IC Voltage Regulators-withCircuit - Design & Theory
IC Voltage Regulators - Circuit diagram and block diagram of linear, fixed, adjustable (positive and negative), and switching voltage regulators.
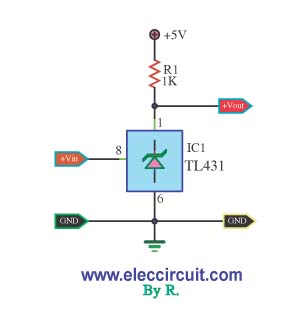
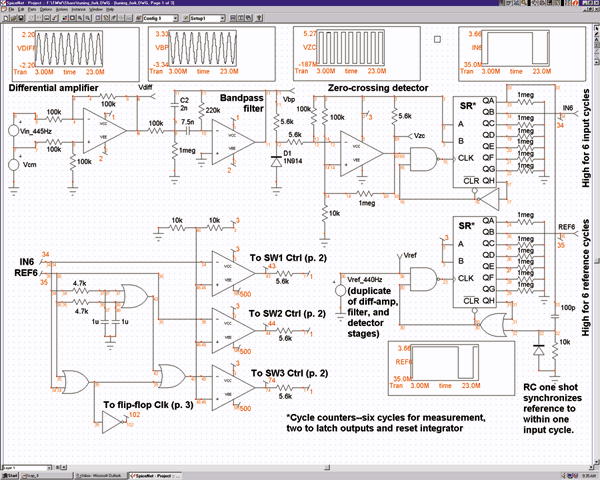
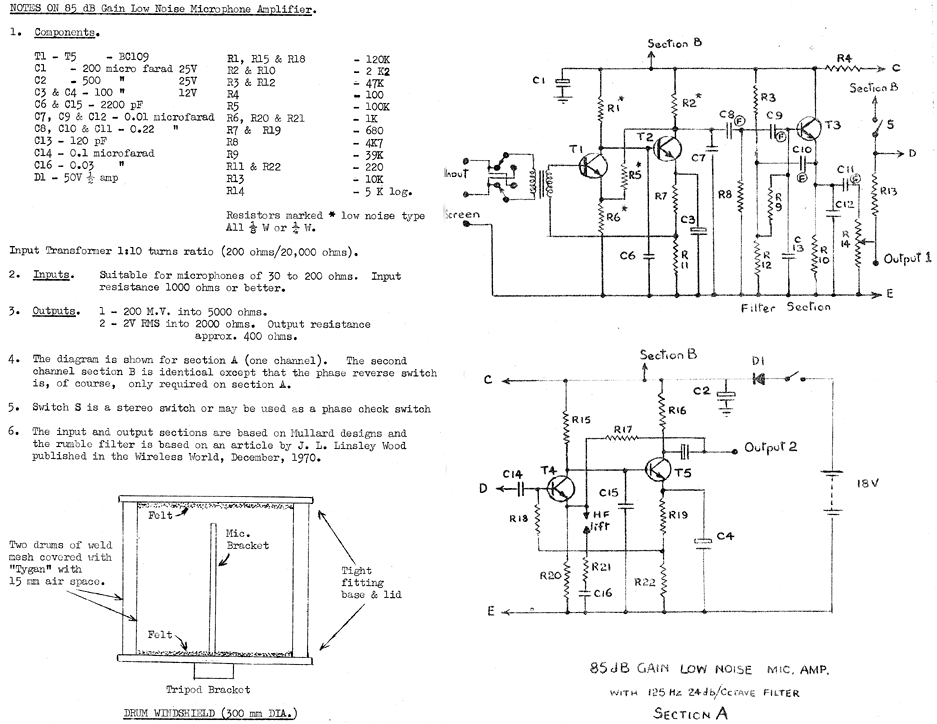
IC voltage regulators are essential components in electronic circuits, providing stable output voltages from a varying input voltage source. They can be categorized into several types, including linear regulators, fixed regulators, adjustable regulators, and switching regulators.
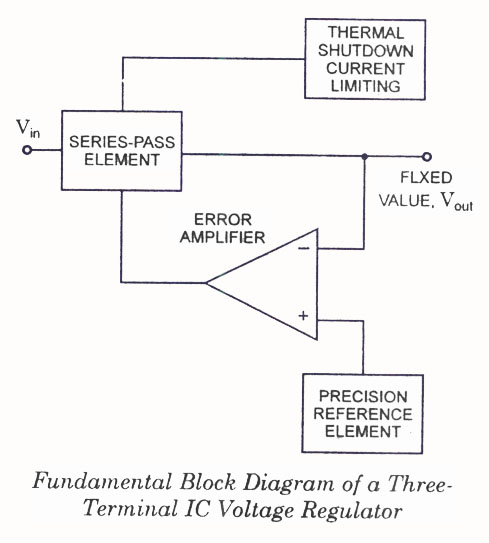
Linear voltage regulators maintain a constant output voltage by using a feedback mechanism to adjust the resistance within the circuit. The block diagram typically illustrates the input voltage, the regulator, and the output voltage, along with feedback paths. Fixed voltage regulators provide a predetermined output voltage, while adjustable voltage regulators allow for output voltage customization through external resistors.
Switching voltage regulators, on the other hand, utilize a different principle. They convert the input voltage to a high-frequency square wave and then use inductors, capacitors, and diodes to filter and smooth the output. This method is more efficient than linear regulation, especially for applications requiring significant power conversion.
The circuit diagrams for these regulators vary based on their design and application. For linear regulators, the schematic often includes a pass transistor, input and output capacitors, and a feedback network. Fixed regulators feature a simpler design, while adjustable regulators incorporate additional components for voltage setting. Switching regulators are more complex, showcasing components like inductors, diodes, and control ICs.
Understanding the differences and applications of these voltage regulators is crucial for designing reliable and efficient electronic systems. Each type serves specific needs, whether it be low dropout voltage in linear regulators or high efficiency in switching regulators, making them indispensable in modern electronics.IC Voltage Regulators -Circuit diagram & Block diagram of Linear,Fixed, Adjustable (positive & negative) & Switching voltage regulators.. 🔗 External reference
IC voltage regulators are essential components in electronic circuits, providing stable output voltages from a varying input voltage source. They can be categorized into several types, including linear regulators, fixed regulators, adjustable regulators, and switching regulators.
Linear voltage regulators maintain a constant output voltage by using a feedback mechanism to adjust the resistance within the circuit. The block diagram typically illustrates the input voltage, the regulator, and the output voltage, along with feedback paths. Fixed voltage regulators provide a predetermined output voltage, while adjustable voltage regulators allow for output voltage customization through external resistors.
Switching voltage regulators, on the other hand, utilize a different principle. They convert the input voltage to a high-frequency square wave and then use inductors, capacitors, and diodes to filter and smooth the output. This method is more efficient than linear regulation, especially for applications requiring significant power conversion.
The circuit diagrams for these regulators vary based on their design and application. For linear regulators, the schematic often includes a pass transistor, input and output capacitors, and a feedback network. Fixed regulators feature a simpler design, while adjustable regulators incorporate additional components for voltage setting. Switching regulators are more complex, showcasing components like inductors, diodes, and control ICs.
Understanding the differences and applications of these voltage regulators is crucial for designing reliable and efficient electronic systems. Each type serves specific needs, whether it be low dropout voltage in linear regulators or high efficiency in switching regulators, making them indispensable in modern electronics.IC Voltage Regulators -Circuit diagram & Block diagram of Linear,Fixed, Adjustable (positive & negative) & Switching voltage regulators.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713