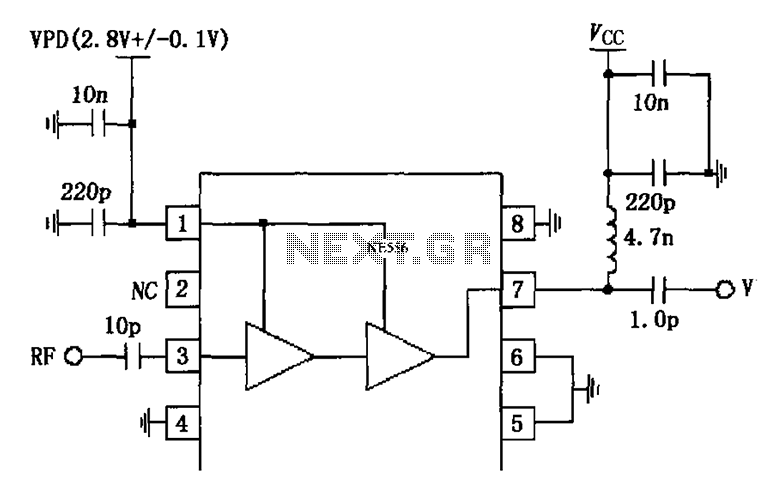
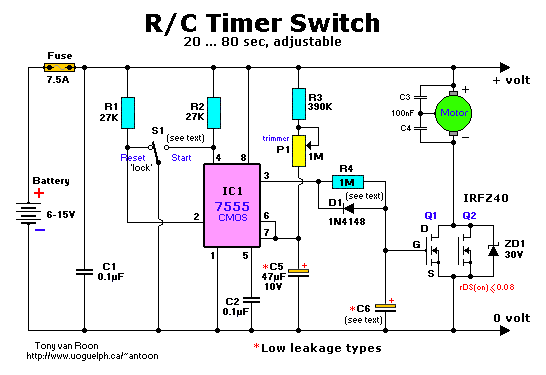
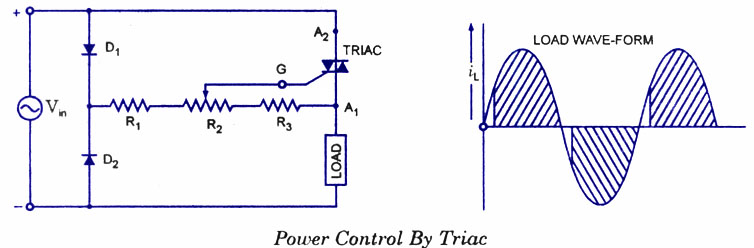
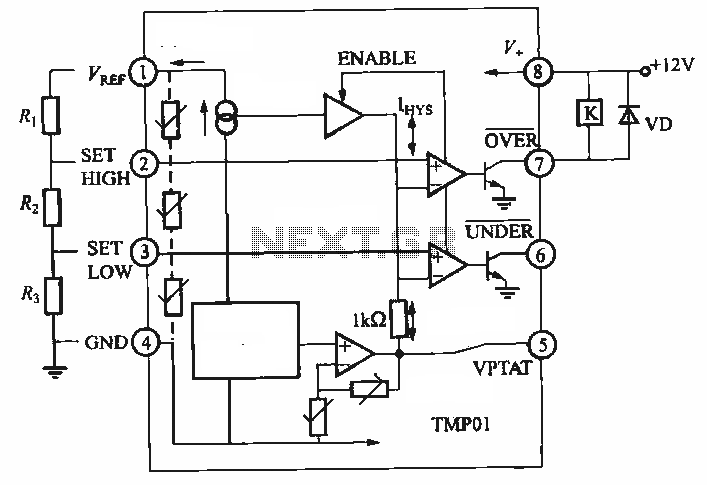
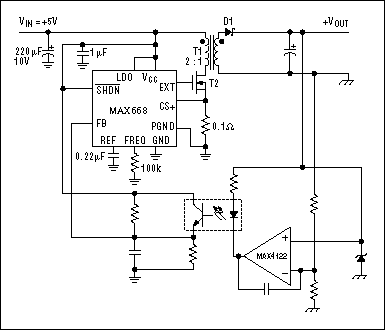
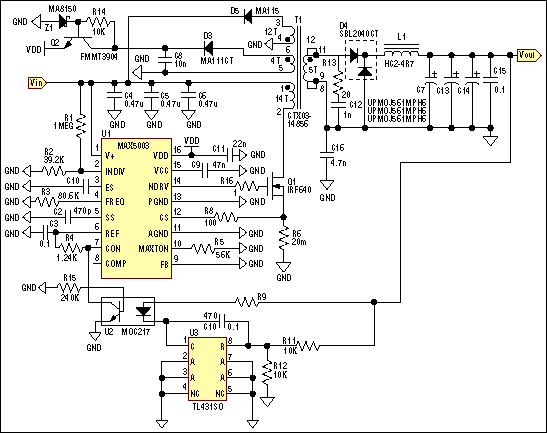
IEEE 802.3af-Compliant Single-Port Power-Sourcing-Equipment Application
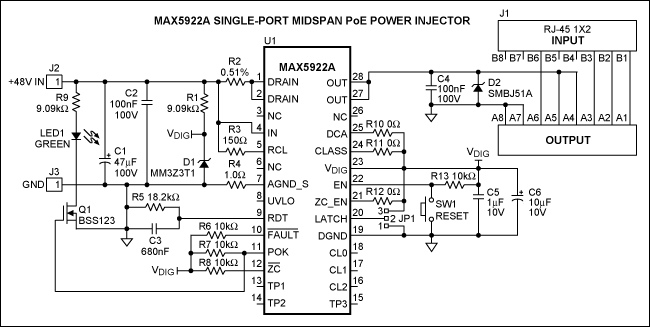
The IEEE 802.3af standard defines the interaction between power-sourcing equipment and powered devices within a power-over-Ethernet system.
The IEEE 802.3af standard, also known as Power over Ethernet (PoE), specifies the mechanisms by which electrical power is transmitted alongside data over standard Ethernet cabling. This standard allows for the delivery of power to devices such as IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points without the need for additional power supplies or outlets.
In a typical PoE system, two main components are involved: the power-sourcing equipment (PSE) and the powered device (PD). The PSE is responsible for supplying power, while the PD receives and utilizes that power. The standard outlines specific voltage levels, typically 44 to 57 volts DC, and a maximum power output of 15.4 watts per port for compliant devices.
The IEEE 802.3af standard employs a detection mechanism to ensure compatibility between the PSE and PD. When a PD is connected to a PSE, the PSE sends a low voltage signal to detect the presence of a compatible device. If a valid PD is detected, the PSE initiates power delivery. This detection process is crucial to prevent damage to non-PoE devices.
Furthermore, the standard includes specifications for power classification, allowing PSEs to identify the power requirements of connected devices. This classification enables dynamic power management, ensuring that the total power supplied does not exceed the capacity of the PSE.
