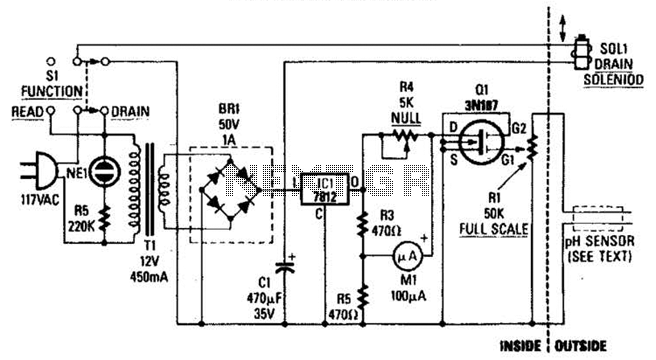
Inverter Circuit
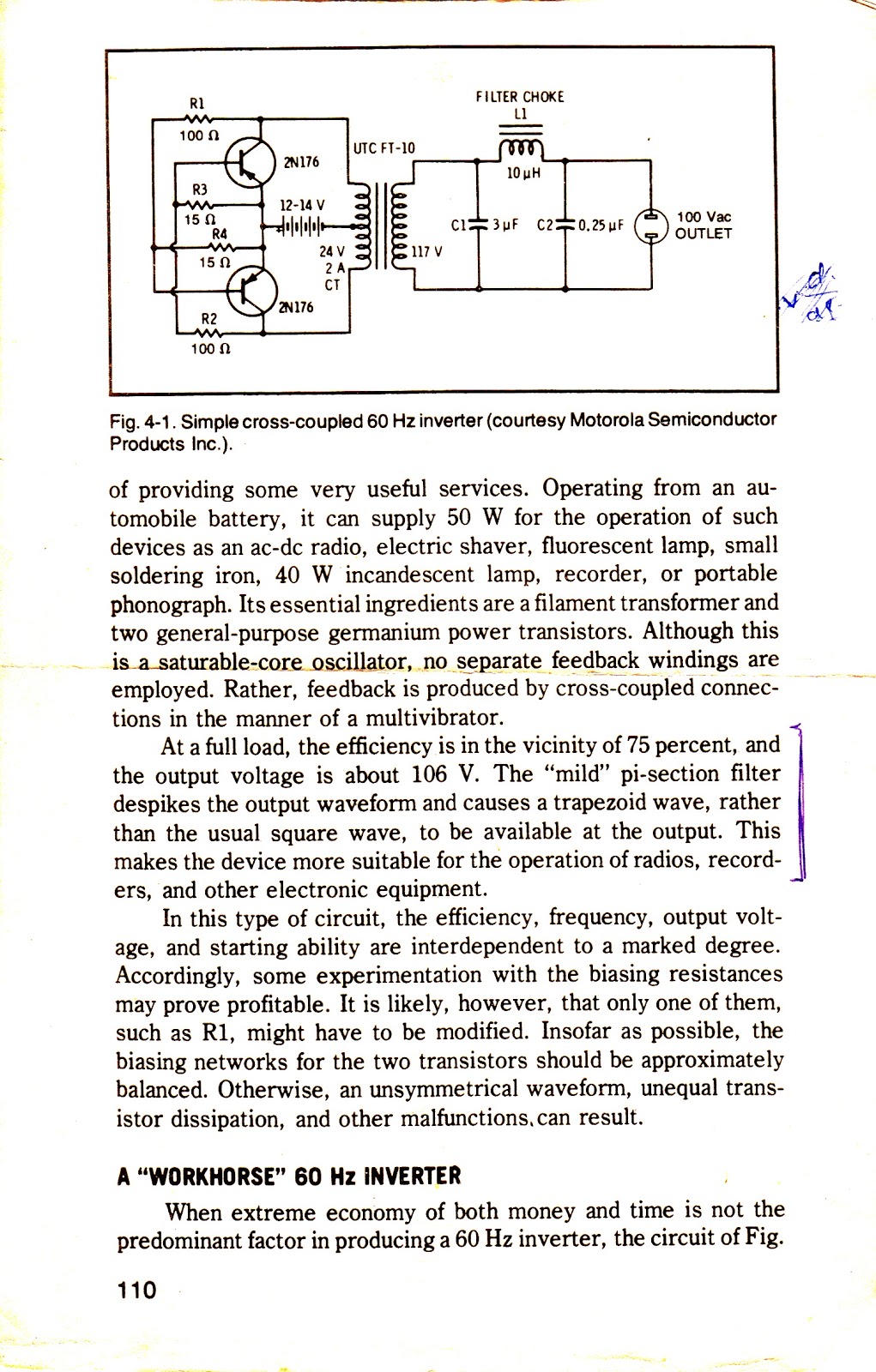
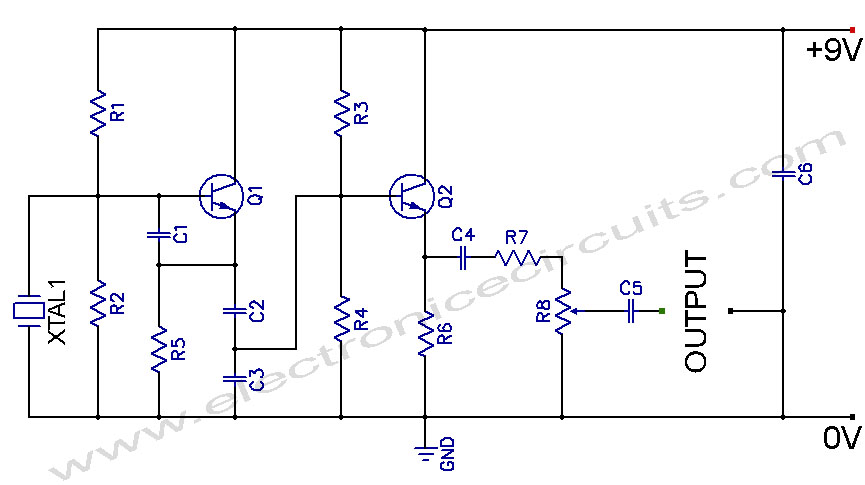
This straightforward design of an inverter circuit is capable of delivering high output power with an efficiency of approximately 75%. It provides guidance on constructing an inverter that can meet most power requirements at a reasonable cost. The article outlines the construction details of a mini inverter, which is not only affordable and compact but also capable of providing a satisfactory power output. While there are numerous inverter circuits available online and in electronic publications, many of these designs tend to be complex and high-end. This often leaves users searching for a simple, low-cost, and efficient inverter solution. The described inverter circuit is one of the smallest in terms of component count yet is powerful enough to meet various needs. It is suitable for powering small electrical devices such as soldering irons, CFL lights, and small portable fans, with an output power of around 70 watts, depending on the load. The efficiency of this inverter is estimated at 75%. It can be connected directly to a vehicle's battery when used outdoors, eliminating the need to carry an additional battery. This mini inverter circuit operates uniquely, differing from conventional inverters that utilize a discrete oscillator stage for transistor operation. Instead, the two sections or arms of the circuit work in a regenerative manner. The operation can be understood through the following points: regardless of how well-matched the two halves of the circuit are, there will always be slight imbalances in parameters such as resistors, Hfe, and transformer winding turns. If the upper half transistors conduct first, they will receive their biasing voltage through the lower half winding of the transformer via R2.
