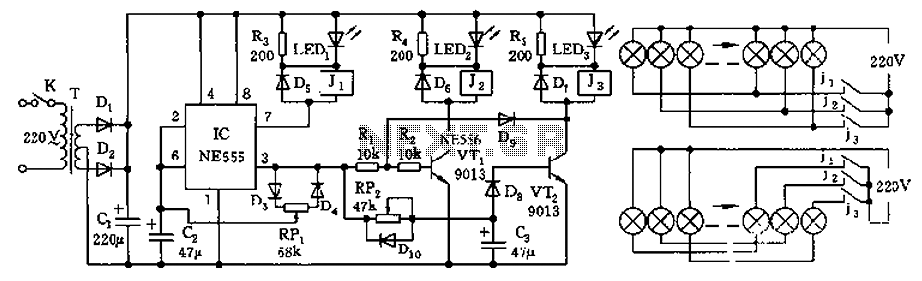
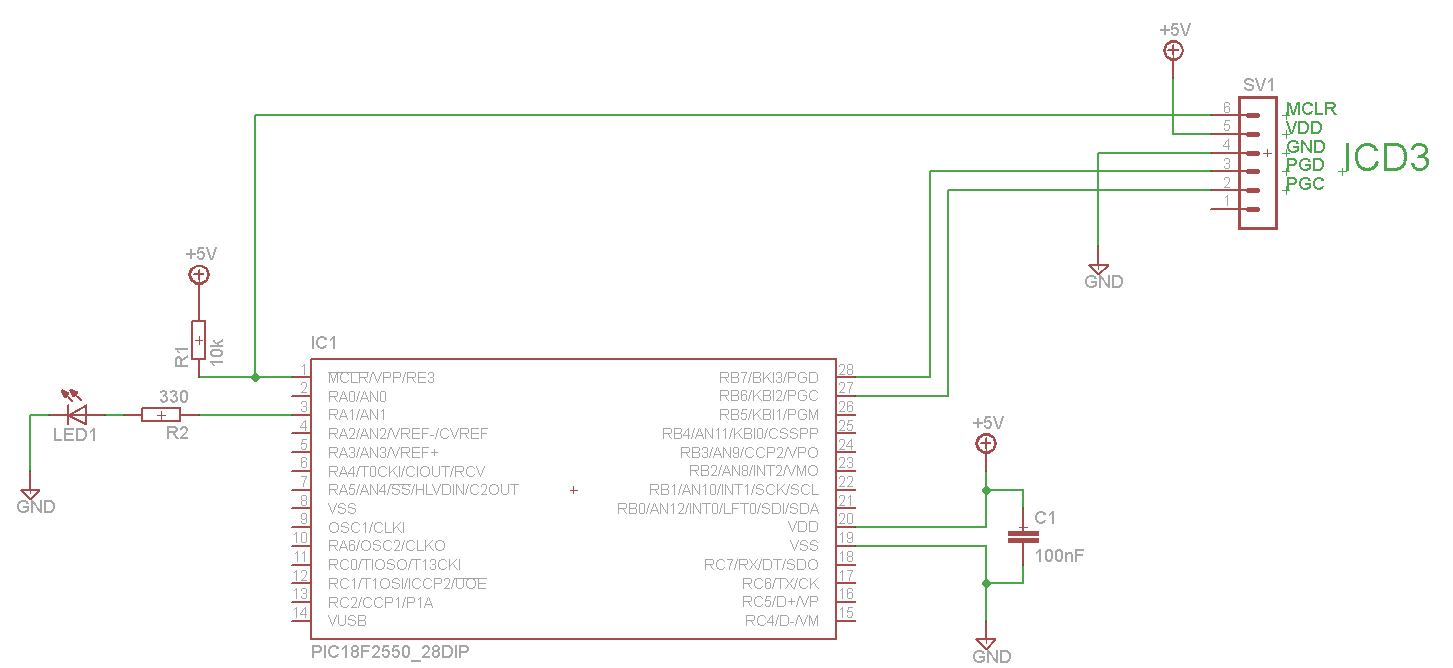
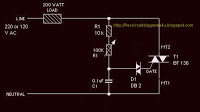
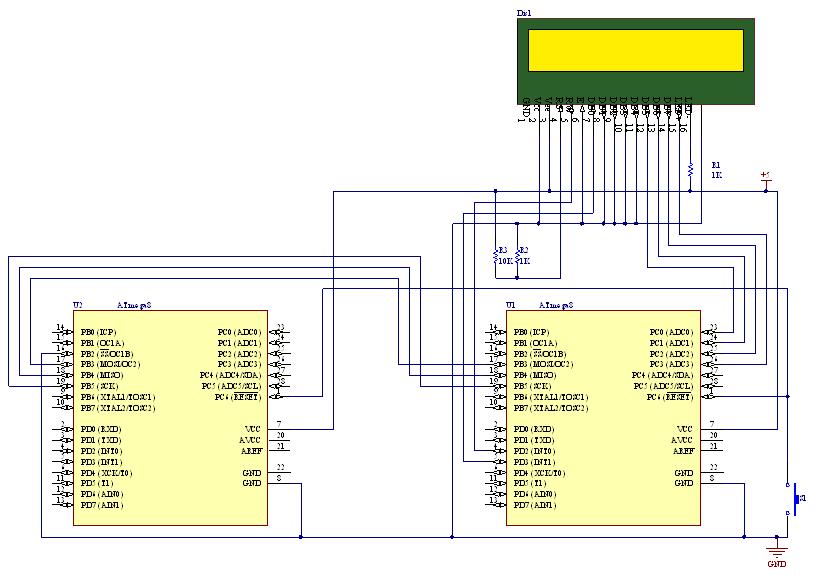
HIP6302V Microprocessor CORE Voltage Regulator Multiphase Buck PWM Controller
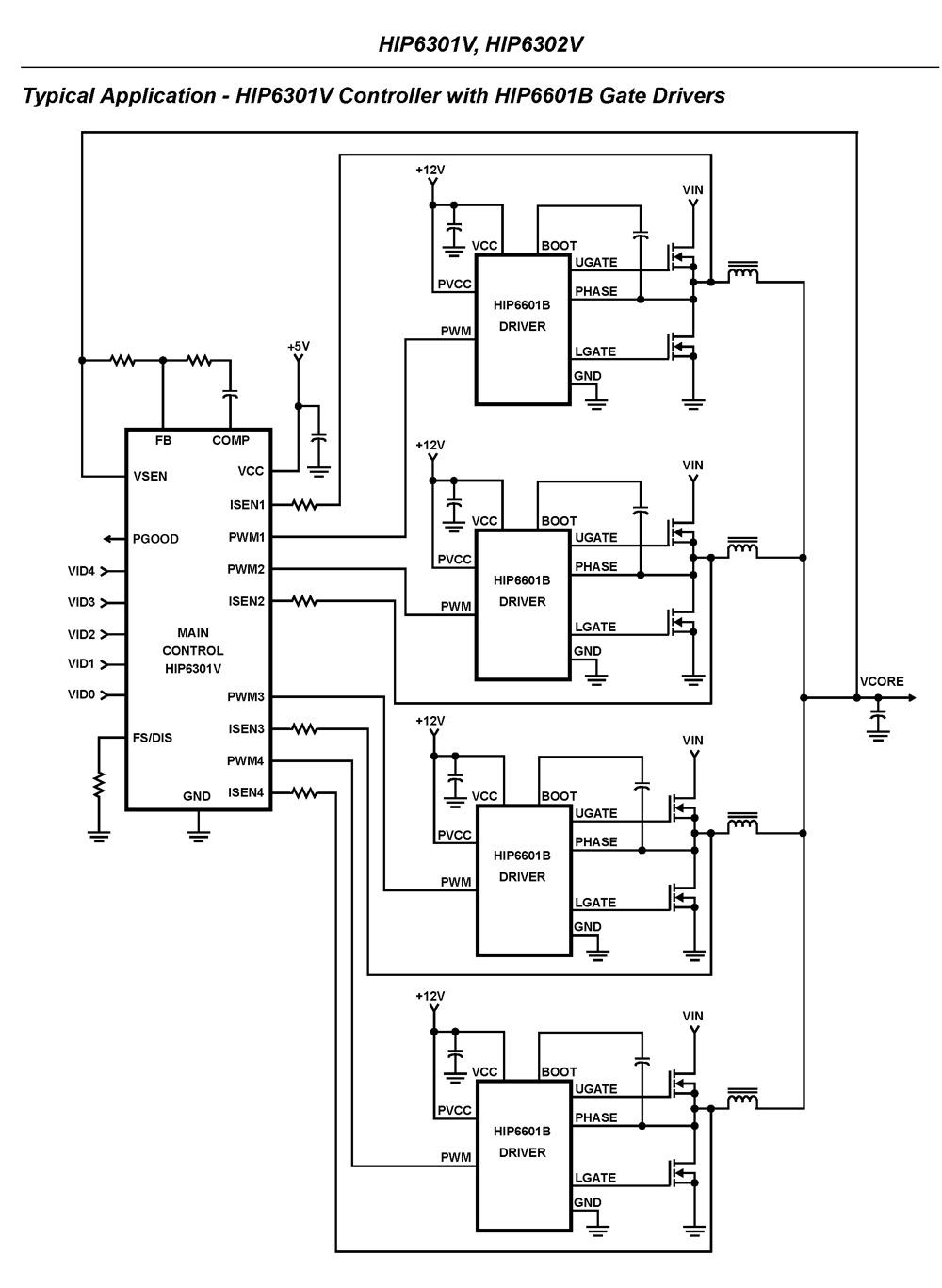
The HIP6301V and HIP6302V control the microprocessor core voltage regulation by driving up to four synchronous-rectified buck channels in parallel. The multiphase buck converter architecture employs interleaved timing to increase ripple frequency and minimize input and output ripple currents. Reduced ripple leads to fewer components, lower component costs, reduced power dissipation, and a smaller implementation area. The HIP6301V serves as a versatile controller for two to four phases, while the HIP6302V is a cost-effective, dedicated two-phase controller. Both controllers are pin-compatible replacements for their predecessors, the HIP6301 and HIP6302. They are the first controllers to utilize Dynamic VID technology, which manages output voltage and current during on-the-fly DAC changes. Dynamic VID allows the HIP6301V and HIP6302V to detect variations in the VID code and incrementally adjust the reference in 25mV steps until the new value is achieved. This gradual adjustment minimizes inrush current and associated voltage swings. Intersil provides a comprehensive range of MOSFET drivers to create highly integrated solutions for high-current, high slew-rate applications. The HIP6301V and HIP6302V regulate output voltage, balance load currents, and offer protective functions for two to four synchronous-rectified buck converter channels. These components feature an integrated high-bandwidth error amplifier for fast and precise regulation, along