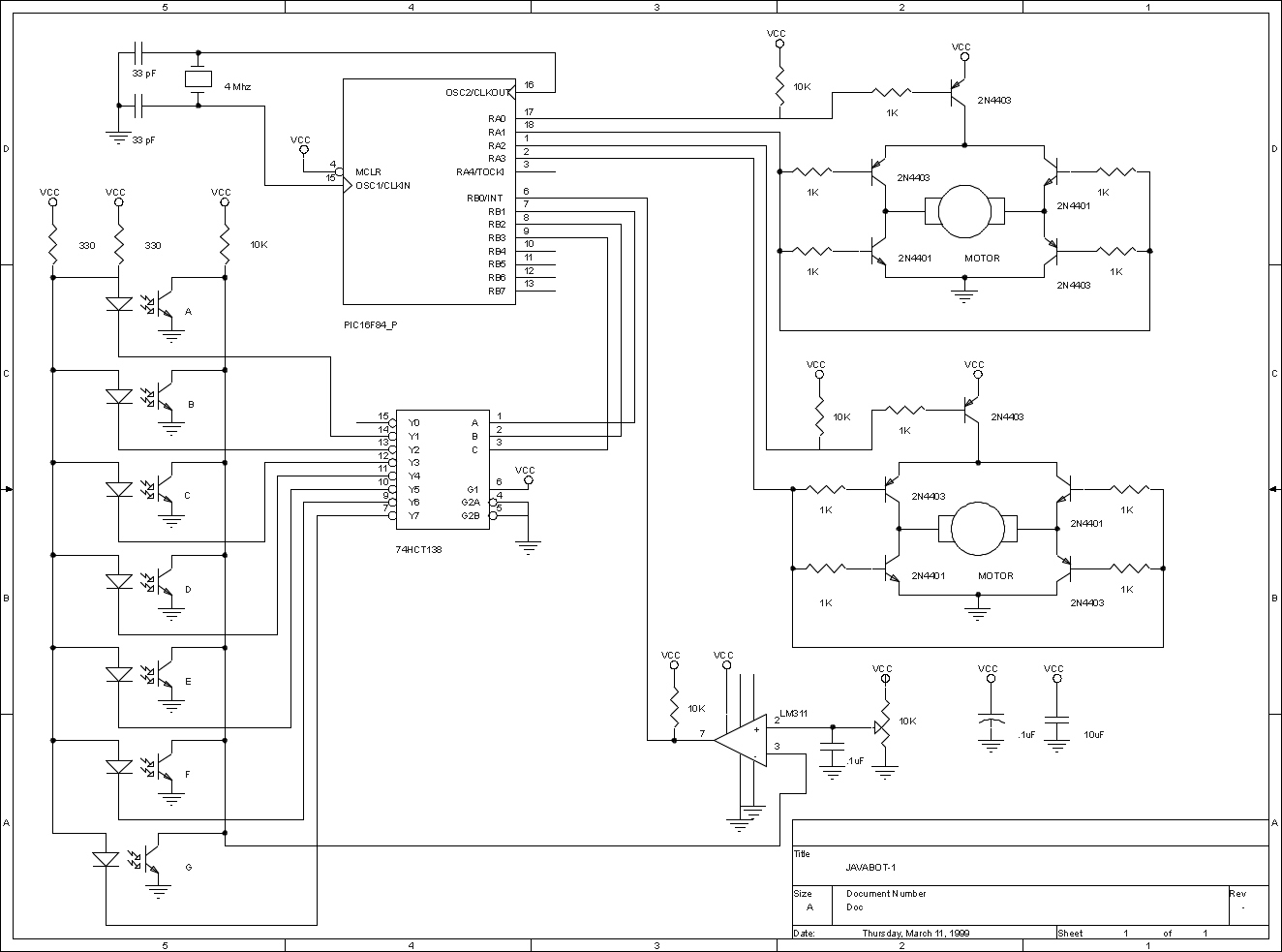
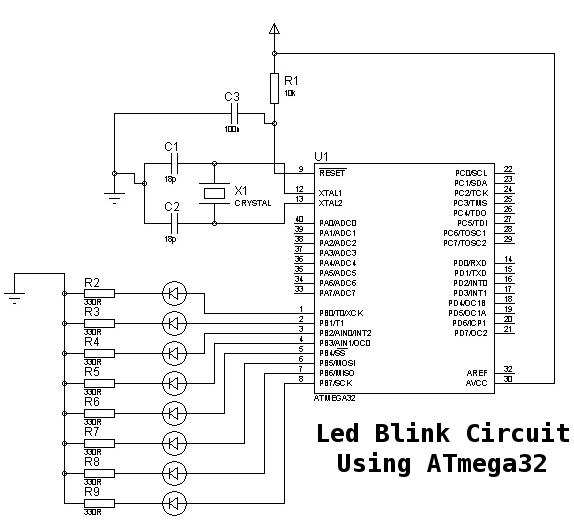
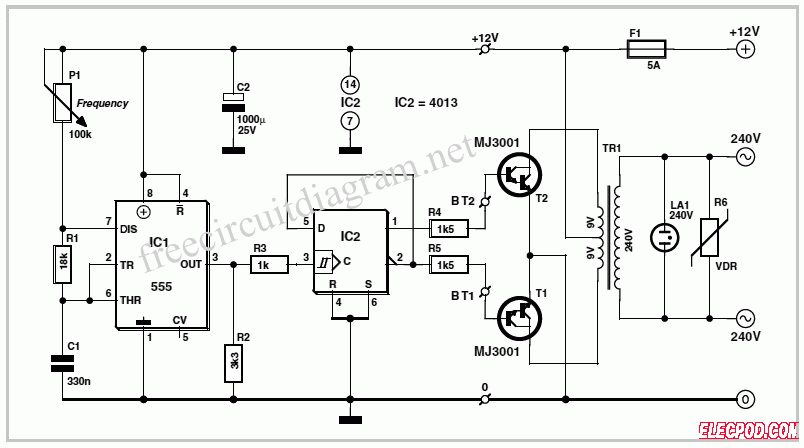
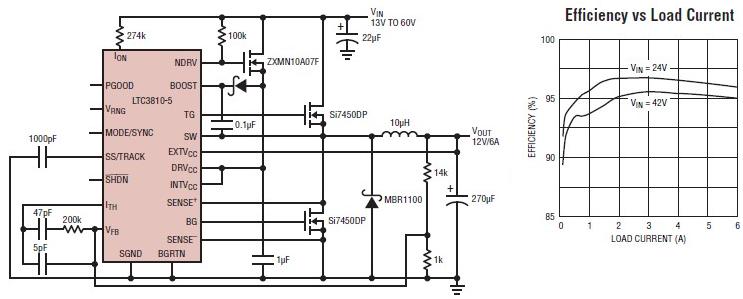
infrared emitter and detector using ic 74ls14
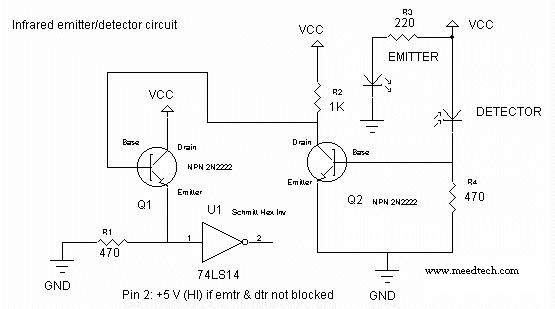
This circuit is designed for line detection in a robot project. A proper match between the transmitter and the detector is crucial for optimal operation, particularly when the hole is large. The robot is equipped with a simple system for object or obstacle detection. Infrared transmitter and detector pairs are relatively straightforward to implement, although they require some degree of testing and calibration to ensure accuracy. These components can be utilized for detecting obstacles, motion, and color. One method for alignment involves using a piece of rope stretched between an LED and a phototransistor. A length of stiff wire or plugs may also be employed to achieve precise alignment. For longer distances, a laser pointer can be directed through a hole to assist in detection.
