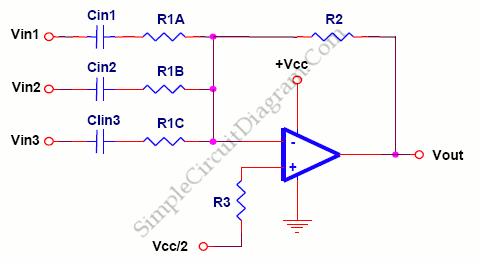
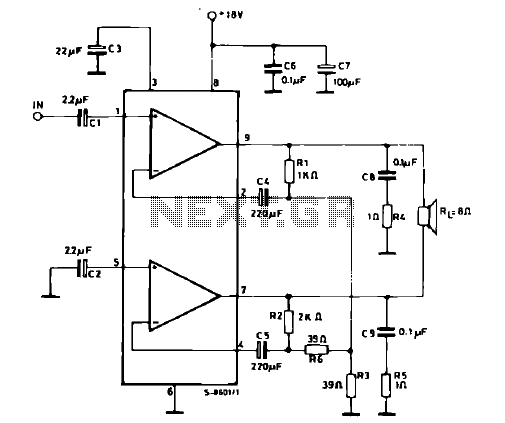
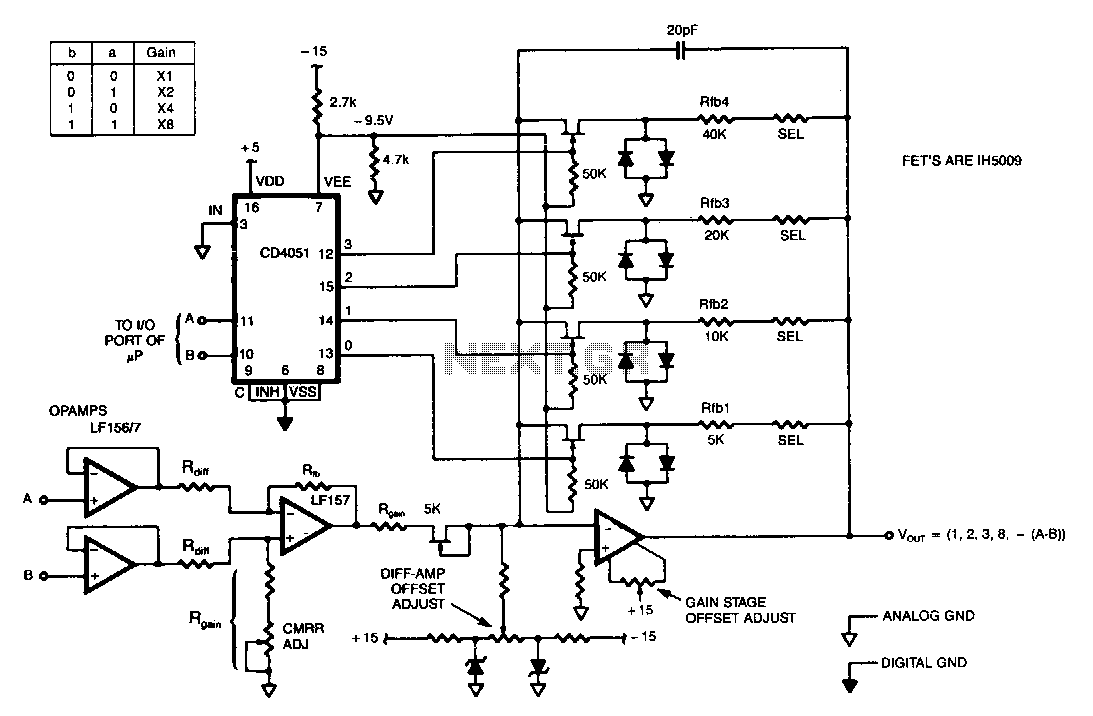
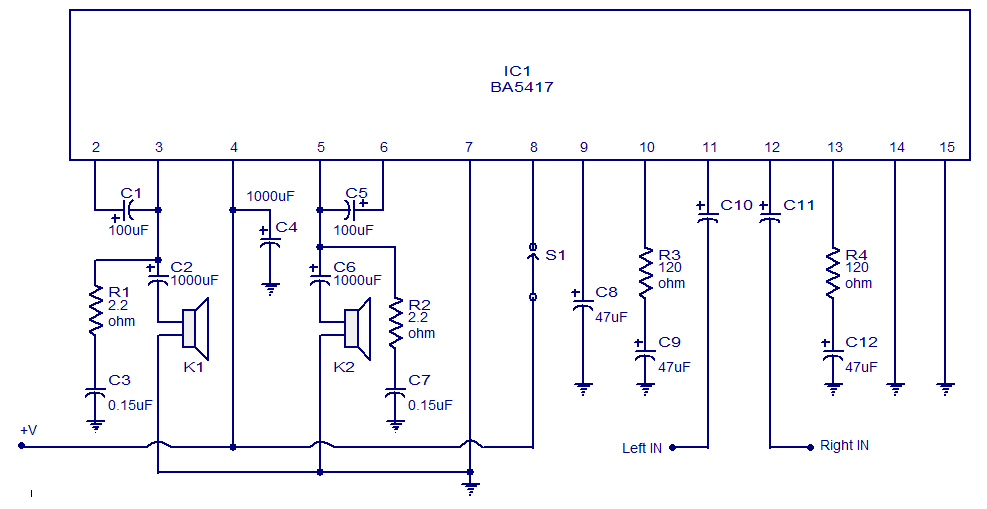
Improved Photodiode Pre-Amp Uses Current-Feedback Amplifier

This design concept addresses a major challenge associated with the use of photodiodes in high-speed applications such as barcode scanners, CD-ROMs, and DVDs, specifically the high output capacitance of the diode. The critical component in the circuit is the Analog Devices AD8014.
The circuit leverages the AD8014 operational amplifier, known for its high-speed performance and low output capacitance, making it suitable for applications where rapid signal processing is essential. The AD8014 features a bandwidth of 100 MHz and a slew rate of 2000 V/µs, allowing it to effectively amplify the small signals generated by photodiodes in fast applications.
In typical configurations, the photodiode is connected in a reverse bias mode to enhance its response time. The output from the photodiode is fed directly into the non-inverting input of the AD8014, where it is amplified. To minimize noise and ensure stability, appropriate feedback resistors and capacitors are used in the circuit design. This configuration not only mitigates the effects of the diode's inherent capacitance but also optimizes the overall frequency response of the system.
The circuit may also include additional components such as biasing resistors, which help to set the operating point of the photodiode, and filtering capacitors to eliminate high-frequency noise. Proper layout techniques should be employed to reduce parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can adversely affect the circuit's performance.
