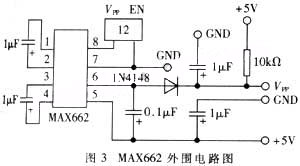
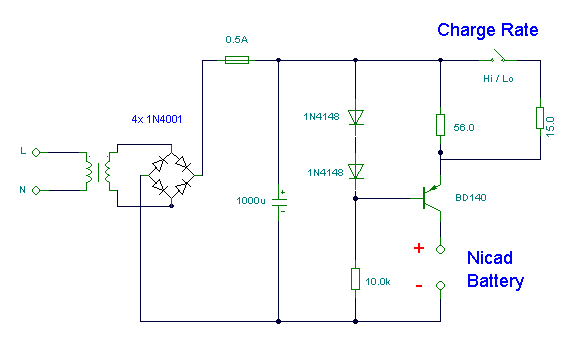
IBM ThinkPad T40 Power Control Circuit With MAX1631 IC
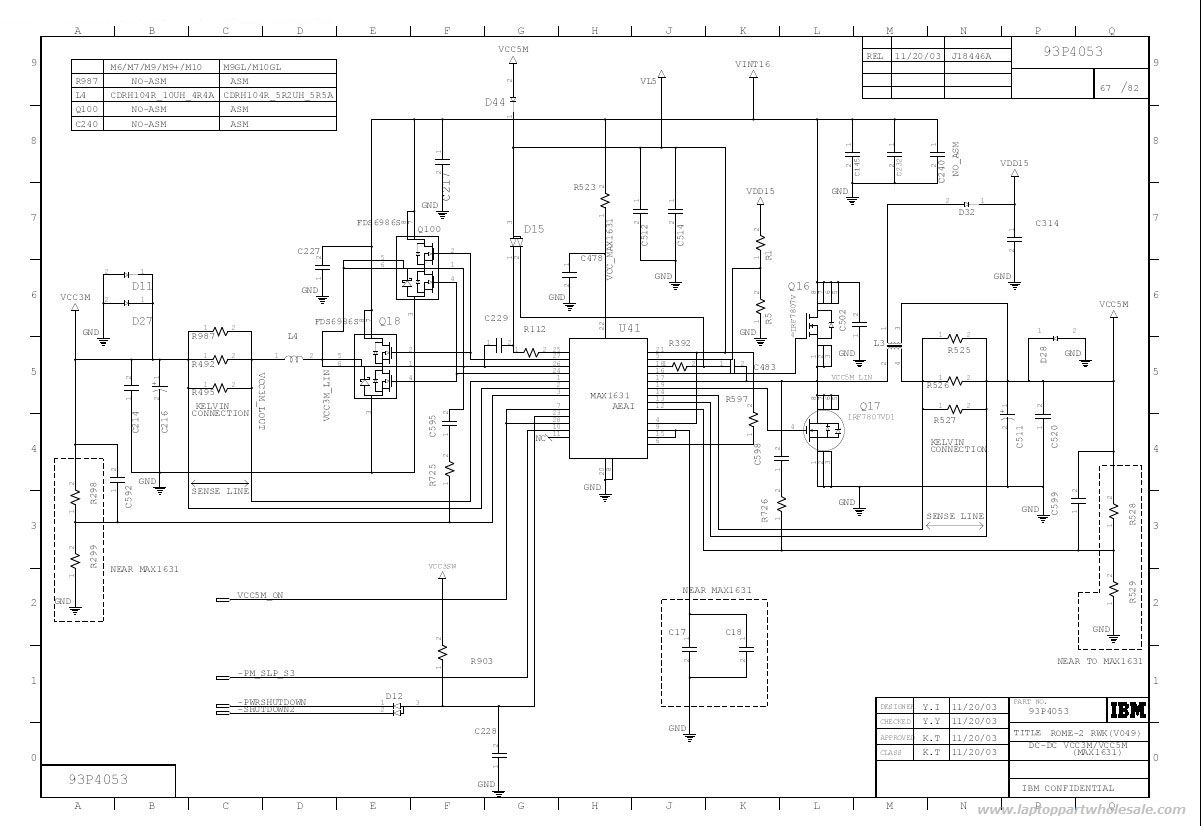
This is an IBM ThinkPad T40 power control circuit. This circuit is based on the MAX1631 IC, which is a multi-output, low-noise power supply.
The IBM ThinkPad T40 power control circuit utilizes the MAX1631 integrated circuit (IC) to provide stable and efficient power management for the laptop. The MAX1631 is designed to deliver multiple output voltages, which are essential for powering various components within the laptop, such as the CPU, memory, and peripheral devices.
The circuit typically includes several key components: the MAX1631 IC itself, input and output capacitors, resistors for voltage setting, and possibly inductors for filtering purposes. The IC operates by receiving a single input voltage, which it regulates down to the required output levels. It features low quiescent current, making it suitable for battery-operated devices where power efficiency is critical.
In this application, the MAX1631 can be configured to provide multiple output voltages, which may include 5V, 3.3V, and 1.8V, depending on the specific needs of the components being powered. The outputs are typically designed with low dropout characteristics, ensuring that the voltages remain stable even under varying load conditions.
To implement this circuit, careful attention must be paid to the layout to minimize noise and ensure proper thermal management. The use of bypass capacitors close to the IC pins is crucial for filtering high-frequency noise, while larger output capacitors can help maintain voltage stability during transient loads.
Overall, the MAX1631-based power control circuit in the IBM ThinkPad T40 is a critical component that ensures reliable operation and performance of the laptop by providing the necessary power with low noise and high efficiency.This is a IBM ThinkPad T40 Power control circuit. This circuit based on the MAX1631 IC. MAX1631 IC is a Multi-Output, Low-Noise Power-Supply .. 🔗 External reference
The IBM ThinkPad T40 power control circuit utilizes the MAX1631 integrated circuit (IC) to provide stable and efficient power management for the laptop. The MAX1631 is designed to deliver multiple output voltages, which are essential for powering various components within the laptop, such as the CPU, memory, and peripheral devices.
The circuit typically includes several key components: the MAX1631 IC itself, input and output capacitors, resistors for voltage setting, and possibly inductors for filtering purposes. The IC operates by receiving a single input voltage, which it regulates down to the required output levels. It features low quiescent current, making it suitable for battery-operated devices where power efficiency is critical.
In this application, the MAX1631 can be configured to provide multiple output voltages, which may include 5V, 3.3V, and 1.8V, depending on the specific needs of the components being powered. The outputs are typically designed with low dropout characteristics, ensuring that the voltages remain stable even under varying load conditions.
To implement this circuit, careful attention must be paid to the layout to minimize noise and ensure proper thermal management. The use of bypass capacitors close to the IC pins is crucial for filtering high-frequency noise, while larger output capacitors can help maintain voltage stability during transient loads.
Overall, the MAX1631-based power control circuit in the IBM ThinkPad T40 is a critical component that ensures reliable operation and performance of the laptop by providing the necessary power with low noise and high efficiency.This is a IBM ThinkPad T40 Power control circuit. This circuit based on the MAX1631 IC. MAX1631 IC is a Multi-Output, Low-Noise Power-Supply .. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713