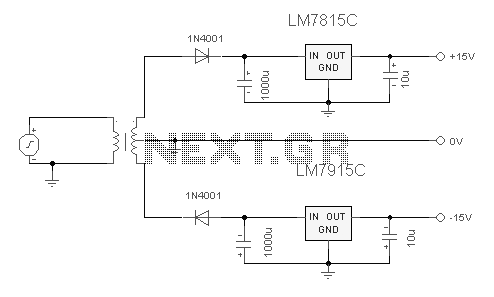
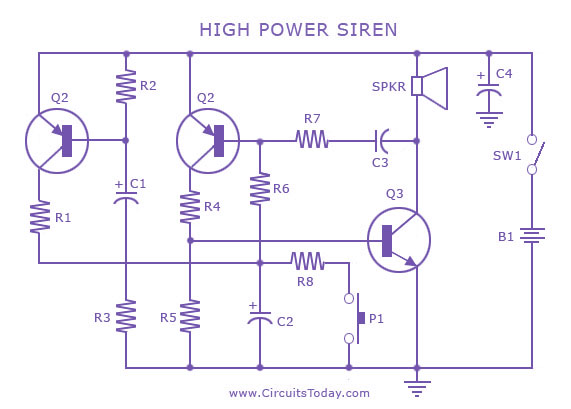
Increasing the power rating of zener diodes
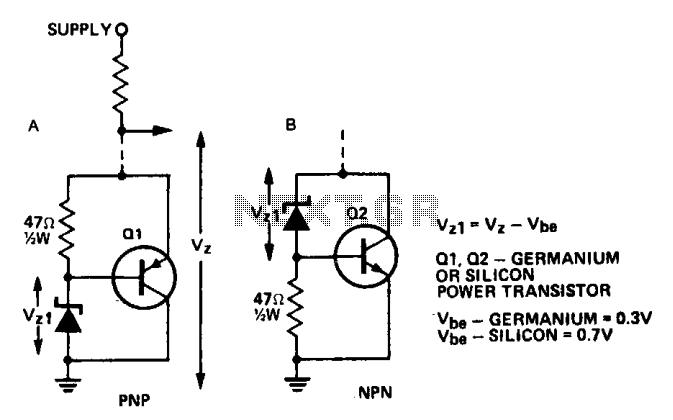
A power transistor can be utilized to supply a high-powered Zener voltage from a low-wattage Zener diode. A 400 mW Zener diode can be employed in applications requiring a 10-watt Zener, or a 1 W Zener can be used where a 50 to 80 watt Zener is necessary by selecting appropriate transistors for Q1 and Q2 in the specified circuits. For lower ratings, Q1 can be an ASZ 15 (germanium) or an AY9140 (silicon), while Q2 may be a 2N2955 (silicon). For higher power applications, Q1 should be an ASZ18 (germanium) or a 2N2955 (silicon), and Q2 can be a 2N3055 (silicon) or an AY8149 (silicon). Additionally, a heatsink is required for the transistor. The circuit in configuration A offers the benefit that power transistors can be directly bolted onto a chassis that may function as a heatsink.
The described circuit configuration employs a power transistor to amplify the Zener voltage output, allowing for the use of lower-rated Zener diodes in applications that demand higher power levels. The selection of transistors is critical: for lower power requirements, the ASZ 15 or AY9140 are suitable choices for Q1, while the 2N2955 serves as a robust option for Q2. In contrast, for higher power demands, the ASZ18 or 2N2955 can be used for Q1, with Q2 being fulfilled by either the 2N3055 or AY8149, both of which are capable of handling increased current loads.
The integration of a heatsink is essential for thermal management, as power transistors dissipate significant heat during operation. The design allows for the transistors to be mounted directly onto a metallic chassis, which not only secures the components but also enhances heat dissipation by utilizing the chassis as a passive heatsink. This configuration promotes efficient thermal management, ensuring the reliability and longevity of the circuit by preventing overheating.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies an effective method to achieve higher power Zener voltage outputs while maintaining manageable thermal conditions through careful component selection and efficient heatsinking strategies.A power transistor can be used to provide a high powered zener voltage from a low wattage zener. A 400 mW zener can be used where a 10 watt zener is required or a 1 W zener can be used where a 50 to 80 watt zener is required by using appropriate transistors for Ql and Q2 in the circuits shown. Where low rating is required, Ql would be an ASZ 15 (germanium) or an AY9140 (silicon). Q2 could be a 2N2955 (silicon). For higher powers, Ql should be an ASZ18 (germanium) or a 2N2955 (silicon) and Q2 a 2N3055 (silicon) or an AY8149 (silicon).
A heatsink on the transistor is required. The circuit in A has the advantage that power transistors can be bolted directly on to a chassis which may serve as a heatsink. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit configuration employs a power transistor to amplify the Zener voltage output, allowing for the use of lower-rated Zener diodes in applications that demand higher power levels. The selection of transistors is critical: for lower power requirements, the ASZ 15 or AY9140 are suitable choices for Q1, while the 2N2955 serves as a robust option for Q2. In contrast, for higher power demands, the ASZ18 or 2N2955 can be used for Q1, with Q2 being fulfilled by either the 2N3055 or AY8149, both of which are capable of handling increased current loads.
The integration of a heatsink is essential for thermal management, as power transistors dissipate significant heat during operation. The design allows for the transistors to be mounted directly onto a metallic chassis, which not only secures the components but also enhances heat dissipation by utilizing the chassis as a passive heatsink. This configuration promotes efficient thermal management, ensuring the reliability and longevity of the circuit by preventing overheating.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies an effective method to achieve higher power Zener voltage outputs while maintaining manageable thermal conditions through careful component selection and efficient heatsinking strategies.A power transistor can be used to provide a high powered zener voltage from a low wattage zener. A 400 mW zener can be used where a 10 watt zener is required or a 1 W zener can be used where a 50 to 80 watt zener is required by using appropriate transistors for Ql and Q2 in the circuits shown. Where low rating is required, Ql would be an ASZ 15 (germanium) or an AY9140 (silicon). Q2 could be a 2N2955 (silicon). For higher powers, Ql should be an ASZ18 (germanium) or a 2N2955 (silicon) and Q2 a 2N3055 (silicon) or an AY8149 (silicon).
A heatsink on the transistor is required. The circuit in A has the advantage that power transistors can be bolted directly on to a chassis which may serve as a heatsink. 🔗 External reference