The described inverter circuit employs a simple yet effective design that maximizes efficiency while minimizing component count. The core of the circuit consists of two transistors configured in a push-pull arrangement, allowing for alternating current (AC) generation from a direct current (DC) source. The power supply for the circuit can be sourced from a standard vehicle battery, providing a practical solution for outdoor applications.
The transformer plays a crucial role in this design, as it steps up the voltage to the desired level for the output. The choice of transformer is essential, as it must be capable of handling the expected power levels and frequency. The winding configuration should be designed to ensure that the two halves of the circuit are balanced, even though slight imbalances may exist.
The feedback mechanism inherent in this design allows for self-regulation of the output voltage and current. When one transistor begins to conduct, it initiates a feedback loop that helps stabilize the operation and maintain consistent output. This regenerative behavior is particularly advantageous, as it enhances the overall efficiency of the inverter.
In terms of component selection, resistors should be chosen with precision to ensure that the biasing conditions for the transistors are optimal. The use of high-quality capacitors can further enhance performance by smoothing out voltage fluctuations and improving transient response.
Overall, this mini inverter circuit represents an efficient and cost-effective solution for powering small electronic devices, combining simplicity in construction with reliable performance. The design is well-suited for hobbyists and those seeking an affordable means of generating AC power from a DC source.This super simple design of aninvertercircuit does not limit it in any way from providing a high output power and an efficiency of a good 75%. Learn how to build aninverterthat will satisfy most of your power requirement at quite an affordable cost.