The line detection circuit primarily employs an infrared (IR) transmitter and receiver configuration, where the IR LED emits light that reflects off surfaces and is detected by a phototransistor. The effectiveness of this setup hinges on the alignment and calibration of the components. The IR light's reflection characteristics can vary based on the surface properties of the detected object, necessitating adjustments to the sensitivity of the phototransistor.
To enhance the circuit's functionality, it may incorporate a microcontroller to process the signals from the phototransistor. This microcontroller can analyze the received signals and determine whether an object is present based on the intensity of the reflected IR light. The logic can be programmed to trigger specific actions, such as stopping the robot or navigating around obstacles.
For calibration, the circuit should include variable resistors to adjust the sensitivity of the phototransistor. This allows for fine-tuning based on environmental conditions and the specific characteristics of the surfaces being detected. Moreover, the use of a laser pointer can improve detection accuracy over longer distances, providing a clear and focused beam that enhances the reliability of the detection mechanism.
In practical applications, the circuit can be integrated into a mobile robot platform, enabling it to navigate autonomously while avoiding obstacles. The simplicity of the IR transmitter and detector pair makes it an accessible choice for hobbyists and professionals alike, while the potential for expansion through microcontroller integration allows for more complex behaviors and functionalities in robotic systems.This circuit have applied to line detection of robot project, Good match between the transmitter and the detector is important for proper operation, especially if the hole is large. Robot with a simple object or obstacle detection. Infrared Transmitter detector pair sensors are relatively easy to implement, although involved some degree of testing
and calibration in order to make correct. They can for the impediment, motion detection, transmitters, encoders are used, and the color detection. This can be done with a piece of rope stretched between and in accordance with LED and phototransistor.
A length of stiff wire or plugs can be used to set the alignment. Another method that can be used for long distances is a laser pointer shone through a hole. 🔗 External reference
The line detection circuit primarily employs an infrared (IR) transmitter and receiver configuration, where the IR LED emits light that reflects off surfaces and is detected by a phototransistor. The effectiveness of this setup hinges on the alignment and calibration of the components. The IR light's reflection characteristics can vary based on the surface properties of the detected object, necessitating adjustments to the sensitivity of the phototransistor.
To enhance the circuit's functionality, it may incorporate a microcontroller to process the signals from the phototransistor. This microcontroller can analyze the received signals and determine whether an object is present based on the intensity of the reflected IR light. The logic can be programmed to trigger specific actions, such as stopping the robot or navigating around obstacles.
For calibration, the circuit should include variable resistors to adjust the sensitivity of the phototransistor. This allows for fine-tuning based on environmental conditions and the specific characteristics of the surfaces being detected. Moreover, the use of a laser pointer can improve detection accuracy over longer distances, providing a clear and focused beam that enhances the reliability of the detection mechanism.
In practical applications, the circuit can be integrated into a mobile robot platform, enabling it to navigate autonomously while avoiding obstacles. The simplicity of the IR transmitter and detector pair makes it an accessible choice for hobbyists and professionals alike, while the potential for expansion through microcontroller integration allows for more complex behaviors and functionalities in robotic systems.This circuit have applied to line detection of robot project, Good match between the transmitter and the detector is important for proper operation, especially if the hole is large. Robot with a simple object or obstacle detection. Infrared Transmitter detector pair sensors are relatively easy to implement, although involved some degree of testing
and calibration in order to make correct. They can for the impediment, motion detection, transmitters, encoders are used, and the color detection. This can be done with a piece of rope stretched between and in accordance with LED and phototransistor.
A length of stiff wire or plugs can be used to set the alignment. Another method that can be used for long distances is a laser pointer shone through a hole. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713