with a five-bit DAC for a digital interface that ensures 0.8% accuracy. A window comparator activates the PGOOD signal if the output voltage deviates from the specified range, thereby protecting the load in case of overvoltage. Current sensing is achieved by measuring the voltage across the lower MOSFETs during their conduction periods, providing essential signals for precision droop, channel-current balancing, load sharing, and over-current protection. This approach reduces costs by leveraging the parasitic on-resistance of the power devices.
The HIP6301V and HIP6302V are designed for high-efficiency voltage regulation in microprocessor applications, where maintaining a stable voltage is crucial for optimal performance. The use of synchronous rectification in the buck converter design enhances efficiency by reducing conduction losses. The interleaved operation of the multiphase architecture not only increases the effective switching frequency but also helps in distributing the load across multiple channels, which further mitigates thermal stress on individual components.
Dynamic VID technology is a significant advancement in power management, allowing for real-time adjustments to the output voltage in response to changing load conditions. This feature is particularly beneficial in modern computing environments where power demands can fluctuate rapidly. The ability to incrementally adjust the reference voltage minimizes the risk of overshoot and undershoot, ensuring that the microprocessor operates within its specified voltage range without introducing instability.
The integrated high-bandwidth error amplifier within the HIP6301V and HIP6302V ensures that the output voltage is regulated with high precision, allowing for quick response to load transients. The five-bit DAC provides fine resolution for programming the output voltage, accommodating a wide range of application requirements. The PGOOD signal serves as a vital feedback mechanism for system monitoring and control, alerting the system to any deviations from expected performance.
Current sensing capabilities are critical for implementing advanced protection features such as over-current protection and load sharing among multiple phases. By measuring the voltage across the lower MOSFETs, the controllers can accurately determine the current flowing through each channel, enabling effective load balancing. This not only enhances reliability but also contributes to overall system efficiency by preventing any single channel from being overloaded.
In summary, the HIP6301V and HIP6302V controllers represent a sophisticated solution for microprocessor voltage regulation, combining advanced features such as Dynamic VID, high-bandwidth error amplification, and integrated current sensing to deliver superior performance in modern electronic systems.The HIP6301V and HIP6302V control microprocessor core voltage regulation by driving up to four synchronous-rectified buck channels in parallel. Multiphase buck converter architecture uses interleaved timing to multiply ripple frequency and reduce input and output ripple currents.
Lower ripple results in fewer components, lower component cost, redu ced power dissipation, and smaller implementation area. The HIP6301V is a versatile two to four phase controller and the HIP6302V is a cost-saving dedicated two-phase controller. The HIP6301V and HIP6302V are exact pin compatible replacements for their predecessor parts, the HIP6301 and HIP6302.
