Humidity Tester Circuit Using Sensor
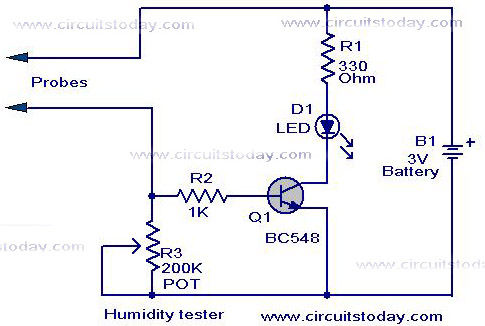
A simple humidity tester circuit using only an LED, a transistor, and a few resistors is explained with a clear circuit schematic.
The humidity tester circuit is designed to provide a visual indication of humidity levels using basic electronic components. The core components include a light-emitting diode (LED), a transistor, and several resistors, which together form a straightforward yet effective humidity sensing mechanism.
In this circuit, the LED serves as an output indicator, illuminating when humidity levels exceed a predetermined threshold. The transistor functions as a switch, controlling the LED based on the input signal derived from a humidity-sensitive element, such as a hygrometer or a humidity sensor. The resistors are used to set appropriate biasing levels for the transistor and to limit the current flowing through the LED to prevent damage.
The schematic layout typically depicts the humidity sensor connected to the base of the transistor. When the sensor detects increased humidity, it generates a voltage signal that turns the transistor on, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter. This action activates the LED, providing a visual cue of the humidity status. Resistors in the circuit assist in stabilizing the transistor's operation and ensuring that the LED operates within safe limits.
The simplicity of this circuit makes it suitable for educational purposes, as well as for practical applications in environments where humidity monitoring is essential, such as greenhouses, storage facilities, or laboratories. The design can be easily modified or expanded to include additional features, such as an adjustable threshold or an audible alarm, by incorporating more components while maintaining the fundamental principles of operation.A simple humidity tester circuit using just a LED, transistor, and a few resistors is explaind with a neat circuit schematic.. 🔗 External reference
The humidity tester circuit is designed to provide a visual indication of humidity levels using basic electronic components. The core components include a light-emitting diode (LED), a transistor, and several resistors, which together form a straightforward yet effective humidity sensing mechanism.
In this circuit, the LED serves as an output indicator, illuminating when humidity levels exceed a predetermined threshold. The transistor functions as a switch, controlling the LED based on the input signal derived from a humidity-sensitive element, such as a hygrometer or a humidity sensor. The resistors are used to set appropriate biasing levels for the transistor and to limit the current flowing through the LED to prevent damage.
The schematic layout typically depicts the humidity sensor connected to the base of the transistor. When the sensor detects increased humidity, it generates a voltage signal that turns the transistor on, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter. This action activates the LED, providing a visual cue of the humidity status. Resistors in the circuit assist in stabilizing the transistor's operation and ensuring that the LED operates within safe limits.
The simplicity of this circuit makes it suitable for educational purposes, as well as for practical applications in environments where humidity monitoring is essential, such as greenhouses, storage facilities, or laboratories. The design can be easily modified or expanded to include additional features, such as an adjustable threshold or an audible alarm, by incorporating more components while maintaining the fundamental principles of operation.A simple humidity tester circuit using just a LED, transistor, and a few resistors is explaind with a neat circuit schematic.. 🔗 External reference