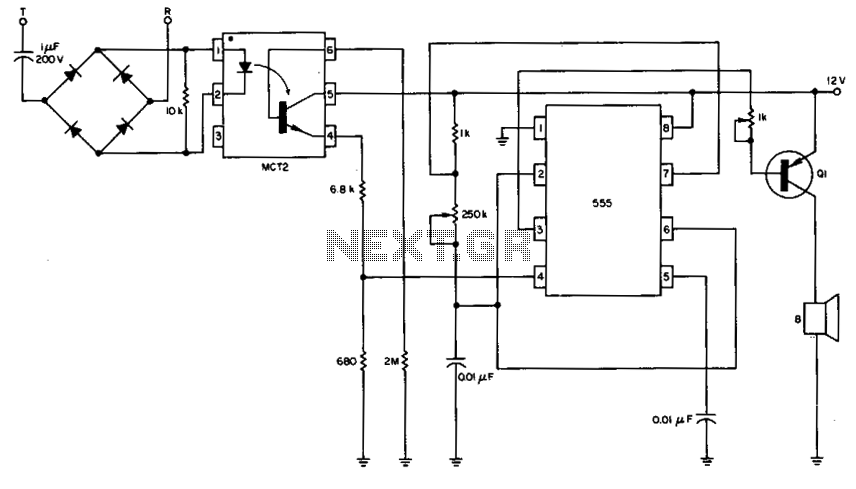
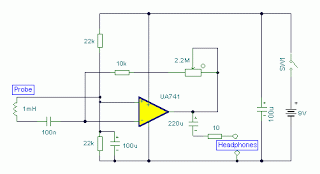
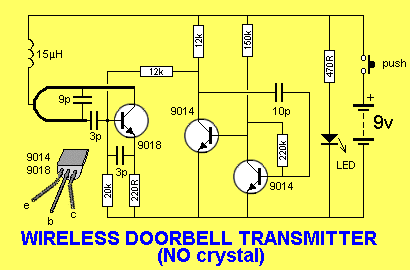
invisible broken wire detector
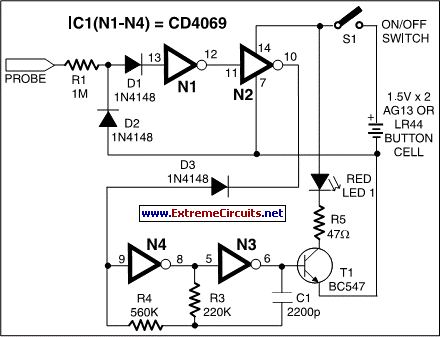
Portable loads such as video cameras, halogen flood lights, electrical irons, hand drills, grinders, and cutters are powered by connecting long 2- or 3-core cables to the mains plug. Due to prolonged usage, the power cord wires are subjected to mechanical strain and stress, which can lead to internal snapping of wires at any point. In such cases, most people opt to replace the core or cable, as locating the exact point of a broken wire can be challenging.
Portable electrical devices such as video cameras, halogen flood lights, electrical irons, hand drills, grinders, and cutters typically rely on long 2- or 3-core cables for connection to the mains power supply. These cables are essential for delivering electrical energy to the devices, allowing them to operate effectively. However, prolonged usage of these cables exposes them to mechanical strain and stress, particularly at points where they are frequently bent or twisted. This strain can lead to the internal snapping of wires within the cable, resulting in intermittent or complete loss of power to the connected device.
When a power cord fails due to internal wire breakage, users often face the dilemma of whether to attempt to repair the cable or to simply replace it. The complexity arises from the difficulty in pinpointing the exact location of the break within the cable, which can be time-consuming and frustrating. Consequently, many individuals choose to replace the entire cable or core, as this is often a more straightforward solution compared to diagnosing and repairing the specific fault.
To mitigate the risks associated with cable wear and tear, several strategies can be employed. Utilizing cables with reinforced strain relief features can help reduce mechanical stress at critical points. Additionally, employing cable management techniques, such as using cable ties or organizers, can minimize bending and twisting of the cables during use. Regular inspection and maintenance of cables can also help in early identification of wear signs, allowing for timely replacement before a complete failure occurs.
In summary, while portable electrical devices are indispensable for various applications, attention to the integrity of their power cables is crucial for ensuring reliable operation and safety.Portable loads such as video cameras, halogen flood lights, electrical irons, hand drillers, grinders, and cutters are powered by connecting long 2- or 3-core cables to the mains plug. Due to prolonged usage, the power cord wires are subjected to mechanical strain and stress, which can lead to internal snapping of wires at any point.
In such a case most people go for replacing the core/cable, as finding the exact location of a broken wire is difficult.. 🔗 External reference
Portable electrical devices such as video cameras, halogen flood lights, electrical irons, hand drills, grinders, and cutters typically rely on long 2- or 3-core cables for connection to the mains power supply. These cables are essential for delivering electrical energy to the devices, allowing them to operate effectively. However, prolonged usage of these cables exposes them to mechanical strain and stress, particularly at points where they are frequently bent or twisted. This strain can lead to the internal snapping of wires within the cable, resulting in intermittent or complete loss of power to the connected device.
When a power cord fails due to internal wire breakage, users often face the dilemma of whether to attempt to repair the cable or to simply replace it. The complexity arises from the difficulty in pinpointing the exact location of the break within the cable, which can be time-consuming and frustrating. Consequently, many individuals choose to replace the entire cable or core, as this is often a more straightforward solution compared to diagnosing and repairing the specific fault.
To mitigate the risks associated with cable wear and tear, several strategies can be employed. Utilizing cables with reinforced strain relief features can help reduce mechanical stress at critical points. Additionally, employing cable management techniques, such as using cable ties or organizers, can minimize bending and twisting of the cables during use. Regular inspection and maintenance of cables can also help in early identification of wear signs, allowing for timely replacement before a complete failure occurs.
In summary, while portable electrical devices are indispensable for various applications, attention to the integrity of their power cables is crucial for ensuring reliable operation and safety.Portable loads such as video cameras, halogen flood lights, electrical irons, hand drillers, grinders, and cutters are powered by connecting long 2- or 3-core cables to the mains plug. Due to prolonged usage, the power cord wires are subjected to mechanical strain and stress, which can lead to internal snapping of wires at any point.
In such a case most people go for replacing the core/cable, as finding the exact location of a broken wire is difficult.. 🔗 External reference