Overall, this design effectively enhances the performance of photodiodes in high-speed applications by utilizing the AD8014, ensuring reliable and efficient operation in systems requiring rapid data processing.This design idea overcomes a significant problem with using photodiodes in fast applications like barcode scanners, CD-ROMs, and DVDs--high output capacitance of the diode. The key part in the circuit is the Analog Devices AD8014 🔗 External reference
The circuit leverages the AD8014 operational amplifier, known for its high-speed performance and low output capacitance, making it suitable for applications where rapid signal processing is essential. The AD8014 features a bandwidth of 100 MHz and a slew rate of 2000 V/µs, allowing it to effectively amplify the small signals generated by photodiodes in fast applications.
In typical configurations, the photodiode is connected in a reverse bias mode to enhance its response time. The output from the photodiode is fed directly into the non-inverting input of the AD8014, where it is amplified. To minimize noise and ensure stability, appropriate feedback resistors and capacitors are used in the circuit design. This configuration not only mitigates the effects of the diode's inherent capacitance but also optimizes the overall frequency response of the system.
The circuit may also include additional components such as biasing resistors, which help to set the operating point of the photodiode, and filtering capacitors to eliminate high-frequency noise. Proper layout techniques should be employed to reduce parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can adversely affect the circuit's performance.
Overall, this design effectively enhances the performance of photodiodes in high-speed applications by utilizing the AD8014, ensuring reliable and efficient operation in systems requiring rapid data processing.This design idea overcomes a significant problem with using photodiodes in fast applications like barcode scanners, CD-ROMs, and DVDs--high output capacitance of the diode. The key part in the circuit is the Analog Devices AD8014 🔗 External reference