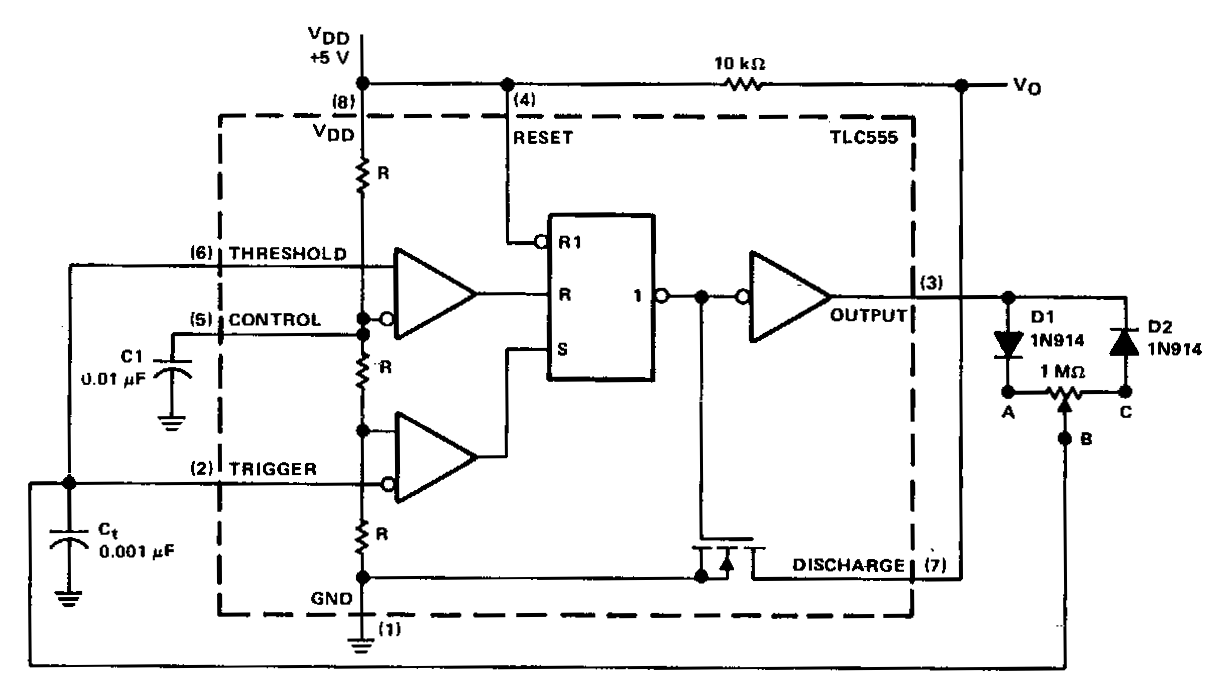
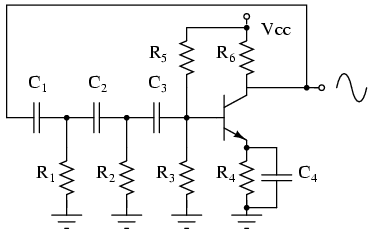
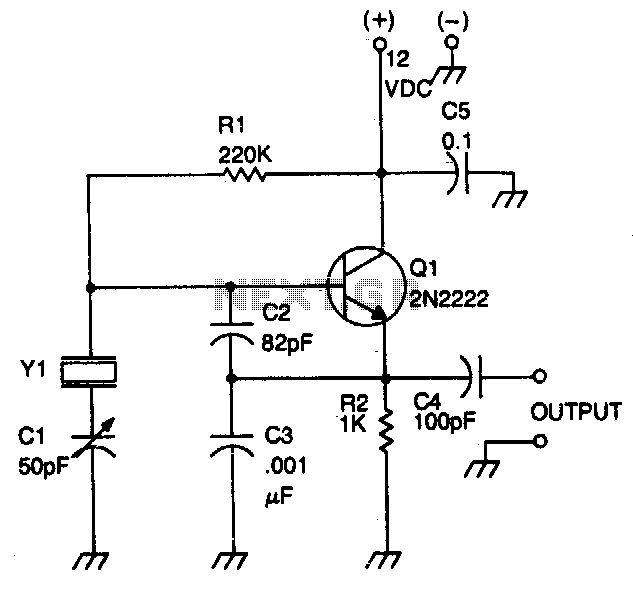
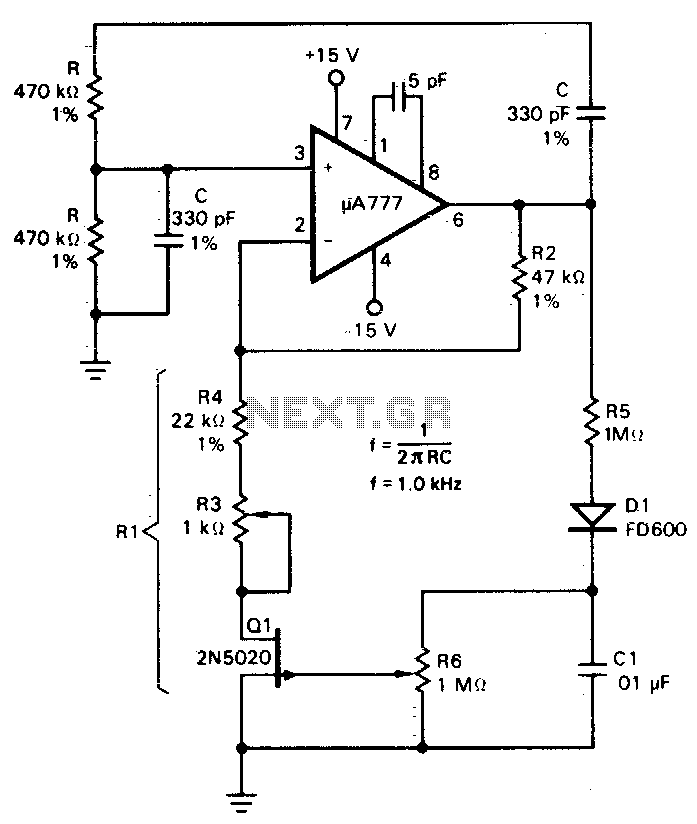
Injection-lock a Wien-bridge oscillator
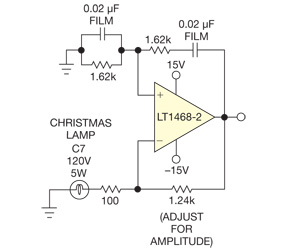
A low-distortion Meacham-bulb-stabilized Wien-bridge oscillator is utilized to acquire the FFT of a pure sinusoid at approximately 5 kHz.
The Meacham-bulb-stabilized Wien-bridge oscillator is a precision oscillator circuit that generates a sine wave output with low distortion. This type of oscillator is particularly effective for applications requiring a stable frequency output, such as signal processing and testing. The Wien-bridge configuration consists of a bridge circuit with resistors and capacitors arranged to provide positive and negative feedback, allowing for oscillation at a specific frequency determined by the component values.
In this setup, the Meacham bulb serves as a temperature-sensitive resistor, which provides automatic gain control to stabilize the oscillation amplitude. As the output signal increases, the bulb's resistance changes due to heating, reducing the gain and preventing distortion. Conversely, if the output decreases, the bulb cools down, increasing the resistance and allowing the gain to rise again. This feedback mechanism ensures that the oscillator maintains a consistent output level.
The oscillator is tuned to produce a frequency of approximately 5 kHz, which is suitable for acquiring the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) of the generated pure sinusoidal signal. The FFT analysis allows for the examination of the frequency components within the signal, providing insights into its harmonic content and aiding in various signal processing applications.
