Intercom Circuit
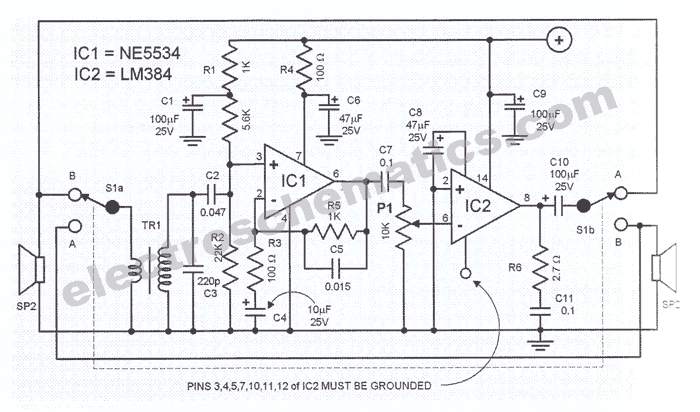
The intercom schematic provides a reliable communication line and is straightforward to construct. The circuit consists of an amplifier, two switches, and two loudspeakers. If additional stations (speakers) are desired, more switches can be incorporated into the circuit. The IC LM382 serves as the final amplifier, delivering nearly 2 watts of audio power with a supply voltage of 15 volts. The amplification is preset to 50. Capacitor C9 acts as a supply bypass. Another integrated circuit is used to boost the input signal before it is fed into the LM384. IC2 is an operational amplifier with an amplification factor of 11. The frequency bandwidth ranges from 160 Hz to 10 kHz. These specifications are selected since the device is intended for intercom use rather than high-fidelity audio amplification. To optimize performance, speakers that can also function as microphones are recommended. The intercom should be housed in a box to ensure optimal microphone functionality. Due to the low impedance of most speakers, an impedance converter is necessary to maintain good audio quality, which is achieved using transformer TR1. TR1 is a standard 220/6V step-down transformer, with the 6V winding connected to the speaker, raising its impedance to approximately 10 kΩ. When constructing the intercom circuit, it is advisable to house the power supply unit separately from the main circuit to prevent interference. Capacitor C1 is used to suppress high-frequency interference. The current consumption is approximately 210 mA with an output of 1.8 watts.
The intercom circuit is designed to facilitate clear communication in various environments, such as homes or offices. The use of the LM382 integrated circuit as the final amplifier is crucial for achieving the desired audio output level, allowing for effective communication over a range of distances. The preset amplification level of 50 ensures that the audio signal is adequately boosted for clarity, making it suitable for intercom applications.
The inclusion of an operational amplifier (IC2) with an amplification factor of 11 further enhances the input signal before it reaches the LM382, ensuring that even quieter sounds are effectively amplified. The frequency response of 160 Hz to 10 kHz is tailored for voice communication, as it covers the essential frequency range for human speech while filtering out unnecessary high-frequency noise that could detract from the clarity of the conversation.
To ensure optimal performance, it is recommended to use speakers that can also act as microphones, as this dual functionality enhances the intercom's effectiveness. The enclosure of the intercom circuit is also a critical design consideration; it should be constructed in a manner that minimizes acoustic feedback and maximizes microphone sensitivity.
The use of transformer TR1 as an impedance converter is a vital aspect of the circuit design. By stepping down the voltage from 220V to 6V, the transformer not only provides the necessary power supply for the circuit but also raises the speaker's impedance to approximately 10 kΩ. This adjustment is essential for maintaining audio quality and preventing distortion, which can occur when connecting low-impedance speakers directly to the amplifier.
Lastly, the separation of the power supply unit from the main circuit is an important design practice that helps to mitigate electromagnetic interference, ensuring that the audio signal remains clear and free from noise. Capacitor C1 plays a significant role in this regard, as it effectively suppresses high-frequency interference that may otherwise compromise audio quality. With a current consumption of about 210 mA and an output power of 1.8 watts, this intercom circuit is both efficient and effective for its intended purpose.The intercom schematic fulfills its tasks to provide a reliable communication line and is very simple to construct. The circuit is made up of an amplifier, two switches and two loudspeakers. If additional stations (speakers) are wished, additional switches are just incorporated into the circuit.