The article deals with the construction details of a miniinverter. Read to know how to build aninve rterwhich can provide reasonably good power output and yet is very affordable and sleek. There may be a huge number ofinvertercircuits available over the internet and electronic magazines. But these circuits are often very complicated and hi-end type of inverters. Thus we are left with no choice but just to wonder how to build aninverterthat can be not only easy to build but also low cost and highly efficient in its working. Well your search for such a circuit ends here. The circuit of aninverterdescribed here is perhaps the smallest as far its component count goes yet is powerful enough to fulfill most of your requirements.
I hope from the above discussions you must have clearly understood how to build aninverterwhich is not only simple to construct but also very affordable to each of you. It can be used to power small electrical appliances like soldering iron, CFL lights, small portable fans etc.
The output power will lie in the vicinity of 70 watts and is loaddependent. The efficiency of thisinverteris around 75%. The unit may be connected to your vehicles battery itself when outdoors so that the trouble of carrying an extra battery is eliminated. The functioning of this miniinvertercircuit is rather unique and different from the normal inverters which involve discrete oscillator stage for powering the transistors.
However here the two sections or the twoarms ofthe circuit operate in a regenerative manner. Its very simple and may be understood through the following points: The two halves of the circuit no matter how much they are matched will always consist a slight imbalance in the parameters surrounding them, like the resistors, Hfe, transformer winding turns etc. Assume that the upper half transistors conduct first, obviously they will be getting their biasing voltage through the lower half winding of the transformer via R2.
🔗 External reference
The described inverter circuit employs a simple yet effective design that maximizes efficiency while minimizing component count. The core of the circuit consists of two transistors configured in a push-pull arrangement, allowing for alternating current (AC) generation from a direct current (DC) source. The power supply for the circuit can be sourced from a standard vehicle battery, providing a practical solution for outdoor applications.
The transformer plays a crucial role in this design, as it steps up the voltage to the desired level for the output. The choice of transformer is essential, as it must be capable of handling the expected power levels and frequency. The winding configuration should be designed to ensure that the two halves of the circuit are balanced, even though slight imbalances may exist.
The feedback mechanism inherent in this design allows for self-regulation of the output voltage and current. When one transistor begins to conduct, it initiates a feedback loop that helps stabilize the operation and maintain consistent output. This regenerative behavior is particularly advantageous, as it enhances the overall efficiency of the inverter.
In terms of component selection, resistors should be chosen with precision to ensure that the biasing conditions for the transistors are optimal. The use of high-quality capacitors can further enhance performance by smoothing out voltage fluctuations and improving transient response.
Overall, this mini inverter circuit represents an efficient and cost-effective solution for powering small electronic devices, combining simplicity in construction with reliable performance. The design is well-suited for hobbyists and those seeking an affordable means of generating AC power from a DC source.This super simple design of aninvertercircuit does not limit it in any way from providing a high output power and an efficiency of a good 75%. Learn how to build aninverterthat will satisfy most of your power requirement at quite an affordable cost.
The article deals with the construction details of a miniinverter. Read to know how to build aninve rterwhich can provide reasonably good power output and yet is very affordable and sleek. There may be a huge number ofinvertercircuits available over the internet and electronic magazines. But these circuits are often very complicated and hi-end type of inverters. Thus we are left with no choice but just to wonder how to build aninverterthat can be not only easy to build but also low cost and highly efficient in its working. Well your search for such a circuit ends here. The circuit of aninverterdescribed here is perhaps the smallest as far its component count goes yet is powerful enough to fulfill most of your requirements.
I hope from the above discussions you must have clearly understood how to build aninverterwhich is not only simple to construct but also very affordable to each of you. It can be used to power small electrical appliances like soldering iron, CFL lights, small portable fans etc.
The output power will lie in the vicinity of 70 watts and is loaddependent. The efficiency of thisinverteris around 75%. The unit may be connected to your vehicles battery itself when outdoors so that the trouble of carrying an extra battery is eliminated. The functioning of this miniinvertercircuit is rather unique and different from the normal inverters which involve discrete oscillator stage for powering the transistors.
However here the two sections or the twoarms ofthe circuit operate in a regenerative manner. Its very simple and may be understood through the following points: The two halves of the circuit no matter how much they are matched will always consist a slight imbalance in the parameters surrounding them, like the resistors, Hfe, transformer winding turns etc. Assume that the upper half transistors conduct first, obviously they will be getting their biasing voltage through the lower half winding of the transformer via R2.
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713