Overall, the Meacham-bulb-stabilized Wien-bridge oscillator is an essential tool for generating low-distortion sine waves, making it ideal for testing and analysis in electronic circuits.A low-distortion Meacham-bulb-stabilized Wien-bridge oscillator is used to acquire the FFT of a pure sinusoid of about 5 kHz.. 🔗 External reference
The Meacham-bulb-stabilized Wien-bridge oscillator is a precision oscillator circuit that generates a sine wave output with low distortion. This type of oscillator is particularly effective for applications requiring a stable frequency output, such as signal processing and testing. The Wien-bridge configuration consists of a bridge circuit with resistors and capacitors arranged to provide positive and negative feedback, allowing for oscillation at a specific frequency determined by the component values.
In this setup, the Meacham bulb serves as a temperature-sensitive resistor, which provides automatic gain control to stabilize the oscillation amplitude. As the output signal increases, the bulb's resistance changes due to heating, reducing the gain and preventing distortion. Conversely, if the output decreases, the bulb cools down, increasing the resistance and allowing the gain to rise again. This feedback mechanism ensures that the oscillator maintains a consistent output level.
The oscillator is tuned to produce a frequency of approximately 5 kHz, which is suitable for acquiring the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) of the generated pure sinusoidal signal. The FFT analysis allows for the examination of the frequency components within the signal, providing insights into its harmonic content and aiding in various signal processing applications.
Overall, the Meacham-bulb-stabilized Wien-bridge oscillator is an essential tool for generating low-distortion sine waves, making it ideal for testing and analysis in electronic circuits.A low-distortion Meacham-bulb-stabilized Wien-bridge oscillator is used to acquire the FFT of a pure sinusoid of about 5 kHz.. 🔗 External reference