IC LM382 is used as the final amplifier. It delivers nearly 2 watts of audio power by 15 volts supply voltage. Amplification is preset to 50. C9 serves as supply bypass. Another IC is used to boost the input signal before it is passed into the LM384. IC2 is an op-amp with an amplification factor of 11. The frequency bandwith is 160 Hz to 10 kHz. These values were chosen since the device is to be used only as intercom and not as HIFI amplifier. To achieve the best performance, use speakers that can also function as microphones. The intercom must be constructed inside a box so that the microphone function is optinum. Since the impedance of most speakers are quite low, an impedance converter is needed to maintain a good audio quality. This is done by the transformer TR1. TR1 is a normal 220/6V step-down transformer. The 6V winding of the transformer is connected to the speaker and raises its impedance to about 10 kohms.
In constructing the intercom circuit, house the power supply unit separately from the main circuit to avoid interference. C1 suppresses HF interference. The current consumption is about 210 mA with 1. 8 watt output. 🔗 External reference
The intercom circuit is designed to facilitate clear communication in various environments, such as homes or offices. The use of the LM382 integrated circuit as the final amplifier is crucial for achieving the desired audio output level, allowing for effective communication over a range of distances. The preset amplification level of 50 ensures that the audio signal is adequately boosted for clarity, making it suitable for intercom applications.
The inclusion of an operational amplifier (IC2) with an amplification factor of 11 further enhances the input signal before it reaches the LM382, ensuring that even quieter sounds are effectively amplified. The frequency response of 160 Hz to 10 kHz is tailored for voice communication, as it covers the essential frequency range for human speech while filtering out unnecessary high-frequency noise that could detract from the clarity of the conversation.
To ensure optimal performance, it is recommended to use speakers that can also act as microphones, as this dual functionality enhances the intercom's effectiveness. The enclosure of the intercom circuit is also a critical design consideration; it should be constructed in a manner that minimizes acoustic feedback and maximizes microphone sensitivity.
The use of transformer TR1 as an impedance converter is a vital aspect of the circuit design. By stepping down the voltage from 220V to 6V, the transformer not only provides the necessary power supply for the circuit but also raises the speaker's impedance to approximately 10 kΩ. This adjustment is essential for maintaining audio quality and preventing distortion, which can occur when connecting low-impedance speakers directly to the amplifier.
Lastly, the separation of the power supply unit from the main circuit is an important design practice that helps to mitigate electromagnetic interference, ensuring that the audio signal remains clear and free from noise. Capacitor C1 plays a significant role in this regard, as it effectively suppresses high-frequency interference that may otherwise compromise audio quality. With a current consumption of about 210 mA and an output power of 1.8 watts, this intercom circuit is both efficient and effective for its intended purpose.The intercom schematic fulfills its tasks to provide a reliable communication line and is very simple to construct. The circuit is made up of an amplifier, two switches and two loudspeakers. If additional stations (speakers) are wished, additional switches are just incorporated into the circuit.
IC LM382 is used as the final amplifier. It delivers nearly 2 watts of audio power by 15 volts supply voltage. Amplification is preset to 50. C9 serves as supply bypass. Another IC is used to boost the input signal before it is passed into the LM384. IC2 is an op-amp with an amplification factor of 11. The frequency bandwith is 160 Hz to 10 kHz. These values were chosen since the device is to be used only as intercom and not as HIFI amplifier. To achieve the best performance, use speakers that can also function as microphones. The intercom must be constructed inside a box so that the microphone function is optinum. Since the impedance of most speakers are quite low, an impedance converter is needed to maintain a good audio quality. This is done by the transformer TR1. TR1 is a normal 220/6V step-down transformer. The 6V winding of the transformer is connected to the speaker and raises its impedance to about 10 kohms.
In constructing the intercom circuit, house the power supply unit separately from the main circuit to avoid interference. C1 suppresses HF interference. The current consumption is about 210 mA with 1. 8 watt output. 🔗 External reference