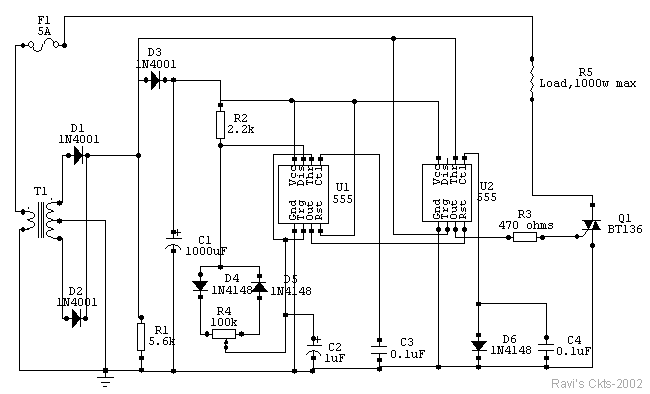
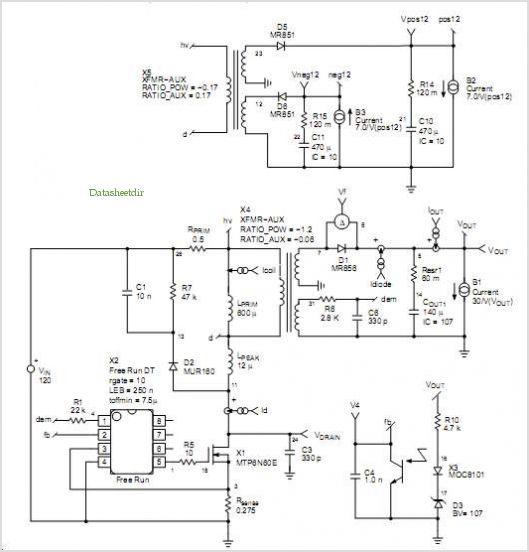
how atx power supply works
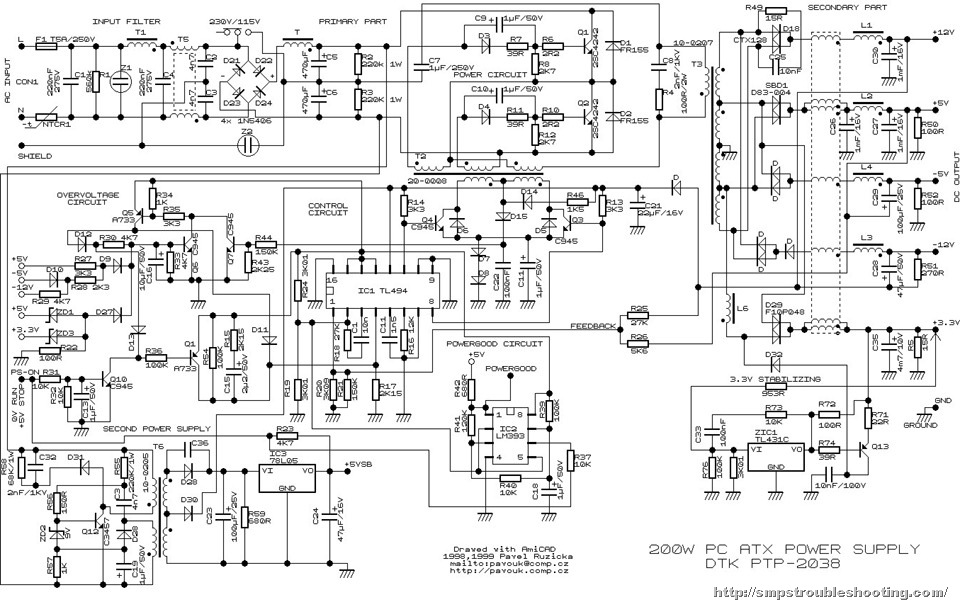
A step-by-step guide on how an ATX power supply operates, including an example of a 200 Watt PC power supply's functionality.
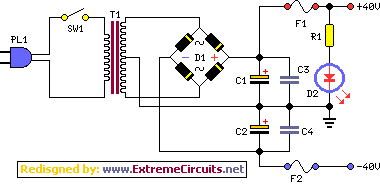
The ATX power supply is a critical component in modern computer systems, providing the necessary electrical power to various components such as the motherboard, CPU, and peripheral devices. The design of ATX power supplies adheres to specific standards set by Intel, ensuring compatibility and efficiency across different systems.