Overall, the IEEE 802.3af standard plays a vital role in simplifying network infrastructure by enabling the integration of power and data transmission, enhancing the versatility and efficiency of network deployments.The IEEE 802.3af standard governs how the power-sourcing-equipment and power device interact with each other in a power-over-ethernet system.. 🔗 External reference
The IEEE 802.3af standard, also known as Power over Ethernet (PoE), specifies the mechanisms by which electrical power is transmitted alongside data over standard Ethernet cabling. This standard allows for the delivery of power to devices such as IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points without the need for additional power supplies or outlets.
In a typical PoE system, two main components are involved: the power-sourcing equipment (PSE) and the powered device (PD). The PSE is responsible for supplying power, while the PD receives and utilizes that power. The standard outlines specific voltage levels, typically 44 to 57 volts DC, and a maximum power output of 15.4 watts per port for compliant devices.
The IEEE 802.3af standard employs a detection mechanism to ensure compatibility between the PSE and PD. When a PD is connected to a PSE, the PSE sends a low voltage signal to detect the presence of a compatible device. If a valid PD is detected, the PSE initiates power delivery. This detection process is crucial to prevent damage to non-PoE devices.
Furthermore, the standard includes specifications for power classification, allowing PSEs to identify the power requirements of connected devices. This classification enables dynamic power management, ensuring that the total power supplied does not exceed the capacity of the PSE.
Overall, the IEEE 802.3af standard plays a vital role in simplifying network infrastructure by enabling the integration of power and data transmission, enhancing the versatility and efficiency of network deployments.The IEEE 802.3af standard governs how the power-sourcing-equipment and power device interact with each other in a power-over-ethernet system.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713