They are the first controllers to incorporate Dynamic VID technology to manage the output voltage and current during on-the-fly DAC changes. Using Dynamic VID, the HIP6301V and HIP6302V detect changes in the VID code and gradually change the reference in 25mV increments until reaching the new value.
By gradually changing the reference setting, inrush current and the accompanying voltage swings remain negligibly small. Intersil offers a wide range of MOSFET drivers to form highly integrated solutions for high-current, high slew-rate applications.
The HIP6301V and HIP6302V regulate output voltage, balance load currents and provide protective functions for two to four synchronous-rectified buck converter channels. These parts feature an integrated high-bandwidth error amplifier for fast, precise regulation and a five-bit DAC for the digital interface to program the 0.
8% accuracy. A window comparator toggles PGOOD if the output voltage moves out of range and acts to protect the load in case of over voltage. Current sensing is accomplished by reading the voltage developed across the lower MOSFETs during their conduction intervals.
Current sensing provides the needed signals for precision droop, channel-current balancing, load sharing, and over-current protection. This saves cost by taking advantage of the power device`s parasitic on resistance. 🔗 External reference
The HIP6301V and HIP6302V are designed for high-efficiency voltage regulation in microprocessor applications, where maintaining a stable voltage is crucial for optimal performance. The use of synchronous rectification in the buck converter design enhances efficiency by reducing conduction losses. The interleaved operation of the multiphase architecture not only increases the effective switching frequency but also helps in distributing the load across multiple channels, which further mitigates thermal stress on individual components.
Dynamic VID technology is a significant advancement in power management, allowing for real-time adjustments to the output voltage in response to changing load conditions. This feature is particularly beneficial in modern computing environments where power demands can fluctuate rapidly. The ability to incrementally adjust the reference voltage minimizes the risk of overshoot and undershoot, ensuring that the microprocessor operates within its specified voltage range without introducing instability.
The integrated high-bandwidth error amplifier within the HIP6301V and HIP6302V ensures that the output voltage is regulated with high precision, allowing for quick response to load transients. The five-bit DAC provides fine resolution for programming the output voltage, accommodating a wide range of application requirements. The PGOOD signal serves as a vital feedback mechanism for system monitoring and control, alerting the system to any deviations from expected performance.
Current sensing capabilities are critical for implementing advanced protection features such as over-current protection and load sharing among multiple phases. By measuring the voltage across the lower MOSFETs, the controllers can accurately determine the current flowing through each channel, enabling effective load balancing. This not only enhances reliability but also contributes to overall system efficiency by preventing any single channel from being overloaded.
In summary, the HIP6301V and HIP6302V controllers represent a sophisticated solution for microprocessor voltage regulation, combining advanced features such as Dynamic VID, high-bandwidth error amplification, and integrated current sensing to deliver superior performance in modern electronic systems.The HIP6301V and HIP6302V control microprocessor core voltage regulation by driving up to four synchronous-rectified buck channels in parallel. Multiphase buck converter architecture uses interleaved timing to multiply ripple frequency and reduce input and output ripple currents.
Lower ripple results in fewer components, lower component cost, redu ced power dissipation, and smaller implementation area. The HIP6301V is a versatile two to four phase controller and the HIP6302V is a cost-saving dedicated two-phase controller. The HIP6301V and HIP6302V are exact pin compatible replacements for their predecessor parts, the HIP6301 and HIP6302.
They are the first controllers to incorporate Dynamic VID technology to manage the output voltage and current during on-the-fly DAC changes. Using Dynamic VID, the HIP6301V and HIP6302V detect changes in the VID code and gradually change the reference in 25mV increments until reaching the new value.
By gradually changing the reference setting, inrush current and the accompanying voltage swings remain negligibly small. Intersil offers a wide range of MOSFET drivers to form highly integrated solutions for high-current, high slew-rate applications.
The HIP6301V and HIP6302V regulate output voltage, balance load currents and provide protective functions for two to four synchronous-rectified buck converter channels. These parts feature an integrated high-bandwidth error amplifier for fast, precise regulation and a five-bit DAC for the digital interface to program the 0.
8% accuracy. A window comparator toggles PGOOD if the output voltage moves out of range and acts to protect the load in case of over voltage. Current sensing is accomplished by reading the voltage developed across the lower MOSFETs during their conduction intervals.
Current sensing provides the needed signals for precision droop, channel-current balancing, load sharing, and over-current protection. This saves cost by taking advantage of the power device`s parasitic on resistance. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713