IC rprecision waveform generator with sweep and frequency modulation
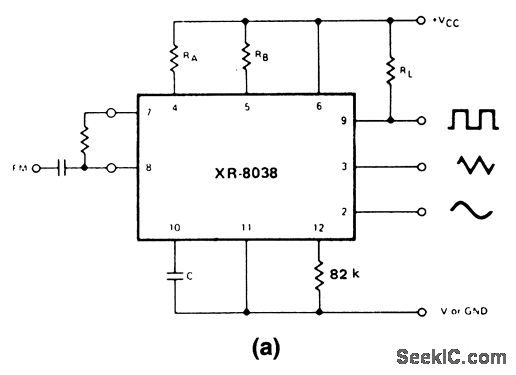
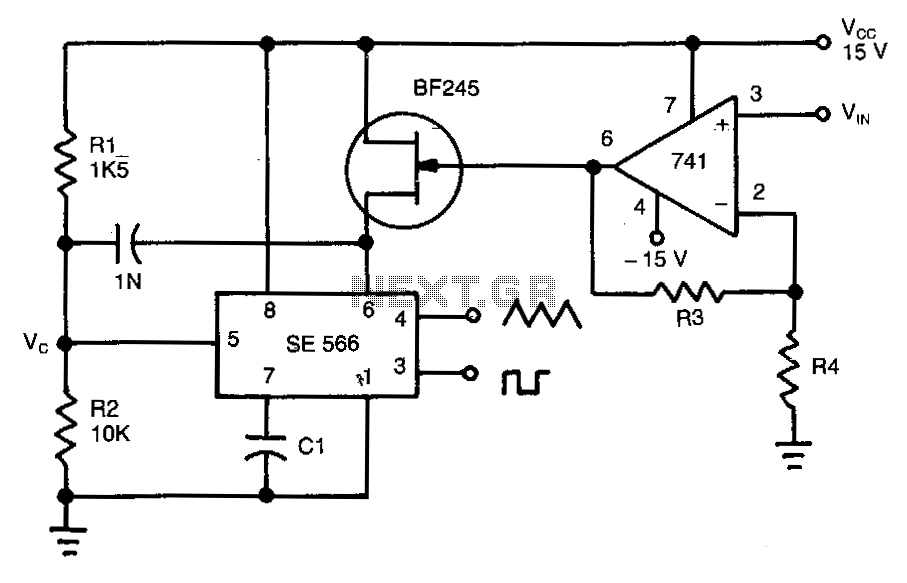
These circuits are similar to that of Fig. 5-47, except that they provide for FM or sweep modulation. Circuit 5-50A is used for FM with small deviations, approximately ±10%. Circuit 5-50B is designed for a sweep range of 1000:1. As a guideline, the sweep frequency approaches 0 Hz when the voltage at pin 8 equals VCC and reaches its maximum at the lower pin-8 voltage limit of VCC - (1/3 VSUPPLY - 2). Waveform symmetry variations can be minimized by adding a 10-MΩ resistor between pins 5 and 11.
The described circuits are designed to facilitate frequency modulation (FM) and sweep modulation, providing flexibility in signal generation for various applications. Circuit 5-50A is specifically tailored for FM applications, allowing for slight frequency deviations, typically around ±10%. This circuit is suitable for applications where maintaining a stable carrier frequency with minor fluctuations is essential, such as in communication systems where signal integrity is crucial.
Circuit 5-50B offers a more extensive sweep range of 1000:1, making it ideal for applications that require a broad frequency range modulation. The modulation characteristics are influenced by the voltage applied to pin 8, where a higher voltage (equal to VCC) results in a sweep frequency that approaches 0 Hz. Conversely, as the voltage at pin 8 decreases to the limit defined by VCC - (1/3 VSUPPLY - 2), the sweep frequency reaches its maximum value. This relationship allows for precise control over the modulation frequency, enabling the user to tailor the circuit's performance to specific requirements.
To enhance waveform symmetry and minimize distortions, it is recommended to incorporate a 10-MΩ resistor between pins 5 and 11. This addition helps balance the circuit's output, ensuring that the generated waveforms maintain a consistent shape and amplitude, which is particularly important in high-fidelity applications. The integration of this resistor can significantly improve the overall performance of the circuit, making it a valuable modification for users seeking optimal results in their FM or sweep modulation needs.These circuits are similar to that of Fig. 5-47, except that the circuits provide for FM or sweep modulation. Use circuit 5-50A for FM (small deviations, about ±10%). Use circuit 5-50B for a sweep range of 1000:1. As a guideline, the sweep frequency approaches 0 Hz when the voltage at pin 8 equals VCC, and reaches maximum at the lower pin-8 voltag e limit of VCC - (1/3 VSUPPLY -2). Waveform symmetry variations can be minimized when a 10-M resistor is added between pins 5 and 11. 🔗 External reference
The described circuits are designed to facilitate frequency modulation (FM) and sweep modulation, providing flexibility in signal generation for various applications. Circuit 5-50A is specifically tailored for FM applications, allowing for slight frequency deviations, typically around ±10%. This circuit is suitable for applications where maintaining a stable carrier frequency with minor fluctuations is essential, such as in communication systems where signal integrity is crucial.
Circuit 5-50B offers a more extensive sweep range of 1000:1, making it ideal for applications that require a broad frequency range modulation. The modulation characteristics are influenced by the voltage applied to pin 8, where a higher voltage (equal to VCC) results in a sweep frequency that approaches 0 Hz. Conversely, as the voltage at pin 8 decreases to the limit defined by VCC - (1/3 VSUPPLY - 2), the sweep frequency reaches its maximum value. This relationship allows for precise control over the modulation frequency, enabling the user to tailor the circuit's performance to specific requirements.
To enhance waveform symmetry and minimize distortions, it is recommended to incorporate a 10-MΩ resistor between pins 5 and 11. This addition helps balance the circuit's output, ensuring that the generated waveforms maintain a consistent shape and amplitude, which is particularly important in high-fidelity applications. The integration of this resistor can significantly improve the overall performance of the circuit, making it a valuable modification for users seeking optimal results in their FM or sweep modulation needs.These circuits are similar to that of Fig. 5-47, except that the circuits provide for FM or sweep modulation. Use circuit 5-50A for FM (small deviations, about ±10%). Use circuit 5-50B for a sweep range of 1000:1. As a guideline, the sweep frequency approaches 0 Hz when the voltage at pin 8 equals VCC, and reaches maximum at the lower pin-8 voltag e limit of VCC - (1/3 VSUPPLY -2). Waveform symmetry variations can be minimized when a 10-M resistor is added between pins 5 and 11. 🔗 External reference