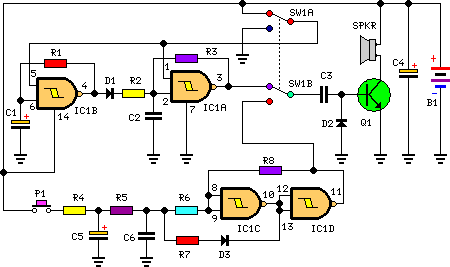
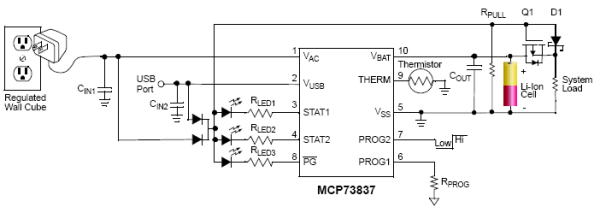
How to Design a Blood Pressure Monitor BPM Using the Flexis QE128 Family from Freescale
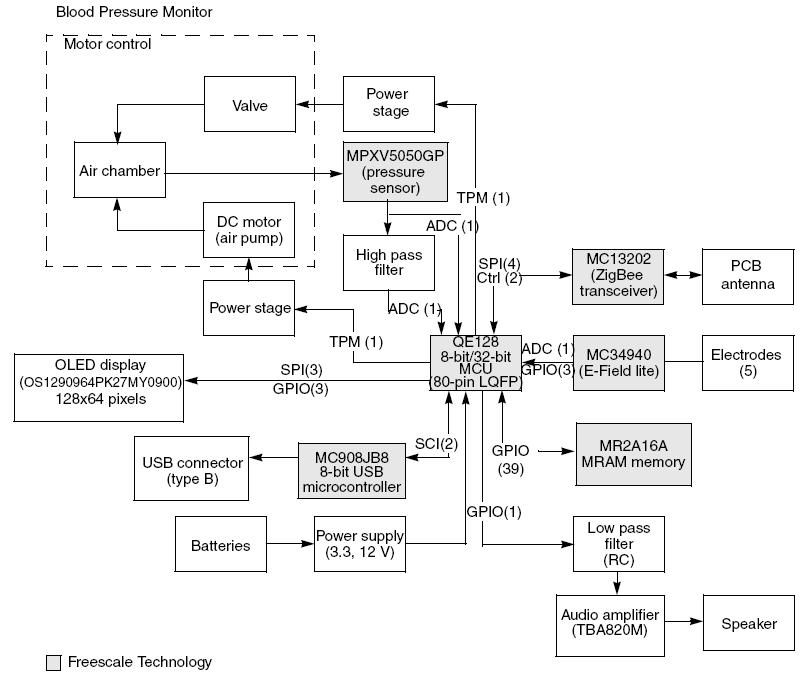
This article demonstrates the implementation of a system capable of measuring arterial blood pressure values.
The arterial blood pressure measurement system typically consists of several key components, including sensors, signal processing units, and display interfaces. The primary sensor used in such systems is a pressure transducer, which converts the mechanical pressure exerted by blood flow into an electrical signal. Common types of pressure transducers include piezoelectric and capacitive sensors, each with specific characteristics suitable for medical applications.
Once the pressure transducer captures the blood pressure data, the signal is often weak and requires amplification. An operational amplifier (op-amp) circuit can be employed for this purpose, enhancing the signal strength while maintaining accuracy. The output from the op-amp is then subjected to analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) to facilitate digital processing.
Microcontrollers or digital signal processors (DSPs) play a crucial role in interpreting the digital signal. They can implement algorithms to calculate systolic and diastolic blood pressure values based on the detected waveforms. These algorithms may also include filtering techniques to eliminate noise and improve measurement reliability.
The processed data can then be displayed on a user interface, which may consist of an LCD or LED display. Additionally, the system can be designed to log data for further analysis or transmit it wirelessly to a connected device, such as a smartphone or computer, for remote monitoring.
Power management is also an essential aspect of the design, ensuring that the system operates efficiently, especially in portable applications. Battery management circuits may be incorporated to provide adequate power supply while optimizing energy consumption.
Overall, the design and implementation of an arterial blood pressure measurement system involve a multidisciplinary approach, integrating principles from electronics, signal processing, and biomedical engineering to achieve accurate and reliable measurements.This article shows how to implement a system that can measure arterial blood pressure values 🔗 External reference
The arterial blood pressure measurement system typically consists of several key components, including sensors, signal processing units, and display interfaces. The primary sensor used in such systems is a pressure transducer, which converts the mechanical pressure exerted by blood flow into an electrical signal. Common types of pressure transducers include piezoelectric and capacitive sensors, each with specific characteristics suitable for medical applications.
Once the pressure transducer captures the blood pressure data, the signal is often weak and requires amplification. An operational amplifier (op-amp) circuit can be employed for this purpose, enhancing the signal strength while maintaining accuracy. The output from the op-amp is then subjected to analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) to facilitate digital processing.
Microcontrollers or digital signal processors (DSPs) play a crucial role in interpreting the digital signal. They can implement algorithms to calculate systolic and diastolic blood pressure values based on the detected waveforms. These algorithms may also include filtering techniques to eliminate noise and improve measurement reliability.
The processed data can then be displayed on a user interface, which may consist of an LCD or LED display. Additionally, the system can be designed to log data for further analysis or transmit it wirelessly to a connected device, such as a smartphone or computer, for remote monitoring.
Power management is also an essential aspect of the design, ensuring that the system operates efficiently, especially in portable applications. Battery management circuits may be incorporated to provide adequate power supply while optimizing energy consumption.
Overall, the design and implementation of an arterial blood pressure measurement system involve a multidisciplinary approach, integrating principles from electronics, signal processing, and biomedical engineering to achieve accurate and reliable measurements.This article shows how to implement a system that can measure arterial blood pressure values 🔗 External reference