An ATX power supply typically converts alternating current (AC) from the wall outlet into direct current (DC) at various voltage levels required by computer components. The standard voltage outputs include +3.3V, +5V, +12V, and -12V, which are utilized by different parts of the computer.
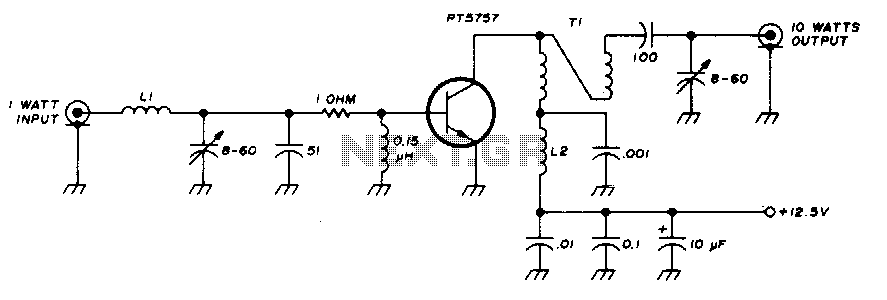
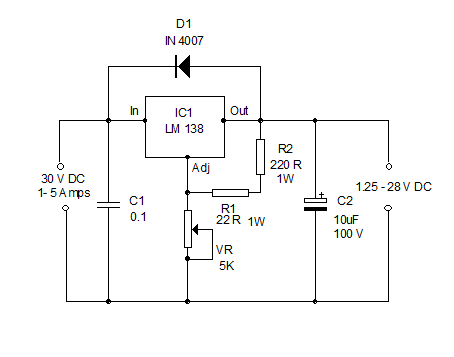
In a 200 Watt PC power supply example, the power supply unit (PSU) consists of several key components: a transformer, rectifiers, filters, and voltage regulators. The transformer steps down the AC voltage to a lower level, which is then rectified using diodes to convert it from AC to DC. After rectification, the DC output is smoothed through filtering capacitors to reduce voltage ripple. Finally, voltage regulators ensure that the output voltages remain stable and within the specified limits, even under varying load conditions.
The ATX power supply features a 24-pin connector that interfaces with the motherboard, along with additional connectors for components such as the CPU and graphics cards. The power supply also includes protective features such as over-voltage, under-voltage, and short-circuit protection to safeguard both the PSU and the connected components.
In summary, the operation of an ATX power supply involves a sequence of processes that convert and regulate electrical power, ensuring that all components of a computer receive the appropriate voltage and current for optimal performance.A step by step guide about how ATX power supply works with an example of a 200 Watt PC Power Supply function.. 🔗 External reference
The ATX power supply is a critical component in modern computer systems, providing the necessary electrical power to various components such as the motherboard, CPU, and peripheral devices. The design of ATX power supplies adheres to specific standards set by Intel, ensuring compatibility and efficiency across different systems.
An ATX power supply typically converts alternating current (AC) from the wall outlet into direct current (DC) at various voltage levels required by computer components. The standard voltage outputs include +3.3V, +5V, +12V, and -12V, which are utilized by different parts of the computer.
In a 200 Watt PC power supply example, the power supply unit (PSU) consists of several key components: a transformer, rectifiers, filters, and voltage regulators. The transformer steps down the AC voltage to a lower level, which is then rectified using diodes to convert it from AC to DC. After rectification, the DC output is smoothed through filtering capacitors to reduce voltage ripple. Finally, voltage regulators ensure that the output voltages remain stable and within the specified limits, even under varying load conditions.
The ATX power supply features a 24-pin connector that interfaces with the motherboard, along with additional connectors for components such as the CPU and graphics cards. The power supply also includes protective features such as over-voltage, under-voltage, and short-circuit protection to safeguard both the PSU and the connected components.
In summary, the operation of an ATX power supply involves a sequence of processes that convert and regulate electrical power, ensuring that all components of a computer receive the appropriate voltage and current for optimal performance.A step by step guide about how ATX power supply works with an example of a 200 Watt PC Power Supply function.. 🔗 External reference