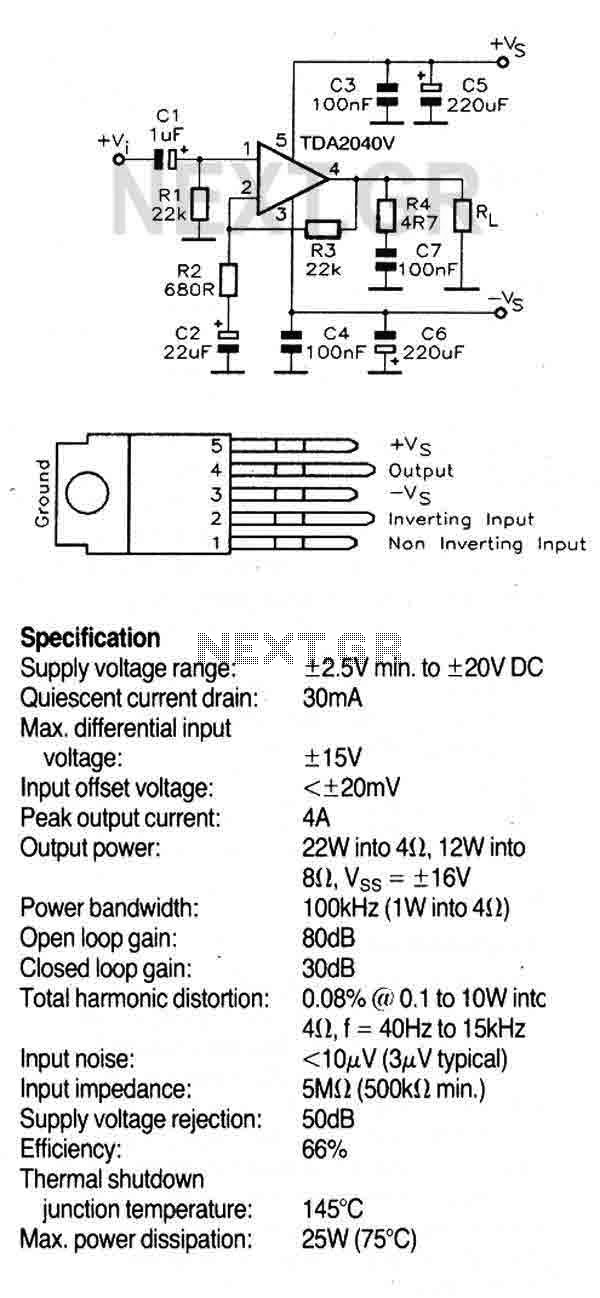
Opamp Based Power Amplifier
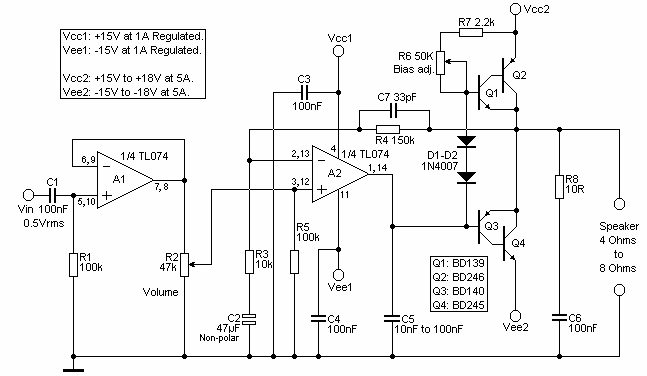
The amplifier is based on the commonly used class-AB complementary power amplifier with compound pair output transistors. The system uses a TL074 quad opamp to drive the output transistors. As can be seen from figure 1, A2 is used to set the voltage gain of the amplifier. Assuming the voltage gain of a common collector stage to be unity, the overall voltage gain of the amplifier is equal to (R4 / R3) + 1, i.e. the gain of a non-inverting OP-AMP (16 or 24dB, in this case).
The class-AB amplifier configuration is a widely adopted design due to its efficiency and linearity, which makes it suitable for audio applications. It operates by using two or more output devices that function in complement to each other. The compound pair output transistors, also known as Sziklai pairs, offer benefits such as improved linearity and higher input impedance, which are critical for achieving the desired audio quality.
The TL074 quad opamp, a Low-Noise JFET-Input Operational Amplifier, plays a crucial role in this system. It is responsible for driving the output transistors, which in turn helps to amplify the input signal. This opamp is characterized by its high slew rate and low input bias and offset currents, making it a suitable choice for high fidelity and audio applications.
The voltage gain of the amplifier is determined by the opamp A2. The equation for the overall voltage gain of the amplifier is (R4 / R3) + 1, which is the standard gain equation for a non-inverting operational amplifier. In this particular case, the gain is either 16 or 24dB, which is a substantial amplification factor.
The schematic also implies that the voltage gain of a common collector stage is assumed to be unity. This is a reasonable assumption as a common collector, or emitter follower, is typically used for impedance matching and does not provide voltage gain. The unity gain of the common collector stage, therefore, does not contribute to the overall amplification of the circuit.
In conclusion, this amplifier circuit combines the efficiency of a class-AB amplifier, the high input impedance of the compound pair output transistors, and the high slew rate of the TL074 quad opamp to achieve a substantial voltage gain of either 16 or 24dB.The amplifier is based on the commonly used class-AB complementary power amplifier with compound pair output transistors. The system uses a TL074 quad opamp to drive the output transistors. As can be seen from figure 1, A2 is used to set the voltage gain of the amplifier. Assuming the voltage gain of a common collector stage to be unity, the overall voltage gain of the amplifier is equal to (R4 / R3) + 1, i.e.
the gain of a non-inverting OP-AMP (16 or 24dB, in this case). 🔗 External reference
The class-AB amplifier configuration is a widely adopted design due to its efficiency and linearity, which makes it suitable for audio applications. It operates by using two or more output devices that function in complement to each other. The compound pair output transistors, also known as Sziklai pairs, offer benefits such as improved linearity and higher input impedance, which are critical for achieving the desired audio quality.
The TL074 quad opamp, a Low-Noise JFET-Input Operational Amplifier, plays a crucial role in this system. It is responsible for driving the output transistors, which in turn helps to amplify the input signal. This opamp is characterized by its high slew rate and low input bias and offset currents, making it a suitable choice for high fidelity and audio applications.
The voltage gain of the amplifier is determined by the opamp A2. The equation for the overall voltage gain of the amplifier is (R4 / R3) + 1, which is the standard gain equation for a non-inverting operational amplifier. In this particular case, the gain is either 16 or 24dB, which is a substantial amplification factor.
The schematic also implies that the voltage gain of a common collector stage is assumed to be unity. This is a reasonable assumption as a common collector, or emitter follower, is typically used for impedance matching and does not provide voltage gain. The unity gain of the common collector stage, therefore, does not contribute to the overall amplification of the circuit.
In conclusion, this amplifier circuit combines the efficiency of a class-AB amplifier, the high input impedance of the compound pair output transistors, and the high slew rate of the TL074 quad opamp to achieve a substantial voltage gain of either 16 or 24dB.The amplifier is based on the commonly used class-AB complementary power amplifier with compound pair output transistors. The system uses a TL074 quad opamp to drive the output transistors. As can be seen from figure 1, A2 is used to set the voltage gain of the amplifier. Assuming the voltage gain of a common collector stage to be unity, the overall voltage gain of the amplifier is equal to (R4 / R3) + 1, i.e.
the gain of a non-inverting OP-AMP (16 or 24dB, in this case). 🔗 External reference